How soon can you get retested after chlamydia treatment?
Nov 18, 2021 · CDC recommends that men and women with chlamydia be retested 3 to 12 months after treatment. Among women, repeated chlamydia infections can increase the risk for pelvic inflammatory disease. Chlamydial infection also increases the risk of HIV transmission.
Can you get chlamydia after four days of treatment?
Jul 22, 2021 · Retesting After Treatment to Detect Repeat Infections. Retesting 3 months after diagnosis of chlamydia, gonorrhea, or trichomoniasis can detect repeat infection and potentially can be used to enhance population-based prevention ( 136, 137 ). Any person who has a positive test for chlamydia or gonorrhea, along with women who have a positive test for trichomonas, …
How long until Chlamydia is cured after treatment?
Apr 20, 2017 · Due to these risks, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that any person who tests positive for chlamydia be retested three months after treatment. If your patient doesn’t return at three months, they should be retested the next time they return in the twelve months following their initial visit.
How long are you contagious after treatment for chlamydia?
Men and women who have been treated for chlamydia should be retested approximately 3 months after treatment, regardless of whether they believe their sex partners were treated; scheduling the follow-up visit at the time of treatment is encouraged ( 753 ).
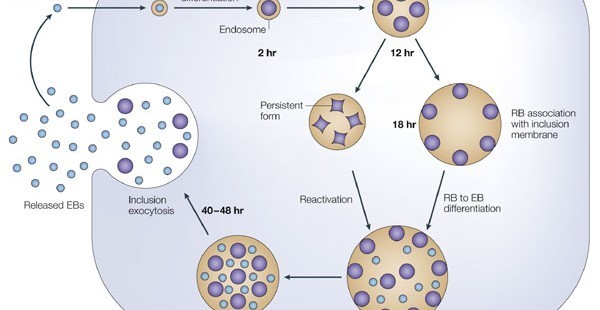
Can you retest for chlamydia 2 weeks after treatment?
Yes. After you finish all of your medicine, wait three or four months and then get tested again. Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics, and your sexual partners need to be treated, too.Mar 3, 2021
How long do you test positive for chlamydia after treatment?
If a TOC for anogenital chlamydia is indicated, we recommend performing it at least 14 days after initiation of treatment, when using modern RNA- and DNA-based assays. A positive result shortly after 14 days probably indicates a blip, rather than a treatment failure or a reinfection.Oct 11, 2016
How do I know if my chlamydia is gone?
When will the signs and symptoms go away?Discharge or pain when you urinate should improve within a week.Bleeding between periods or heavier periods should improve by your next period.Pelvic pain and pain in the testicles should start to improve quickly but may take up to two weeks to go away.Jun 24, 2021
Is chlamydia gone after 7 days?
It takes 7 days for the medicine to work in your body and cure Chlamydia infection. If you have sex without a condom during the 7 days after taking the medicine, you could still pass the infection to your sex partners, even if you have no symptoms.
How long after chlamydia treatment should I retest?
Due to these risks, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that any person who tests positive for chlamydia be retested three months after treatment.
How long does it take to retest for chlamydia?
Retesting for reinfection of chlamydia is done routinely. A test-of-cure, however, is performed three to four weeks after treatment and is only done under the following circumstances: If concern exists regarding persistence of infection despite treatment.
When to retest for chlamydia?
Retesting a few months after diagnosis and treatment of chlamydia can detect repeat infection for earlier treatment to prevent complications and further transmission. Retesting is not the same as a test-of-cure (TOC). Retesting for reinfection of chlamydia is done routinely.
How common is chlamydia?
Chlamydial reinfections are very common—as many as 1 in 5 people will have a repeat infection with chlamydia within the first few months after they are treated for their initial infection. Untreated chlamydia can increase a woman’s risk for developing: pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain.
Chlamydial Infection Among Adolescents and Adults
Chlamydial infection is the most frequently reported bacterial infectious disease in the United States, and prevalence is highest among persons aged ≤24 years ( 141, 784 ). Multiple sequelae can result from C. trachomatis infection among women, the most serious of which include PID, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
Chlamydial Infection Among Neonates
Prenatal screening and treatment of pregnant women is the best method for preventing chlamydial infection among neonates. C. trachomatis infection of neonates results from perinatal exposure to the mother’s infected cervix. Initial C.
Chlamydial Infections Among Infants and Children
Sexual abuse should be considered a cause of chlamydial infection among infants and children. However, perinatally transmitted C. trachomatis infection of the nasopharynx, urogenital tract, and rectum can persist for 2–3 years (see Sexual Assault or Abuse of Children).
How long after chlamydia treatment should you retest?
Women and men with chlamydia should be retested about three months after treatment of an initial infection, regardless of whether they believe that their sex partners were successfully treated. Infants infected with chlamydia may develop ophthalmia neonatorum (conjunctivitis) and/or pneumonia.
What are the risks of multiple chlamydial infections?
Women whose sex partners have not been appropriately treated are at high risk for re-infection. Having multiple chlamydial infections increases a woman’s risk of serious reproductive health complications, including pelvic inflammatory disease and ectopic pregnancy.
Can you take medication for chlamydia?
It is important to take all of the medication prescribed to cure chlamydia. Medication for chlamydia should not be shared with anyone. Although medication will stop the infection, it will not repair any permanent damage done by the disease.
Can chlamydia be cured with antibiotics?
Expedited Partner Therapy (EPT) Infographic: A Patient Resource. Chlamydia can be easily cured with antibiotics. HIV-positive persons with chlamydia should receive the same treatment as those who are HIV-negative. Persons with chlamydia should abstain from sexual activity for 7 days after single dose antibiotics or until completion ...
Why do you have to wait 3 months to retest for chlamydia?
In fact, women who become reinfected with chlamydia have an even higher risk for PID and ectopic pregnancy than those with a first infection. Due to these risks, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends that any person who tests positive for chlamydia be retested three months after treatment.
Why do I have to wait 7 days after chlamydia treatment?
If you’re being treated for chlamydia, it’s important to avoid sex until 7 days after finishing your medicine. This gives your body time to clear up the infection completely to make sure it doesn’t get passed on to anyone.
Does it really take 7 days to cure chlamydia?
It takes 7 days for the medicine to work in your body and cure Chlamydia infection. If you have sex without a condom during the 7 days after taking the medicine, you could still pass the infection to your sex partners, even if you have no symptoms.
Why do I still have chlamydia after treatment?
Nope! Chlamydia is easily cured with antibiotics. Chlamydia is a bacterial infection (like strep throat or an ear infection), which means that once you’ve been treated and tested negative for it (to make sure the antibiotics worked), it’s gone.
Can Chlamydia come back on its own after being treated?
Yes, you can contract chlamydia more than once, although it’s rare for it to reoccur or persist after correct treatment.
Can chlamydia antibiotics not work?
Many people believe that they can become resistant to antibiotics by taking too many. This is untrue; in fact, this practice actually contributes to antibiotic resistance. If you are prescribed treatment for chlamydia, you should make sure that you take all the recommended medication.
Is it possible to still have chlamydia after treatment?
If you’ve had chlamydia and were treated in the past, you can still get infected again. This can happen if you have unprotected sex with someone who has chlamydia.