How much does an ECT treatment cost?
The cost to the consumer for ECT varies depending on if the person has health insurance, if the insurance covers this procedure, and to what extent. The cost of each ECT session is about $2,500, for a total of $25,000 for the 10 sessions an average course of treatment entails. That does not include the cost of a hospital stay if necessary.
How many ECT treatments does it take to work?
Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more.
Does insurance cover ECT?
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) may help cover the cost of ECT services you receive in an outpatient setting. You are eligible for this coverage only if your doctor certifies that the treatment is medically necessary and you get ECT in a Medicare-approved facility.
What are the long term side effects of ECT?
What are the side effects of ECT?
- Memory loss. Many people experience memory loss after having ECT. Some people find this only lasts for a short time and their memories gradually return as they recover from ECT.
- Immediate side effects. You may experience other side effects immediately after treatment. ...
- Longer-term side effects. Was this page useful? ...
See more

Does insurance cover ECT treatment?
An ECT session costs around $2,500 per session, including anesthesia. There may be extra costs if a hospital stay is needed. ECT costs are covered by most health insurance plans, Medicaid, and Medicare.
How long does a ECT last?
A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes).
How many sessions does ECT treatment have?
People undergoing ECT need multiple treatments. The number needed to successfully treat severe depression can range from 4 to 20, but most people need a total of 6 to 12 treatments. The treatments are usually given three times a week — Monday, Wednesday, and Friday.
How quickly does ECT work?
Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more.
Does ECT reset your brain?
ECT has been referred to as a “reset button for the brain,” which not only directly improves depressive symptoms, but also allows current medications to work more effectively.
Does ECT damage the brain?
The review of literature and present evidence suggests that ECT has a demonstrable impact on the structure and function of the brain. However, there is a lack of evidence at present to suggest that ECT causes brain damage.
Does ECT worsen anxiety?
The concern of some psychiatrists is that while ECT may help with depressive symptoms, it could worsen anxiety symptoms, including obsessional thoughts or panic attacks.
Does ECT cause weight gain?
During ECT, all patients increased their caloric intake (280 +/- 180 to 1,510 +/- 60 kcal/day, mean +/- SEM) to exceed their basal energy expenditure; major improvements in their depressive symptoms and weight gain were seen in five of the six patients.
Who qualifies for ECT?
Who can get ECT in California? Any adult age 18 or older with an appropriate clinical diagnosis and who is capable of giving voluntary informed consent can receive ECT. Others, including adolescents between 13 and 17 years of age, may receive ECT after special reviews and legal procedures are followed.
Can you feel worse after ECT?
ECT can't prevent future depression, or fix any ongoing stresses or problems that are contributing to how you're feeling. Some people have very bad experiences of ECT, for example because they feel worse after treatment or are given it without consent. You might not want to risk the possibility of getting side effects.
Can ECT cause personality changes?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
When should ECT not be used?
The following strategies should not be used routinely: augmentation of an antidepressant with a benzodiazepine for more than 2 weeks as there is a risk of dependence. augmentation of an antidepressant with buspirone*, carbamazepine*, lamotrigine* or valproate* as there is insufficient evidence for their use.
What is the success rate of ECT?
What is the Success Rate of Electroconvulsive Therapy? ECT is an effective medical treatment option, helping as many as 80-85 percent of patients who receive it. Most patients remain well for many months afterwards.
Does ECT worsen anxiety?
The concern of some psychiatrists is that while ECT may help with depressive symptoms, it could worsen anxiety symptoms, including obsessional thoughts or panic attacks.
Can ECT make you more depressed?
ECT can't prevent future depression, or fix any ongoing stresses or problems that are contributing to how you're feeling. Some people have very bad experiences of ECT, for example because they feel worse after treatment or are given it without consent. You might not want to risk the possibility of getting side effects.
How much does an ECT cost?
The cost of each ECT session is about $2,500, for a total of $25,000 for the 10 sessions an average course of treatment entails.
What is ECT therapy?
