Medication
Brucella spp. may be isolated from neonatal patients with titer levels lower than 1:160. 39, 40 ● Treatment: Dual-combination antimicrobial therapy should be administered for several weeks. Duration and dose of treatment should be made in consultation with the patient’s neonatologist or pediatrician. Prevention: As Brucella
Nutrition
Treatment. Before treatment begins, a diagnosis of brucellosis infection must be made by a doctor. Tests will be performed to look for bacteria in samples of blood, bone marrow, or other body fluids. In addition, a blood test can be performed to detect antibodies against the bacteria. Once a diagnosis is made, a doctor can prescribe antibiotics.
What are the treatment options for Brucella infection in neonatal patients?
Finally, an accidental injection with the livestock vaccine used against Brucella abortus can also lead to brucellosis in humans. Human-to-human transmission is very rare (via blood transfusion, organ and tissue transplantation, sexual contact, and breastfeeding).
What is the treatment for brucellosis?
Brucella abortus7 days 2 hours 24 hours or 7 days Brucella canisNot a Select Agent N/A N/A 2 hours 24 hours or 7 days Brucella ceti, pinnipedialisNot a Select Agent N/A N/A 2 hours 24 hours or 7 days
Can Brucella abortus be transmitted to humans?
How long does Brucella abortus take to work?
How is Brucella abortus treated?
You will generally be given doxycycline and rifampin a in combination for 6-8 weeks. You must take the antibiotics for many weeks to prevent the disease from returning. The rate of relapse following treatment is about 5-15% and usually occurs within the first six months after treatment.
How do you treat brucellosis in humans?
Two-drug regimen consisting of streptomycin and doxycycline (streptomycin for 2 to 3 weeks and doxycycline for 8 weeks) or gentamicin plus doxycycline (gentamicin for 5-7 days and doxycycline for 8 weeks) should be recommended as the treatment of choice for uncomplicated brucellosis.
Can Brucella be cured in humans?
In general, the prognosis for patients infected with Brucella is very good. If individuals are treated appropriately within the first few months of symptom onset, they are curable with antibiotics and usually don't develop chronic disease.
Can humans get Brucella abortus?
Brucellosis is a bacterium that infects the genitourinary tract of cattle (Brucella abortus) and pigs (Brucella suis). Humans become infected after exposure to infected animals or contaminated meat or dairy products.
What are the signs of brucellosis in humans?
Signs and Symptomsfever.sweats.malaise.anorexia.headache.pain in muscles, joint, and/or back.fatigue.
Can ciprofloxacin treat Brucella?
Ciprofloxacin can be considered as an alternative drug for the treatment of brucellosis, more effective (clinically and immunologically) than a combination of two antibiotics: doxycycline and rifampicin.
How is Brucella abortus transmitted?
Overview. Brucellosis is a bacterial infection that spreads from animals to people. Most commonly, people are infected by eating raw or unpasteurized dairy products. Sometimes, the bacteria that cause brucellosis can spread through the air or through direct contact with infected animals.
How long does it take brucellosis to heal?
Depending on the timing of treatment and severity of illness, recovery may take a few weeks to several months. Death from brucellosis is rare, occurring in no more than 2% of all cases. Generally, the antibiotics doxycycline and rifampin are recommended in combination for a minimum of 6-8 weeks.
Diagnosis
Doctors usually confirm a diagnosis of brucellosis by testing blood or bone marrow for the brucella bacteria or by testing blood for antibodies to the bacteria. To help detect complications of brucellosis, your doctor may order additional tests, including:
Treatment
Treatment for brucellosis aims to relieve symptoms, prevent a relapse of the disease and avoid complications. You'll need to take antibiotics for at least six weeks, and your symptoms may not go away completely for several months. The disease may also return and become chronic.
Preparing for your appointment
If you think you may have brucellosis, you're likely to start by seeing your family doctor or a general practitioner. You may be referred to an infectious disease specialist.
How to prevent brucellosis?
Brucellosis may be prevented with the following steps: Do not drink or eat unpasteurized dairy products. Wear rub ber gloves if you work in the animal processing industry. If you have come in contact with an animal infected with Brucella, tell your health care provider -- even if you do not have symptoms.
What is the cause of brucellosis?
