
- Farmers use digesters for manure management and create an energy source.
- Brewers use digesters in wastewater treatment for pollution prevention and create biogas for use in their boilers reducing natural gas consumption.
- Distillers use digesters to convert waste to energy and control pollution.
Full Answer
What are the biggest problems in wastewater treatment?
- Increasing/expanding regulations. Concerns over increasing regulations consistently ranked near the top of the list for every geographical region, pushing the topic into the No. ...
- Technology changes. Information technologies jumped to the No. ...
- Aging workforce. In the No. ...
- Water scarcity. ...
How does a digester work?
How Does Anaerobic Digestion Work Two Digester systems for Sewage Plants are normally used with one being heated and mixed so that bacteria can have contact and breakdown the volatile organic material then the Biosolids are transferred over to the second Digester in order to settle out and separate the solids from water which is sent back to ...
How does the digester work?
The digester tanks are made of 14-inch-thick concrete walls and thick floors, which contain heating coils. Once inside the digester, the thick slurry is stirred by an agitator while being heated to 101 degrees. “We’re trying to create the same environment that the cow has in her stomach, or one compartment of her stomach, known as the rumen ...
What is a sludge digester?
- Tank sizes are not less than 6 m diameter and not more than 55 m diameter.
- Liquid depth may be 4.5 to 6 m and not greater than 9 m.
- The digester capacity may be determined from the relationship V = [V f -2/3 (V f - V d )]t 1 + V d t 2 where V = capacity ...
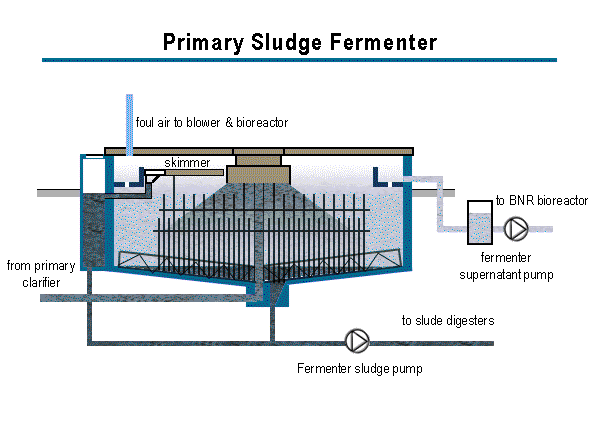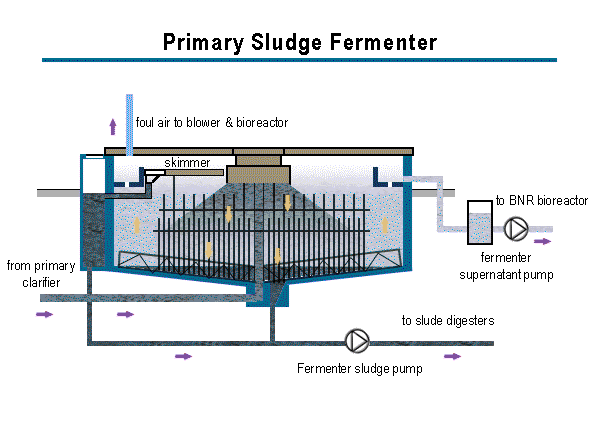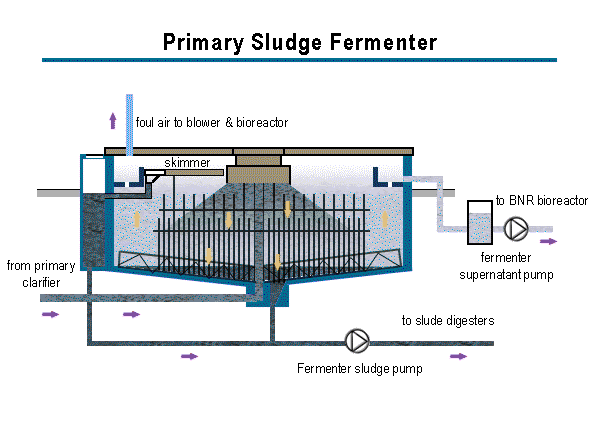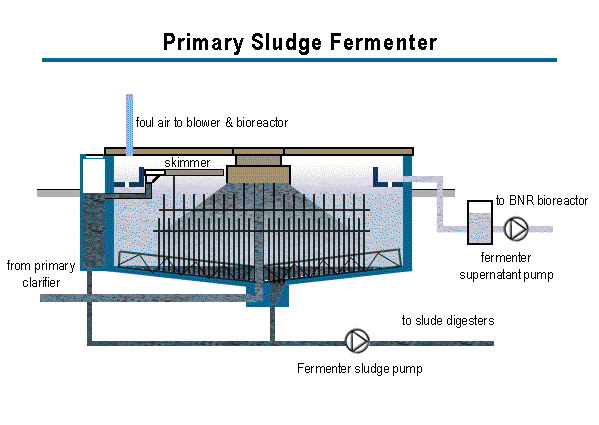
What is the purpose of anaerobic digesters in wastewater treatment?
