
Medication
Legionella disinfection using temperature control. Controlling water temperatures is one of the most effective ways of preventing the growth and spread of Legionella bacteria. The ideal temperature range for the growth of the bacteria is between 20 and 45 degrees Celsius. Outlet temperatures for cold water should therefore be kept below 20 ...
Nutrition
Possible long-term effects include the following:
- Confusion
- Short term memory loss
- Long term memory loss
- Fatigue
- Onset of asthma (although it is unclear, when this occurs, whether Legionnaires' disease is the sole cause)
What kills Legionella bacteria?
What Is The Incubation Period For Legionnaires Disease?
- Detailed Study on Incubation Period And Death Rate of Legionnaires’ Disease. ...
- When The Problem Remains in Untreated Condition. Health condition of individuals with untreated Legionnaires’ disease often becomes worse during the initial weeks.
- Death Rate of The Disease. ...
What are the long-term effects of Legionnaires' disease?
Legionnaires’ disease is normally acquired by inhalation or aspiration of legionellae from a contaminated environmental source. The first evidence of the association between potable water from shower and nosocomial legionellosis was reported approximately 20 years ago (), and the hot water system is thought to be the most frequent source of cases or outbreaks within a hospital (2,3), where ...
What is the incubation period for Legionnaires disease?
Do water heaters protect you from Legionnaires' disease?
See more
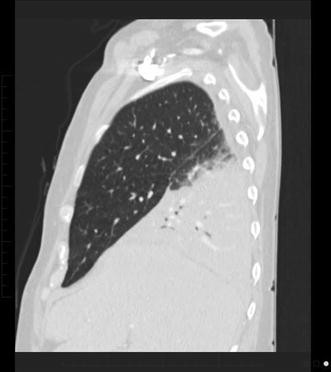
How long does it take to get over Legionella pneumonia?
Recovery. Most patients should respond to treatment within three to five days.
What antibiotics treat Legionella pneumonia?
Medication Summary Mild Legionnaires disease can be treated with a single oral antibiotic regimen that have activity against legionella pneumophila including fluroquinolones such as levofloxacin, and moxifloxacin, macrolides like azithromycin, clarithromycin.
How is Legionella infection treated?
Legionnaires' disease is treated with antibiotics. The sooner therapy is started, the less likely the chance of developing serious complications. In many cases, treatment requires hospitalization. Pontiac fever goes away on its own without treatment and causes no lingering problems.
What is the prognosis for Legionnaires disease?
About 1 out of every 10 people who gets sick with Legionnaires' disease will die due to complications from their illness. For those who get Legionnaires' disease during a stay in a healthcare facility, about 1 out of every 4 will die.
What is the incubation period for Legionnaires disease?
How soon do symptoms occur/appear? The incubation period for Legionnaires' disease ranges from two to 10 days, but is usually five to six days.
What is the best antibiotic for Legionella?
Macrolides and fluoroquinolones should be the drugs of choice for the treatment of established Legionellosis. Oral macrolides should be prefered in patients with mild to moderate pneumonia; within the macrolides, azithromycin has the most favourable profile of activity.
Can Legionnaires be cured?
Pontiac fever usually clears on its own, but untreated Legionnaires' disease can be fatal. Although prompt treatment with antibiotics usually cures Legionnaires' disease, some people continue to have problems after treatment.
What are the long term effects of Legionnaires disease?
According to Victor L. Yu, MD, an infectious disease specialist and Legionnaires' disease expert, “As with any acute illness, patients who recover from Legionnaires' disease can suffer long term side effects. The most common are fatigue and lack of energy for several months.”
How long does it take to develop Legionnaires?
The period of time between breathing in the bacteria and developing symptoms is normally between 2 – 10 days. However, it can take up to 2 weeks. Symptoms tend to develop quickly as the infection spreads across your lungs.
How long does it take for antibiotics to work for walking pneumonia?
Antibiotics are very effective against walking pneumonia – typically a five to seven day course is prescribed. It may take about 10 to 14 days before you actually start feeling back to baseline, but once the walking pneumonia is treated, symptoms should resolve completely.
Does Legionnaires affect the brain?
Cerebral and cerebellar symptoms are frequently associated with Legionnaires' disease. However, corresponding brain lesions are difficult to demonstrate using either computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Can you get Legionella twice?
These diseases aren't contagious. The bacteria are not spread from one person to another person. You can get the diseases again if you are exposed to the bacteria again. Legionnaires' disease typically affects people older than 45, especially if they smoke or have a long-term lung disease such as asthma.
What antibiotics are effective against Legionella?
Many antibiotics are highly effective against Legionella bacteria. The two most potent classes of antibiotic are the macrolides (azithromycin), and the quinolones (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin, gemifloxacin, trovofloxacin).
What is Legionnaires disease?
Legionnaires' disease is a severe, often lethal, form of pneumonia. It's caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila found in both potable and nonpotable water systems.
Can Legionnaires disease be admitted to intensive care?
