
Nutrition
Patients with active TB disease should receive at least three drugs as their initial TB drug treatment. Fewer than three drugs can result in the development of resistance; Never add a single TB drug to a failing regimen. A regimen simply means the course of treatment, in this instance the combination of TB drugs;
How many TB drugs should be given to a patient?
There are 10 drugs currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treating TB. Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: isoniazid (INH) rifampin (RIF) ethambutol (EMB) pyrazinamide (PZA) TB Regimens for Drug-Susceptible TB.
What drugs are used to treat tuberculosis (TB)?
One TB drug must never be taken on it’s own. Several TB drugs, or TB medication, must always be taken together. If only one TB drug is taken then resistance may develop to the drug. This means that the drug won’t work and the patient isn’t cured of TB. It is often now that several TB drugs are combined together in one tablet or pill.
Can you take one TB drug on it’s own?
This consists of a two month intensive phase followed by a four month continuation phase. For the two month intensive TB treatment phase they should receive: for the continuation treatment phase. It is recommended that patients take the TB drugs every day for six months.
How long does it take to treat tuberculosis (TB)?

How many pills do you take for TB?
For the treatment of tuberculosis: Adults and children 15 years of age and older weighing 55 kilograms (kg) (121 pounds) or more—6 tablets per day. Adults and children 15 years of age and older weighing between 45 and 54 kg (99 and 119 pounds)—5 tablets per day.
What is the standard TB treatment?
The preferred regimen for treating adults with TB remains a regimen consisting of an intensive phase of 2 months of isoniazid (INH), rifampin (RIF), pyrazinamide (PZA), and ethambutol (EMB) followed by a continuation phase of 4 months of INH and RIF. (See table 2 for more information on drug regimens.)
Which drug is included in all TB treatment?
Rifampin (RIF),Isoniazid (INH),Pyrazinamide (PZA), and.Ethambutol (EMB)
How long is the standard regimen treatment for TB?
Treatment of Tuberculosis Resistant to a Single Drug TB that is resistant to isoniazid (with or without resistance to streptomycin) can be treated with rifampin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol for 6 months. Therapy should be extended to 9 months if the patient remains culture-positive after 2 months of treatment.
Why is TB treated with 4 drugs?
Regimens for the treatment of TB disease must contain multiple drugs to which the bacteria are susceptible. The standard of care for initiating treatment of TB disease is four-drug therapy. Treatment with a single drug can lead to the development of a bacterial population resistant to that drug.
What are 3 drugs for TB?
Pulmonary TB 2 antibiotics (isoniazid and rifampicin) for 6 months. 2 additional antibiotics (pyrazinamide and ethambutol) for the first 2 months of the 6-month treatment period.
What are second-line TB drugs?
Second-line anti-tuberculosis drugs. Group 2. Moxifloxacin, high dose levofloxacin (fluoroquinolones) Group 3. Linezolid, delamanid, bedaquiline (newer drugs with increased evidence)
Which drugs are used for first-line treatment of TB?
First-line agents for treatment of active TB consist of isoniazid, a rifamycin (rifampin or [less frequently] either rifapentine or rifabutin), pyrazinamide, and ethambutol; in addition, moxifloxacin is a first-line agent when administered in combination with isoniazid, rifapentine, and pyrazinamide [6].
Why is multiple drug therapy used for tuberculosis?
The bacteria that cause tuberculosis (TB) can develop resistance to the antimicrobial drugs used to cure the disease. Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) is TB that does not respond to at least isoniazid and rifampicin, the 2 most powerful anti-TB drugs.
How many stages of TB treatment are there?
The standard six month course of treatment consists of two phases. The first phase lasts two months and is called the intensive phase. The second phase lasts four months and is called the continuous phase.
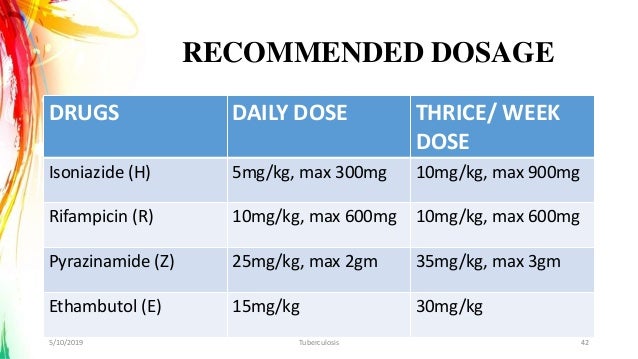
WHO TB drug doses?
Weight-based oral anti-TB drug daily dosing in adults ≥30 kgDRUGSDAILY DOSE>70 KGIsoniazid4–6 mg/kg once daily300 mgRifampicin8–12 mg/kg once daily600 mgPyrazinamide20–30 mg/kg once daily2000 mgEthambutol15–25 mg/kg once daily1200 mg15 more rows
Can TB be cured in 3 months?