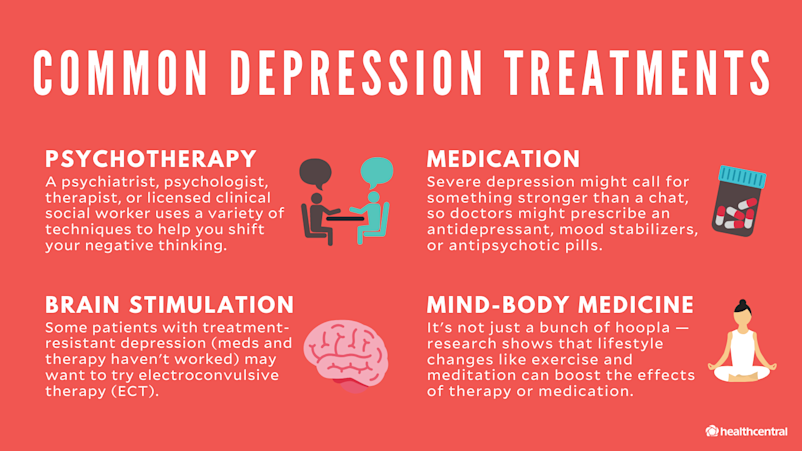
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a non-medication medical treatment that addresses severe psychiatric symptoms, after trials of medications and psychotherapy have been unsuccessful or a mental health disorder is determined to be severe and acute enough to warrant this intervention. During this brain stimulation procedure, ...
How long does it take for ECT to work?
ECT relieves symptoms of depression within one to two weeks after beginning treatments. After a course of ECT, some patients will continue to have maintenance ECT, while others will return to or continue antidepressant or other psychiatric medications to maintain their mental health on a long-term basis.
Why is ECT important in psychiatry?
ECT is quite useful in psychiatry for the care of certain patients with significant depression, particularly for those who cannot take or are not responding to antidepressants, suffer from severe depression, or are at a high risk for suicide.
How long does it take to get awake after ECT?
A person usually needs six to 12 treatments for this medical therapy to be effective. The patient is awake in five to 10 minutes. The most common side effects of ECT include brief confusion immediately after the procedure, as well as a temporary loss of short-term memory, which usually resolves within about six weeks.
Does ECT cause headaches?
Other side effects may include headache, high or low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, nausea, and sore muscles, although the muscle relaxant given to the ECT recipient decreases the frequency and severity of muscle soreness.
Does ECT work?
Formerly known as electroshock therapy in the days when it often caused injury and severe side effects, ECT practices today include drugs that relax the skeletal muscles so the patient does not move or thrash as the seizure affects the brains electrical functioning. How ECT works isn't clear, but it's effectiveness is.
Is ECT a stigma?
The study's lead researcher, Eric L. Ross, explained that among clinicians familiar with ECT, there is far less stigma surrounding the treatment than among the public: "Psychiatrists know that this is a very effective treatment, but it is still not widely used," he told MedPage Today.
Is electroconvulsive therapy effective?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is efficacious and also cost effective for patients with treatment-resistant major depression, and it should be considered after failure of two prior trials of pharmacotherapy and/or psychotherapy, new research suggests.
How many treatments are there for ECT?
Typically the ECT treatment course lasts eight to 12 treatments -- sometimes as few as six, sometimes as many as 15 treatments can occur in a course. Your doctor will determine how many you need depending on your response. After patients have received a course of ECT they're usually placed back on medication.
How long can you be on maintenance ECT?
Maintenance ECT involves getting treatments every two weeks to every month, usually for a period of six months to a year. But patients have gone on maintenance ECT for up to three years, depending on their response. ...
How many times a week is electroconvulsive therapy?
Email this article. — -- Question: How long will I need to do electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), and what is maintenance ECT? Answer: ECT is usually given two or three times a week -- usually on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday. Typically the ECT treatment course lasts eight to 12 treatments -- sometimes as few as six, ...
How long does it take for a patient to get back on medication after ECT?
After patients have received a course of ECT they're usually placed back on medication. However patients given medication after ECT have about a 50/50 chance of relapsing or having another episode of depression. Usually this episode occurs within one to three months after ECT -- but it can occur within the six months after ECT. ...
How long does an ECT procedure last?
How long is an ECT procedure? A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes). Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total ...
How does ECT work?
Why does ECT work? No one is sure how ECT helps certain psychiatric disorders. It may promote changes in how brain cells communicate with each other at synapses and it may stimulate the development of new brain cells. ECT may flood the brain with neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to be involved in conditions like ...
How long does it take to drive after ECT?
Usually this takes about 20 to 25 minutes. Patients who are given ECT on an outpatient basis must have someone drive them home after the procedure and stay with them until they go to sleep at night. People should not drive in the 24 hours following ECT.
What are the two electrodes used for?
Two of these electrodes are for monitoring the brain waves. The other two are for delivering a short, controlled set of electrical pulses for a few seconds. The electrical pulses must produce a generalized seizure to be effective.