It is not uncommon for patients with Legionnaires' disease to be admitted to the intensive care unit. Some will suffer long-term impaired health-related quality of life. A study of outbreak survivors showed persistence of fatigue (75%), neurologic symptoms (66%) and neuromuscular symptoms (63%) in months after an outbreak.
How long do you have to stay in a hospital for Legionella?
Patients with an overnight stay in a healthcare facility within 14 days before symptom onset. Patients with an epidemiologic link to a setting with a confirmed source of Legionella or that has been associated with at least one laboratory-confirmed case of Legionnaires’ disease.
Why is it important to report Legionella?
Timely identification and reporting of legionellosis cases are also important because this allows public health officials to act quickly.
What is the most common test for Legionnaires disease?
The most commonly used laboratory test for diagnosis of Legionnaires’ disease is the urinary antigen test (UAT), which detects a molecule of the Legionella bacterium in urine. If the patient has pneumonia and the test is positive, then you should consider the patient to have Legionnaires’ disease. The test can remain positive for a few weeks after infection, even with antibiotic treatment. The UAT detects the most common cause of Legionnaires’ disease, L. pneumophila serogroup 1. However, all species and serogroups of Legionella are potentially pathogenic, so a patient with a negative urinary antigen result could have Legionnaires’ disease caused by other Legionella species or serogroups, which is why using culture and UAT in combination is recommended.
What is the best test for Legionella?
The preferred diagnostic tests for Legionnaires’ disease are culture of lower respiratory secretions (e.g., sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage) on selective media and the Legionella urinary antigen test. Serological assays can be nonspecific and are not recommended in most situations. Best practice is to obtain both sputum for culture and urine for the urinary antigen test concurrently. Sputum should ideally be obtained prior to antibiotic administration, but antibiotic treatment should not be delayed to facilitate this process. The urinary antigen test can detect Legionella infections in some cases for days to weeks after treatment.
Can a culturing specimen detect Legionella?
Unlike the urinary antigen test, culturing specimens from patients can detect all species and serogroups of Legionella. Isolating Legionella from clinical specimens helps investigators identify where exposure occurred and prevent additional cases.
Where do Legionnaires disease outbreaks occur?
The majority of recognized Legionnaires’ disease outbreaks are associated with travel (hotels, resorts, cruise ships) or healthcare settings (hospitals, long-term care facilities). 2 Approximately 10–15% of all reported cases of Legionnaires’ disease occur in people who have traveled during their exposure period.
Can a negative urinary antigen cause Legionella?
However, all species and serogroups of Legionella are potentially pathogenic, so a patient with a negative urinary antigen result could have Legionnaires’ disease caused by other Legionella species or serogroups, which is why using culture and UAT in combination is recommended.
What percent of pneumonia is Legionella?
Community-acquired pneumonia — Legionella accounts for approximately 1 to 10 percent of cases of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) [ 1-4 ]. For most patients with CAP, the etiology is not known at the time of diagnosis, and empiric treatment is appropriate.
Is Legionella a pathogen?
Legionella bacteria are intracellular pathogens and are important causes of community-acquired and nosocomial pneumonia. Pneumonia caused by Legionella bacteria is termed Legionnaires' disease. Legionnaires' disease can be severe, and early administration of appropriate antimicrobial therapy is associated with improved outcomes.
Can Legionella cause Pontiac fever?
Legionella infection can also cause Pontiac fever, a nonspecific febrile illness typically identified during outbreaks. Pontiac fever is typically self-limited and resolves without antimicrobial therapy. The majority of Legionella infections are acquired sporadically, but some are associated with outbreaks.
Can Legionella be acquired sporadically?
The majority of Legionella infections are acquired sporadically, but some are associated with outbreaks. Early identification of common environmental sources of infection, such as contaminated water supplies, is key to prevention. The treatment and prevention of Legionella infections will be reviewed here.
What is Legionella disease?
What is Legionnaires’ disease? Legionnaires’ disease, or legionellosis, is a common type of bacterial pneumonia (lung infection) that can be very serious and sometimes life-threatening. A particular strain of bacteria called Legionella causes the illness.
Where do Legionella bacteria live?
Legionella bacteria live best in warm water. They are found in some freshwater lakes and streams. When certain man-made water structures aren’t maintained with proper disinfectants, the bacteria can grow and cause a health risk. But it has also been found in natural water and even soil.
How many people die from Legionnaires disease?
Because of the potentially serious nature of this disease, many people who get Legionnaires’ disease need to be treated in a hospital. About 1 in 10 people who get the disease die from complications of their illness.
Can you test for Legionella on a chest X-ray?
Legionnaires’ disease can look similar to regular pneumonia on a chest X-ray. Your doctor may test a sample of your urine or phlegm (mucus) to confirm you have Legionnaires’ disease. A blood test can also check for antibodies to Legionella.
Can Legionnaires disease be spread by drinking water?
This is when water “goes down the wrong pipe,” sending liquid down the windpipe and into your lungs instead of down your esophagus and into your stomach. Legionnaires’ disease cannot be spread from person to person.
Is Legionnaires disease a lung infection?