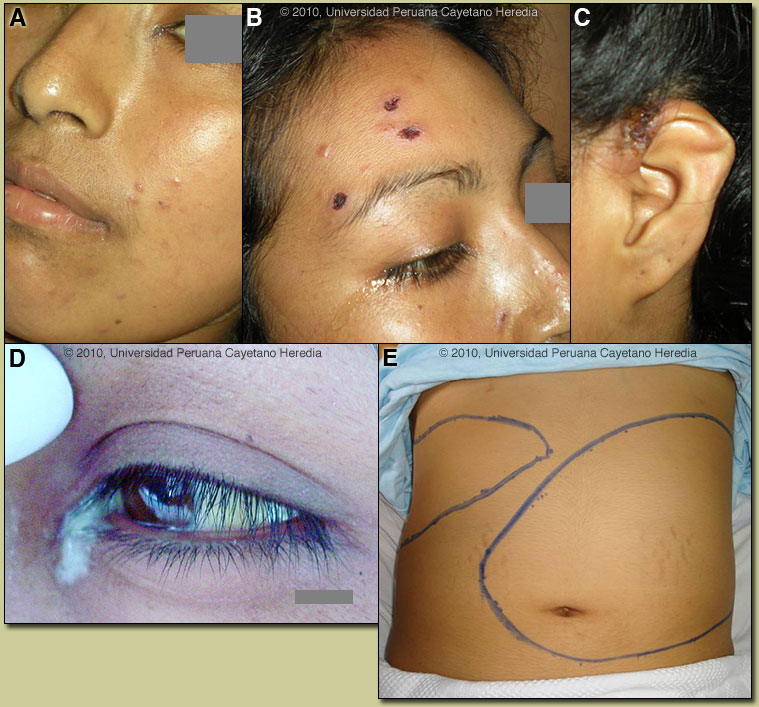
Severe brucellosis may cause: Infection of the central nervous system. Endocarditis (infection of the lining of the heartor valves) Liverabscess. Brucellosis can cause long-lasting symptoms that are similar to systemic exertion intolerance disease.
How does brucellosis spread?
Brucellosis in humans occurs when a person comes into contact with an animal or animal product infected with the Brucellabacteria. Very rarely, the bacteria may spread from person to person. Breastfeedingmoms with brucellosis may pass the bacteria to their baby. Brucellamay also be spread through sexual contact.
What is the most common type of brucellosis?
Four types of Brucellabacteria cause the majority of brucellosis infections in humans: B. melitensis. This type causes most cases of human brucellosis and is mainly found in sheep and goats.
How many people in the world have brucellosis?
Brucellosis is considered a significant health threat in other parts of the world. The disease has been reported in more than a half-million people each year in 100 countries, according to the World Health Organization.
Where does Brucellosis occur?
Brucellosis due to this strain most often occurs in the Southeast and California. It also occurs in Europe, South America, and Southeast Asia. B. canis. The infection from this type of bacteria spreads from dogs.
Can you get brucellosis from a dog?
You are more likely to get brucellosis from an infected dog if you come in contact with bloodor other fluids from the animal. Veterinarians have an increased risk of brucellosis. If you have a weakened immune system due to medicationsor certain diseases, you should not touch dogs that are infected with Brucella.
What is the best treatment for brucellosis?
The cornerstone of treatment for brucellosis is antibiotics. Because of the high relapse rate associated with the disease, the use of a multidrug (two or more) antibiotic regimen is recommended. The antimicrobials most commonly used include doxycycline ( Vibramycin ), streptomycin, rifampin ( Rifadin ), gentamicin ( Garamycin ), ...
What is the best way to diagnose brucellosis?
In general, blood tests and blood/tissue cultures are necessary for making the diagnosis of brucellosis.
How is brucellosis diagnosed?
Brucellosis is typically diagnosed through blood tests and by isolating the organism from blood and other body tissues. A multidrug antibiotic regimen is the cornerstone of treatment for brucellosis. The complications of brucellosis may involve various organ systems. Brucellosis can be prevented by animal-disease-control measures, ...
How long does it take for brucellosis to develop?
Share Your Story. The symptoms and signs of brucellosis may develop from days to months after the initial exposure to the organism (incubation period). While some individuals may develop mild symptoms, others may go on to develop long-term chronic symptoms.
How many cases of brucellosis are there in the world?
Human brucellosis is a disease that is found worldwide, and it has an annual occurrence rate of more than 500,000 cases. Brucellosis tends to occur more commonly in regions with less established animal disease control programs and in areas where public-health initiatives may be less effective.
What is the cause of brucellosis?
Brucellosis Facts. Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by bacteria from the genus Brucella. Brucellosis is an infection of certain animals that is transmitted to humans. Humans acquire brucellosis when they come in contact with contaminated animals or animal products, most commonly from the ingestion of raw milk or cheese.
When was Brucella banned?
The use of brucellosis for biological warfare purposes was later banned in 1969 by President Nixon.
How long does a Brucella abortus live?
Brucella abortus survived in a model system using sterilized milk and lactic acid for 34 days at a pH range of 5.0–5.8, but when the pH dropped to 3.9, the survival period decreased to only 2 days. The same species showed 90% survival after 3 h exposure to pH 3.8 and this dropped to only 60% survival after 24 h.