Existing Infrastructure – Many wastewater treatment facilities in the Pacific Southwest (US Region 9) and across the country, use anaerobic digesters to reduce the volume of the biosolids (sewage sludge) before they are taken off site.
What is sludge digested?
The digested sludge is de-watered, dried up and used as sewage sludge fertilizer while the gases produced are used as fuel or for driving gas engines. The supernatant liquor is re-treated at the treatment plant along with the raw sewage. The tanks in which sludge digestion is carried out are called sludge digestion tanks.
What are the stages of digestion of sludge?
These are (1) acidification (2) lysis/ liquefaction or a period of acid digestion and (3) gasification or conversion of acids into methane and carbon dioxide.
What is anaerobic digestion?
There are two distinct uses of Anaerobic Digestion in Wastewater Treatment: 1 As a treatment process in its own right for primary sewage treatment/ organic industrial effluent, as known as a “UASB” 2 As a method of treating the sludge produced by Wastewater Treatment Plants.
How is sewage sludge disposed of?
The remaining sewage sludge after digestion can be disposed of sustainably , and without the heavy metals and other substance it may contain causing the problems which can occur when it is spread on land. This is done by a process known as “pyrolysis and/ or gasification”.
What is the stage of methane gasification?
It is the stage when more resistant materials like proteins and organic acids are broken up. Large volumes of methane gas of high calorific value, along with comparatively smaller volumes of carbon dioxide are evolved. The pH value goes to the alkaline range i.e., above 7 and a tarry odour appears. Gasification finally becomes very slow; the sludge becomes well adjusted and is stable enough for disposal. This stage in the digestion of sludge is also termed as alkaline fermentation.
How is flow balanced in a UASB reactor?
The flow rate is then balanced with the geometry of the tank so that a “blanket” of sludge, which is particles of organic matter and bacteria constantly falling gently in the water at the same speed as the water rises, stays perpetually suspended . In effect it is balanced in a horizontal layer, above the bottom, within the UASB reactor vessel while the micro-organisms digest it.
What is the energy hidden in wastewater?
The energy hidden in wastewater is an untapped resource with the potential to offset 12% of the US electric demand. That’s thousands of POWER PLANTS are ready to be turned on.
Where are biosolids pumped?
Biosolids are pumped into our stirred tank reactors, where they can also be co-digested with outside organic waste. As anaerobic bacteria break down the volatile solids in the digester, biogas is released and can be combusted to generate electricity.
What is digester used for?
Biogas collected from the anaerobic digester systems is often used to generate electricity, to fuel boilers or furnaces, or to provide combined heat and power.
How does a batch digester work?
In a batch digester, feedstocks are loaded into the digester all at once. Following loading there is a set period of time for digestion to occur. Following this time period, the digester is manually emptied and reloaded.
What is the purpose of anaerobic digesters?
The primary purpose of anaerobic digesters at WRRFs is to treat wastewater solids. As a result, these digesters are subject to EPA biosolids regulations ( 40 CFR Part 503 ). WRRF digesters vary in a number of ways including:
What temperature do digesters run at?
The temperature ranges are typically 86 - 100 ○ F for mesophillic and 122 - 140 ○ F for thermophilic. There are different populations of anaerobic microbes that thrive in these temperature zones.
What is biogas used for?
Biogas collected from the anaerobic digester systems is often used to generate electricity, to fuel boilers or furnaces, or to provide combined heat and power. As of January 2019 there are 248 operating digesters on livestock farms in the United States. This data is tracked by EPA’s AgSTAR program.
What is a co digester?
Some digesters are designed to process one type of feedstock and other digesters are designed to process multiple feedstocks. Co-digestion is often a driver for the development of anaerobic digesters. Many feedstocks require or can benefit from pre-processing before digestion (e.g., blending, screening, thermal conditioning, etc.)
What feedstock is processed in stand alone digesters?
The primary feedstock processed in stand-alone digesters is food waste . However, digesters built to process food waste can also co-digest other organic materials, such as yard waste, manures and waste water solids.
What is anaerobic digestion?