Legionnaires' Disease. Legionnaires’ disease, or legionellosis, is a common type of bacterial pneumonia (lung infection) that can be very serious and sometimes life-threatening. Most cases of Legionnaires’ disease are successfully treated with antibiotics.
Can Legionnaires disease be treated with antibiotics?
Most cases of Legionnaires’ disease are successfully treated with antibiotics. Sometimes, however, Legionnaires’ disease can lead to lung failure or other complications. These complications can be hard to treat. They can even be life-threatening for some people.
How long does it take for Legionnaires to recover?
Serious sequelae, fortunately, are rare. In our experience, most patients will recover completely within one year.
How many people are infected with Legionella?
It's caused by the bacterium Legionella pneumophila found in both potable and nonpotable water systems. Each year, an estimated 10,000 to 18,000 people are infected with the Legionella bacteria in the United States. It is not uncommon for patients ...
Can Legionnaires disease be admitted to intensive care?
It is not uncommon for patients with Legionnaires' disease to be admitted to the intensive care unit. Some will suffer long-term impaired health-related quality of life. A study of outbreak survivors showed persistence of fatigue (75%), neurologic symptoms (66%) and neuromuscular symptoms (63%) in months after an outbreak.
What is the best antibiotic for Legionnaires?
Your exact treatment will depend on your case. In general, doctors can treat Legionnaires’ quickly with medications. You may get one of three types of antibiotics: Fluoroquinolones. Levofloxacin ( Levaquin) is the top choice. Others include ciprofloxacin (Cipro) and moxifloxacin (Avelox).
How long does it take for a pontiac fever to go away?
Legionnaires’ symptoms can take up to 2 weeks. Pontiac fever will go away on its own without treatment, often within 3 to 5 days. But Legionnaires’ disease can become life-threatening.
Can Legionella be found in water?
Legionella thrives in warm water. It often spreads through a building’s contaminated water system. It’s actually an airborne disease. The bacterium is so tiny that it can hitch a ride inside tiny water droplets such as mist and water vapor.
How to diagnose Legionella?
To diagnose Legionnaires’ disease among other types of pneumonia, your doctor may order urine tests and a sputum culture to determine the presence of the Legionella bacteria.
How long does it take for Legionnaires to set in?
Legionnaires’ disease usually begins with flu-like symptoms similar to other types of bacterial pneumonia. These include: Within two or three days, the illness will have fully set in and patients typically experience more severe cough and difficulty breathing.
What is the number to call for lung cancer?
If you have questions about your diagnosis and what to expect, you can call the Lung Association's Lung HelpLine at 1-800-LUNGUSA to talk to a trained respiratory professional who can help answer your questions and connect you with support.
What are the next steps for a doctor to diagnose pneumonia?
If they suspect pneumonia, the next steps include a chest X-ray and blood tests.
Can Legionnaires disease be fatal?
Legionnaires’ disease can be fatal, so it is important to get prompt medical attention. Your doctor may determine that you have contracted a less severe version of the same disease, called Pontiac fever. This milder condition will clear up on its own without treatment and cause no lingering problems.
How many people survived Legionnaires disease?
This study followed the health of 122 people who survived a significant outbreak of Legionnaires’ disease in that region in 1999. Those who took part in the study were asked to complete a questionnaire nearly 18 months after they were diagnosed. The study revealed that 75% of those who had been infected by the bacteria suffered fatigue even ...
What are the symptoms of Legionnaires?
Neurologic symptoms were reported by 66% of participants. Typical Legionnaires’ symptoms reported included memory loss. It is also known that some who recover from the disease suffer from a lack of concentration.
How many people are fatigued after being infected?
The study revealed that 75% of those who had been infected by the bacteria suffered fatigue even after they had been successfully treated. It was not possible to ascertain whether the fatigue was directly caused by the disease or through experiencing pneumonia in general.
Can Legionnaires disease last longer?
Surviving the long-term effects of Legionnaires’ disease. Yet as we have seen from the study from the Netherlands, some people may experience side effects for much longer than this. Some may never fully recover, with fatigue and a lack of energy persisting for many more months and possibly years. It is not known whether ...
Is it better to have a positive diagnosis or a long term prognosis?
The sooner a positive diagnosis is made , the better the prognosis will be. This appears to relate to the chance of developing long-term effects as well. Similarly, some people are more ill than others, perhaps developing more severe symptoms when they contract the disease. This too can affect the odds of suffering long-term complications.
Can Legionnaires be contracted by smoking?
Most people have heard of Legionnaires’ disease – a disease that can be contracted by those who inhale fine water droplets contaminated with Legionella bacteria deep into their lungs. Legionnaires’ disease is a serious type of pneumonia that is more likely to affect the over 50s, those with a history of smoking, ...

Sensitivity and Specificity of Diagnostic Tests
Advantages and Disadvantages For Each Diagnostic Test
Treatment
Prevention
Specialist to consult
Reporting
- Sensitivity varies depending on the quality and timing of clinical specimen collection, as well as technical skill of the laboratory worker performing the test. The table below provides general ranges for the sensitivity and specificity of each diagnostic test. 1 Cross reactions with other species and serogroups have been documented. 2Avni T, Biebe...