How long does it take to sleep before ECT?
During the procedure, the patient receives a short acting anesthetic agent which puts the patient to sleep for approximately 5-10 minutes.
How can families help with ECT?
Families can help by providing a gentle reminder of the day and date and that feeling confused is to be expected. Family members should inform the nurse of any concern they have about their loved one. View a Powerpoint Presentation for Families about ECT.
Can memories be lost after ECT?
Memories formed closer to the time of ECT are at greater risk of being lost while those formed long before ECT are at less risk of being lost. The ability to form new memories is also impaired after a course of ECT treatments but this ability usually makes a full recovery in the weeks and months following the last treatment.
How effective is ECT?
What is clear is that for severe illness, such as psychotic depression or catatonia, where patients can lose 40-50 pounds and can be at some risk of death, ECT has been shown to be 80-95% effective.
What is true about every patient who seeks treatment with ECT?
Ultimately, Seiner said, two things are true generally about every patient who seeks treatment with ECT. “One is that they’re really struggling, and two, they’re terrified about what we do. It’s important to get them better, but our job is to walk them through it, to be there with them. This is what we’re committed to.
How long after ECT do you get better?
The research indicates that if you wait two months after ECT, or six months, after the ‘dust’ of the ECT has settled, most people do much better on neuropsychological testing than they did before ECT. That’s because when people aren’t depressed, they think better and test better.”.
Is ECT good for depression?
Using ECT to Treat Depression. Effective treatments for depression include counseling, psychotherapy, and prescription medications. However, for an estimated 100,000 people a year in the United States, like Neville, these options fall short. And for them, ECT is safe, reliable, and effective. The treatment has evolved since ...
How long does ECT last?
Generally, ECT is a short-term treatment where the patient receives 6-12 treatments over the course of 2-4 weeks. However, in some cases, continuation ECT or maintenance ECT is used. These two therapies continue ECT beyond the initial 6-12 sessions used in acute treatment.
Why do people need ECT?
Maintenance ECT: Why Some People Need Continuation ECT. Electroconvulsive therapy, once known as shock therapy, is a safe and effective treatment for depression and other mental illnesses. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is most often used in cases of severe, intractable, hard to treat (treatment-resistant) depression.
What is maintenance ECT?
Maintenance ECT consists of ECT treatments given infrequently over a long period of time after the index series and continuation ECT. The goal of maintenance ECT is to prevent the reoccurrence of the mental illness.
Is ECT effective for relapse?
Relapse after a positive response to ECT is common. Most frequently, prevention of relapse is accomplished through the use of medication but continuation ECT has also been shown effective for the prevention of illness relapse.
What is ECT therapy?
ECT stands for electroconvulsive therapy and is another name for what was known in the past as electroshock therapy . This form of therapy has been used since 1938 as a psychiatric treatment for certain mental health disorders. Today, doctors and psychiatrists use ECT most commonly to treat severe cases of depression when other forms ...
What is the deductible for ECT?
With Original Medicare Part A, you are responsible for the deductible for each benefit period. As of 2019 this amount is $1364.00.
How much does Medicare Part B cost?
You are also responsible for paying the Part B deductible, which is $185.00 per year as of 2019. ECT may provide effective treatment for patients with severe, psychotic, or suicidal depression. ...
How much is the coinsurance for 2019?
As of 2019 this amount is $1364.00. A benefit period begins on the day of your admission to the hospital and ends after 60 consecutive days of not receiving inpatient hospital care. The coinsurance payment is $0 for days 1-60 of in-hospital care.
How long does it take to get ECT?
Depending on the individual circumstances, ECT treatments can take place 3 times a week for a total of 6 to 12 sessions. Each session of ECT takes about 15 minutes. Before each session, preparation takes an hour, and after a session, you can expect an hour for recovery.
Can pregnant women take ECT?
ECT may also be considered as an option for pregnant women who need treatment and cannot take medications, or for older people who have problems with the side effects of drugs. It is also important to note that ECT is never performed on someone who does not want this form of treatment. Costs of ECT. In the United States, the average cost ...
Does Medicare cover ECT?
Medicare Part B (Medical Insurance) may help cover the cost of ECT services you receive in an outpatient setting. You are eligible for this coverage only if your doctor certifies that the treatment is medically necessary and you get ECT in a Medicare-approved facility. With Original Medicare Part B, you will likely pay 20 percent ...