After taking TB medicine for several weeks, a doctor will be able to tell TB patients when they are no longer able to spread TB germs to others. Most people with TB disease will need to take TB medicine for at least 6 months to be cured.
What should a clinic decide on TB treatment?
Clinicians should choose the appropriate treatment regimen based on drug susceptibility results of the presumed source case (if known), coexisting medical conditions (e.g., HIV. ), and potential for drug-drug interactions. Consultation with a TB expert is advised if the known source of TB infection has drug-resistant TB.
What is the name of the drug that is used to treat TB?
Isoniazid (INH) Rifapentine (RPT) Rifampin (RIF) These medications are used on their own or in combination, as shown in the table below. CDC and the National Tuberculosis Controllers Association (NTCA) preferentially recommend short-course, rifamycin-based, 3- or 4-month latent TB infection treatment regimens over 6- or 9-month isoniazid ...
Is 6H or 9H better for TB?
Although effective, 6H and 9H have higher toxicity risk and lower treatment completion rates than most short-term treatment regimens. All treatment must be modified if the patient is a contact of an individual with drug-resistant TB disease.
How many drugs are there for TB?
There are more than twenty drugs available for TB treatment. Which ones have to be taken depends on the circumstances of the patient. If you are having TB treatment (sometimes known as antitubercular treatment or ATT), then this should always be supervised by an experienced doctor or other health person.
What are the best drugs for TB?
The drugs that a patient should take depends on whether the patient has ever had TB treatment before. If the patient has never had treatment before then it can be assumed that the bacteria in the patient's body will respond, and be sensitive to all the TB drugs. So the patient can then be given the following drugs: 1 Isoniazid 2 Rifampicin 3 Pyyrazinamide 4 & Ethambutol.
Why does TB treatment fail?
It is often suggested that TB treatment fails because a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs correctly. However there can be a number of different reasons for TB treatment failure. It is certainly true that if a patient doesn’t take their TB drugs properly that this can lead to the development of drug resistant TB.
What is the second exception to isoniazid?
The second exception is if the patient has been known to be in contact with a patient who is known to have drug resistant TB.
What is the responsibility of a doctor for TB?
A patient must take their drugs properly. But it is also the responsibility of the doctor to make sure that the patient has the correct drugs. The doctor must also explain to the patient how to take the drugs correctly. In many countries there are "alternative" medicines available.
What happens if you take only one or two TB drugs?
If only one or two TB drugs are taken then only some of the bacteria may be killed. They may then become resistant to the TB drugs which then don't work. If the person becomes sick again then different TB drugs called second line drugs may be needed.
How often should I take isoniazid?
Isoniazid. plus rifampicin. for the continuation treatment phase. It is recommended that patients take the TB drugs every day for six months. Taking the drugs three times a week used to be considered satisfactory but is no longer recommended by the WHO. It is essential that all the recommended TB drugs are taken.
What is the best treatment for TB?
First line drugs. These are the antitubercular drugs that generally have the greatest activity against TB bacteria. This medicine for TB is particularly used for someone with active TB disease who has not had TB drug treatment before. All the other drugs are generally referred to as second line TB drugs.
What is considered a new patient for TB?
Patients who have not had any TB treatment before, or they have had less than one month of anti TB drugs, are considered to be new patients. New patients are presumed to have drug susceptible TB (i.e. TB which is not resistant to any of the TB drugs) unless there is a high level of isoniazid resistance in new patients in the area. The other people who may have drug resistant TB are people who have developed active TB disease after they have been in contact with someone who is known to have drug resistant TB.
What is the trade name for ethambutol?
For example ethambutol is known in India by a variety of trade names which include Abitol (made by Alpic Remedies), Actuate (made by Biocin Genetics) and Albutol (Alkem Laboratories). 3“Tuberculosis - Drugs for its Treatment”.
What is the best antitubercular drug for TB?
Pyrazinamide (Z/Pza) Ethambutol (E/Emb) These are the antitubercular drugs that generally have the greatest activity against TB bacteria. This medicine for TB is particularly used for someone with active TB disease who has not had TB drug treatment before.
How are drug regimens described?
Drug regimens are described in a standard manner . The drugs are listed by their single letter abbreviations. The order is the order that is roughly the order that they were introduced into clinical practice. The number of months that the drug should be given for is denoted by a prefix.
What is the first line of anti-TB?
For example some anti TB drugs, the first line drugs, are only used for the treatment of new patients who are very unlikely to have resistance to any of the TB drugs. There are other TB drugs, the second line drugs, that are only used for the treatment ...
Why won't TB treatment work?