What is the pH of brucella abortus?
Brucella abortus is a rod-shaped, non-motile, catalase-positive and oxidase-positive organism. The optimum growth pH varies from 6.6 to 7.4. The optimum growth temperature is 36–38°C, but this species can grow between 20°C and 40°C. It is a causative agent of brucellosis, a zoonosis of worldwide importance, also called ‘Malta fever’, ...
What is the disease of brucellosis?
Brucellosis is a disease occurring in cattle ( Brucella abortus ), dogs ( B. canis ), goats and sheep ( B. melitensis ), and pigs ( B. suis). Humans are affected mainly through ingestion of contaminated milk products, by contact, or by inhalation. Brucellosis (also known as relapsing, undulant, Malta, or Mediterranean fever) is a systemic bacterial disease of acute or insidious onset characterized by fever, headache, weakness, sweating, chills, arthralgia, depression, weight loss, and generalized malaise. Transmission can occur as a result of contact with tissues, blood, urine, vaginal discharges; however, brucellosis is predominantly spread by ingestion of raw milk and dairy products from infected animals. The disease may last from a few days to a year or more. Complications include osteoarthritis and relapses. Case fatality is under 2 percent, but disability is common and can be pronounced.
What are the proteins in the Brucella abortus genome?
Genome sequence analyses reveal that Brucella abortus genome encodes 10 proteins with predicted PAS domains, 8 are associated with histidine kinase domains and 2 are associated with GGDEF/EAL domains, among which 5 proteins (BAB1_0640, 1139, 1621, 2101, and 0220) are predicted to contain a haem as a prosthetic group though it is not proved experimentally (Carrica Mdel, Fernandez, Martí, Paris, & Goldbaum, 2012 ). NtrY (BAB1_1139) is the histidine kinase in the NtrY/NtrX two-component system found in Brucella spp. that are facultative intracellular gram-negative bacteria that belong to the α2 proteobacteria group. The expression of all the denitrification enzymes is increased in low O2 tension in these bacteria, which is partly triggered by the NtrY/NtrX two-component system ( Al Dahouk et al., 2009; Roop & Caswell, 2012 ). NtrY from B. abortus is a homologue to NtrY that is involved in nitrogen metabolism and/or fixation in Azorhizobium caulinodans and Azospirillum brasilense ( Ishida et al., 2002; Pawlowski, Klosse, & de Bruijn, 1991 ), which contains predicted transmembrane regions at the N-terminus followed by a HAMP, PAS, and histidine kinase domains ( Carrica Mdel et al., 2012). The PAS domain binds a haem, which shows the Soret, α, and β bands at 408, 558, and 533 nm, and 423, 555, and 527 nm in the ferric and ferrous states, respectively ( Carrica Mdel et al., 2012 ). While a stable O 2-bound NtrY does not form due to an autoxidation to produce the ferric form, NO and CO can bind to the ferrous haem in NtrY to form a 5-coordinate nitrosyl haem and 6-coordinate CO-bound haem, respectively (Carrica Mdel et al., 2012 ). Ferrous NtrY possesses much higher autokinase activity than ferric NtrY. The autokinase activity of CO-bound and NO-bound NtrY is similar to that of ferrous NtrY ( Carrica Mdel et al., 2012 ), though the coordination structures of the CO- and NO-bound haems are different from each other. The reason of this unique property is not obvious at present. Based on these results, it is proposed that NtrY acts as a redox sensor, not a gas sensor ( Carrica Mdel et al., 2012 ). Alignments of amino acid sequences among NtrY and other haem-containing PAS domains reveal that NtrY does not show a conserved His as the proximal haem ligand within its PAS domain, which suggests that the haem binds to the PAS domain in NtrY in a different manner to that described for other haem-containing PAS domains. However, more detailed characterisation with spectroscopic and structural methods is required to prove this hypothesis with identification of the coordination structure of the haem in NtrY.
How long does B. abortus stay in cheese?
This microorganism may remain active in cheese for up to 60 days. In general, full-cream dairy products are good media for B. abortus.
How does brucellosis spread?
Transmission can occur as a result of contact with tissues, blood, urine, vaginal discharges; however, brucellosis is predominantly spread by ingestion of raw milk and dairy products from infected animals . The disease may last from a few days to a year or more. Complications include osteoarthritis and relapses.
Where is Brucellosis most common?
The disease is primarily seen in Mediterranean countries, the Middle East, India, central Asia, and Central and South America. Brucellosis occurs primarily as an occupational disease of people working with and in contact with tissues, blood, and urine of infected animals, especially goats and sheep.