Anaerobic digestion is a biological process in which bacteria help to break down organic matter, including solid waste. What distinguishes anaerobic digestion is that there is no oxygen involved in the process.
Is anaerobic digester good for wastewater treatment?
Anaerobic digester mixing systems can play an important role in the treatment of wastewater; in fact, digester wastewater treatment can be both a cost-effective and environmentally friendly way to treat sludge, sewage, and beyond.
What is the final step of wastewater treatment?
10. The final step of wastewater treatment is the deep inspection of service water. Aim of this inspection is to analyse the contamination level and ensure that the treated water complies with the highest standards, defining its release or reuse for domestic and/or industrial purposes.
What happens to wastewater pollution after primary treatment?
This is the point where primary pre-treatment ends and secondary wastewater treatment starts. After the primary treatment, level of wastewater pollution drops to 60%.
What happens during the biological stage of a sludge treatment?
6. During the biological stage, the excess sludge (i.e. excess bacteria) is pumped out and moved before the settling tanks. Here, the sludge settles and is transported to digestion tanks for further treatment.
How long does it take for sludge to dry out?
9. Sludge, digested and dewatered to the optimal degree, is finally disposed of at the dump. In about a month, sludge is adequately dried out and ripe. If it complies with agricultural standards, it can be reused for fertilisation of industrial crops.
How is wastewater drained to the WWTP?
1. Firstly, wastewater is drained to the WWTP by gravity through the main sewer system of the size of a car. Having such size, objects you could hardly imagine reach the WWTPs, ranging from mattresses, fridges, tree branches to wallets disposed of by thieves in order to get rid of the evidence. 2.
What is wastewater water?
Wastewater can be divided into two major groups: Sewage water is all wastewater used in domestic dwellings (e. g. originating from toilets, showers or sinks). Industrial wastewater originates from production, industrial and commercial activities, and has a different chemical composition to sewage water.
What is wastewater in agriculture?
What is wastewater? It is used water originating from domestic, industrial, agricultural, and medical or transport activities. Used water becomes wastewater upon the change of its quality, composition and/or temperature. However, wastewater does not include water released from ponds or reservoirs for fish farming.
What is biological wastewater treatment?
Biological wastewater treatment (anaerobic and aerobic digestion reactors) takes advantage of the ability of certain microorganisms (including bacteria) to assimilate organic matter and nutrients dissolved in the water for their own growth, thus removing soluble components in the water. Soluble organic matter is assimilated by microorganisms as ...
Why is organic matter used in wastewater treatment?
In most cases, the organic matter constitutes the energy and carbon source that the microorganisms need in order to grow.
How is sludge separated in decantation?
Decantation: The sludge formed is separated by gravity in secondary settlers.
Why is O2 important in wastewater?
Aerobic systems: The presence of O2 makes this element the electron acceptor, which is why elevated energetic outputs are obtained, causing an important generation of mud due to the high growth of aerobic bacteria. Its application to wastewater may be very conditioned by the low solubility of the oxygen in the water.
Why are fats removed from wastewater?
Oils and fats are also removed at this stage to prevent the biological treatment from slowing down, as both the performance and the quality of the effluent decreases. Both physical and mechanical operations are used for this. The main operations used depend on the wastewater source, its quality and subsequent treatment:
What happens if you don't dispose of water treatment?
Large size solids arriving at the water treatment plant are first removed. If not disposed of effectively, these materials can lead to serious equipment failure. Stones, sand, tin cans, etc. cause significant wear on pipes as well as pumps.
When is a screening required for wastewater?
Screening: This operation is required when wastewater contains large amounts of floating solids or debris. Sieves of different thickness are used.

Common Ways to Describe Digesters
Stand-Alone Digesters
- Most stand-alone digesters accept and process feedstocks from one or more sources for a tipping fee. Stand-alone digesters can be operated as organics recycling businesses, community-based operations or built by a municipality to manage residential food waste. Other stand-alone digesters are built to process industry specific wastes. This is common...
On-Farm Digesters
- On-farm digesters can bring great value to farmers The most common digester system technologies on farms in the United States are: plug flow, complete mix, and covered lagoons. Learn more about on-farm digesters and how value can be recovered from waste (manure) The type of digester used on farms is typically determined by the manure management practices in …
Digesters at Water Resource Recovery Facilities
- Plant operators, industry associations, research institutions, The use of anaerobic digestion at WRRFs in the United States dates back to the early 1900’s. Over the last century, there have been both advancements and setbacks in the development of the technology. Anaerobic digestion is both a biological process and an engineered system that requires expertise in both disciplines f…