This is because the TB bacteria develop resistance to the TB drugs. The patient is then still ill, and to be cured they then have to take drugs for the treatment of drug resistant TB.
How long does it take to cure TB?
TB treatment takes at least six months, patients need to take many tablets each day and side effects are common. This can be very difficult for people to manage, but it’s crucial that they take their treatment as prescribed and complete the course, to ensure they are completely cured and prevent them developing drug-resistant TB.
What is drug resistant TB?
Drug-resistant TB requires a longer course of treatment, with different combinations of drugs that can have more side effects. A patient will be tested to find out the exact course of treatment that should work for them.
Can TB go away?
With any medication, it is possible to experience side effects. Most are nothing to worry about and will go away. The TB nurse or doctor should advise patients of these before they start treatment.
Can latent TB be treated?
Most cases of latent TB are not considered for treatment, as 90% of people with latent TB do not go on to become ill with active TB. Treatment is recommended for people whose immune systems are weaker as they are more likely to go on to develop an active infection. This includes children and people living with HIV.
What is the new drug for TB?
Bedaquiline and Delamanid are new drugs. Ethambutol, Pyrazinamide, Thioamides, Cycloserine, Para-aminosalicylic acid, Streptomycin, and Clofazimine are possibly effective. Kanamycin, Capreomycin and Amikacin are injectable second-line. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, ...
How to cure MDR TB?
To cure MDR TB, healthcare providers must turn to a combination of second-line drugs, several of which are shown here. Second-line drugs may have more side effects, the treatment may last much longer, and the cost may be up to 100 times more than first-line therapy. MDR TB strains can also grow resistant to second-line drugs, ...
What drugs target DNA?
Rifamycins, Oxazolidinones and Macrolides act on DNA. Tuberculosis drugs target various aspects of Mycobacterium tuberculosis biology, including inhibition of cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or nucleic acid synthesis. For some drugs, the mechanisms of action have not been fully identified.
Who took the photo of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
The photo of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CDC/Dr. Ray Butler, Janice Carr. This illustration is in the public domain. Please credit the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).
Is XDR TB resistant to isoniazid?
NIAID. XDR TB occurs when a Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain is resistant to isoniazid and rifampin, two of the most powerful first-line drugs, as well as key drugs of the second line regimen—any fluoroquinolone and at least one of the three injectable drugs shown above. XDR TB strains may also be resistant to additional drugs, ...
How often should I watch TB patients?
If your provider is worried that you may not be taking all the medicines as directed, they may arrange to have someone meet with you every day or a few times a week to watch you take your TB drugs. This is called directly observed therapy.
How long after taking TB medicine can you stay home?
For the first 2 to 4 weeks after starting the medicines, you may need to stay home to avoid spreading TB to others. Ask your health care provider when it is OK to be around other people. Your provider is required by law to report your TB to the local public health department.
What is latent TB?
This means the TB bacteria remain inactive (dormant) in a small area of your lungs. This type of infection may be present for years and is called latent TB. With latent TB:
How long does it take to get rid of latent TB?
Even though you do not feel sick, you need to take medicines to treat latent TB for 6 to 9 months. This is the only way to make sure all of the TB bacteria in your body are killed and you do not develop active infection in the future.
What happens if you don't take your TB medicine?
If you do not take your TB medicines the right way, or stop taking the medicines early: Your TB infection may become worse. Your infection may become harder to treat. The drugs you are taking may no longer work. This is called drug-resistant TB.
Is TB contagious?
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection that involves the lungs, but may spread to other organs. The goal of treatment is to cure the infection with medicines that fight the TB bacteria.
Overview
Medical uses
Use
Causes
Specialist to consult
Treatment
Names
- Generally anti TB drugs, that is TB medicine, is taken for the treatment of active TB or TB disease. One exception to this is when TB drugs are taken for the treatment of latent TB.
Nomenclature
- It is often now that several TB drugs are combined together in one tablet or pill. This is known as a FDC, or Fixed Dose Combination. It can fuel the development of drug resistance leading to the loss of streptomycin as a second line agent in MDR-TB treatment. It can delay a patient receiving proper treatment for drug resistant TB and if a patient has drug susceptible disease it can expos…
Side effects
- TB is caused by bacteria which are in a persons body. The TB drugs have the aim of killing all the TB bacteria in the persons body. This means that the person is then cured of TB. However TB bacteria die very slowly, and so the drugs have to be taken for quite a few months. Even when a patient starts to feel better they can still have bacteria alive in their body. So the person needs t…
Categories
- All the drugs must be taken for the entire period of TB treatment. If only one or two TB drugs are taken then the bacteria may not all be killed. They may then become resistant to the TB drugs which then dont work. If the person becomes sick again then different TB drugs may be needed. A regimen means a course of treatment. For TB this means a comb...