Full Answer
How does a wetland remove pollution?
Apr 05, 2022 · These functional microorganisms can remove pollutants from CWs by catalyzing chemical reactions, biodegradation, biosorption, and supporting plant growth, etc. Regarding microbial alpha diversity, heavy metals and high concentrations of nitrogen and phosphorus significantly reduce microbial richness and diversity, whereas antibiotics can cause large …
What role do microorganisms play in constructed wetlands?
Constructed wetlands (CWs) have been proven as a reliable alternative to traditional wastewater treatment technologies. Microorganisms in CWs, as an important component, play a key role in processes such as pollutant degradation and nutrient transformation. Therefore, an in-depth analysis of the com …
Can wetlands be used to treat wastewater?
these functional microorganisms can remove pollutants from cws by catalyzing chemical reactions, biodegradation, biosorption, and supporting plant growth, etc. regarding microbial alpha diversity,...
Why is water purification important in wetlands?
bacterial species, rhizospheric and endophytes bacteria, and their specific role in the pollutant removal process. The roots of plants release oxygen and exudates, which act as a substrate for...

What are the main mechanisms of nutrient removal from wastewater in constructed wetlands?
The main mechanisms of nutrient removal from wastewater in constructed wetlands are microbial processes such as nitrification and denitrification as well as physicochemical processes such as the fixation of phosphate by iron and aluminum in the soil filter.
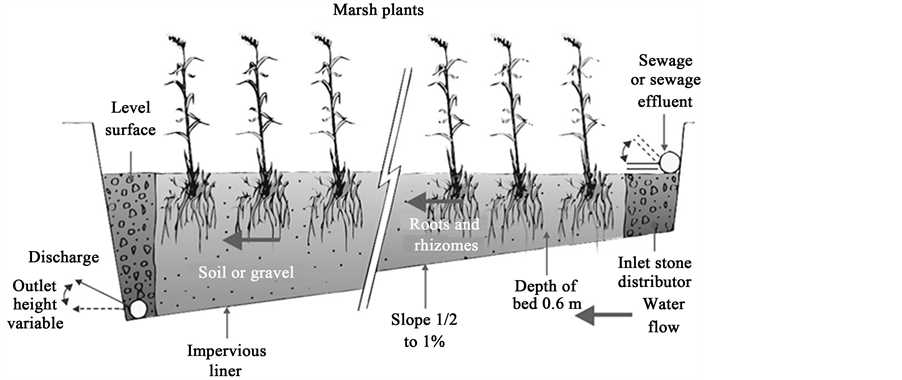
How does oxygen enter the soil filter?
In intermittently charged vertical filters, oxygen mainly enters the soil filter by virtue of the suction effect of the water as it flows downwards. By contrast, in subsurface horizontal flow systems oxygen is chiefly input by the marsh plants (helophytes).
Who was the first person to study the removal of phenols by helophytes in hydroponic
One of the pioneers of using helophytes to treat wastewater was Seidel (1968). She was the first person to study the removal of various phenols by helophytes in hydroponic vessels as well as the tolerance of plants to phenols. Because these studies were carried out as batch experiments under nonsterile conditions, the uptake is likely to have been caused by both microorganisms and the plants themselves. In addition, no constant test concentrations were established during her investigation of tolerance to contaminants.
What is the role of soil in the rhizosphere?
The soil is the main supporting material for plant growth and microbial films. Moreover, the soil matrix has a decisive influence on the hydraulic processes.
How to design a constructed wetland system?
The first step in designing a constructed wetland system is to size the wetlands. One way to size constructed wetlands is to consider them to be plug flow reactors, in which linear first order reaction kinetics are involved.
What is a wetlands?
Wetlands are soils which are more or less water saturated and constructed wetlands are a copy of natural marshes. They all are based on the same principles; to feed basins or channels that contain a soil (Sand, Gravel or Natural soil) in which wetland plants or macrophytes can grow.
What is a natural treatment system?
Natural treatment systems such as constructed wetlands (CWs) are more economical to build and operate. This is a new approach for decreasing environmental pollution, based on the purification of waste waters with vegetation’s planted in them.
Why is natural ecosystems important?
ADVERTISEMENTS: The use of natural eco-systems for waste water treatment is an important and emerging aspect of environmental management using constructed wetlands. There is a large and growing need to better treat many municipal, industrial, agricultural waste waters, especially those which are more difficult to handle because of their nature ...
What are the biogeochemical processes that occur in wetland communities?
Wetlands microbes mediate many of the vital biogeochemical processes needed in the environment. The carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and iron cycles all have some role in wetland communities and the bacteria present in the anoxic hydric soils are often responsible for the various oxidations and reductions that occur.
Why is water purification important in wetlands?
One big area of recent research has been the area of wastewater treatment. The extensive diversity of plant, animal, and microbial life allows wetlands to remove pollutants and purify water at an extremely high rate (USEPA, 1993). It has been repeatedly observed that suspended solids and oxidized nutrients are readily used by wetland organisms. As the water percolates through the system, these substrates are removed from the aquatic environment either through adsorption to the soil (phosphates and large organic compounds), microbially mediated removal (biochemical reactions), or uptake into plants (heavy metals, and some organic compounds). The resulting output of water is substantially cleaner than the inflow, showing how effective wetlands can be at water purification.
Why are wetland soils unique?
Because of the continual presence of water, conditions are created that support the growth of specially adapted plants and the formation of characteristic wetland soil – hydric soils. Wetlands are unique in that they actively support both aquatic and terrestrial species throughout the year (USEPA).
How do wetlands help the ecosystem?
As the most productive ecosystem on earth, wetlands provide an enormous amount of dissolved organic matter through the process of photosynthesis and subsequent death and decomposition.
What are the most common bacteria in wetland environments?
Bacteria are present in high diversity in wetland environments. The largest group of wetland bacteria is proteobacteria – capable of a number of important functions ranging from nitrogen fixation, to denitrification, to iron and sulfate reducers. These are chemotrophs – gaining their energy from chemical sources as opposed to light (or photosynthetic) energy. Other chemotrophic bacteria are actinomycetes and firmicutes. Both of these are found in lower abundance in wetland communities due to low decomposition rates, but they are present in small amounts. Some examples include:
Why are fungi important in the wetland ecosystem?
Normally an important decomposer, fungi are present in relatively low amounts in wetland communities because of the constant saturation and anoxic conditions. Because of the anoxic conditions, decomposition rates are low, limiting the importance of fungi in the environment.
Why are wetland habitats important?
Wetlands are particularly important habitats for amphibians and reptiles because of the proximity of open water to vegetated areas. Also, because of the wide array of insects inhabiting the ecosystem, a plentiful source of food is available for the amphibians and reptiles.