The standard of care for HIV treatment is highly active anti-retroviral therapy (HAART), also called combination anti-retroviral therapy. HAART involves the use of several drugs at the same time, which are sometimes combined in a single pill. Each drug combats HIV in a slightly different way to stop or delay the virus from multiplying.
What is HAART and how does it work?
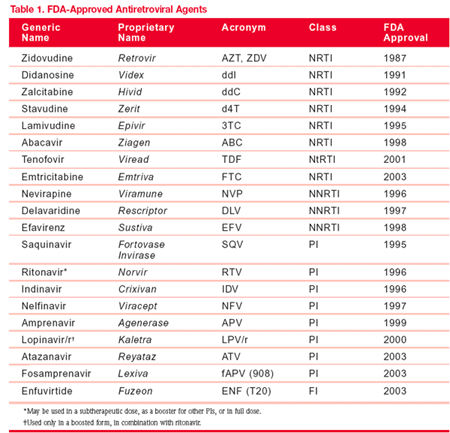
Jan 20, 2007 · There are currently six classes of antiretroviral drugs able to treat HIV, each of which inhibits a specific stage in the virus's life cycle: Entry/attachment inhibitors. Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) Protease inhibitors ...
How is the HAART regimen for HIV infection initiated?
Nov 25, 2021 · Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is a medication regimen used to manage and treat human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). It is composed of several drugs in the antiretroviral classes of medications. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, and contraindications for various HAART medications in the management of HIV.
Why is adherence to a HAART regimen important?
HAART is a customized combination of different classes of medications that a physician prescribes based on such factors as the patient’s viral load (how much virus is in the blood), the particular strain of the virus, the CD4+ cell count, and other considerations (e.g., disease symptoms). Because HAART cannot rid the body of HIV, it must be taken every day for life.
What is highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)?
Here’s how our program works. It includes: An initial intake interview. Medical examination and laboratory tests. Supervised urine testing. A signed treatment contract and treatment plan. Addiction counseling. Regular medical follow up. Daily methadone or Buprenorphine dose.

How do the HAART work?
How does antiretroviral treatment work?
HIV is treated with antiretroviral medicines, which work by stopping the virus replicating in the body. This allows the immune system to repair itself and prevent further damage. A combination of HIV drugs is used because HIV can quickly adapt and become resistant.
How long does HAART therapy take?
What does HAART therapy consist of?
Does ARVs change body shape?
What are the two most common adverse effects of highly active antiretroviral therapy HAART?
What are the 3 active antiretrovirals comprised of?
What are the side effects of efavirenz?
- nausea.
- vomiting.
- stomach pain.
- diarrhea.
- indigestion.
- headache.
- confusion.
- forgetfulness.
When should HAART be initiated?
How many drugs are in HAART therapy?
What is HAART medication?
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is a medication regimen used to manage and treat human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). It is composed of several drugs in the antiretroviral classes of medications. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, and contraindications for various HAART medications in the management of HIV. This activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse event profile, and other key factors pertinent to the interprofessional healthcare team members in the care of patients with HIV-1 and related conditions.
Why is a HAART regimen important?
Proper utilization and adherence to a HAART regimen are essential to ensure a therapeutic response and prevent viral resistance . Healthcare professionals should obtain a detailed history and screening before initiating a regimen and consider factors such as comorbid conditions (cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, renal dysfunction, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, psychiatric conditions, tuberculosis, drug abuse), desire to become pregnant, commitment to contraception usage, pill burden of the regimen, financial burden, prior HAART usage, and drug interactions. Patients living in a resource-limited setting with a history of substance misuse or a history of psychiatric illness are considered at high risk of non-compliance. Healthcare providers should be vigilant to ensure optimal health outcomes. [8][30][50][30]
What is a HAART regimen?
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is a treatment regimen typically comprised of a combination of three or more antiretroviral drugs. HAART may also be called antiretroviral therapy (ART) or combination antiretroviral therapy (cART). A key cornerstone of HAART is the co-administration of different drugs that inhibit viral replication by several mechanisms so that the propagation of a virus with resistance to a single agent becomes inhibited by the action of the other two agents. Management of a HAART regimen is a multifaceted process that should be administered by, or in consultation with, a provider with specific training as defined by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. This approach is central to optimizing patient care, as studies have demonstrated provider experience positively correlates with improved patient outcomes. [1][2][3][4]
What is a HAART?
Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is a medication regimen used to manage and treat human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1). It is composed of several drugs in the antiretroviral classes of medications. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, and contraindications for various HAART medications in the management ...
How many classes of HAART are there?
There are six main classes of HAART agents that target different stages in the viral lifecycle. A fundamental cornerstone of HAART is the co-administration of different drugs that inhibit HIV replication by several mechanisms so that the propagation of a virus with resistance to a single agent is inhibited by the action of the other two agents. Some agents may be co-formulated to increase ease of patient compliance with these medications.
How does HAART help with HIV?
Improve immune function. Reducing the transmission of HIV-1 to others is a primary goal of HAART. With the use of HAART, a reduction of HIV-1 RNA levels has been shown to reduce the risk of sexual transmission to partners to nearly zero in some studies, even among couples that engaged in condomless sexual acts.
Is HAART good for pregnant women?
A combination of these drugs is also available for uninfected patients who engage in high-risk behavior and has been demonstrated to reduce the risk of acquiring HIV infection by more than 90%. For pregnant patients, the use of HAART is critical in the prevention of mother-to-child transmission.
How many patients can Haart treat?
Intakes are conducted on a first-come, first-serve basis. HAART is able to admit up to three patients into treatment each day. Be sure to have a valid photo ID and insurance card (if applicable) when you arrive for an intake. Without a valid photo ID, you cannot be admitted for treatment at HAART.
Does Haart take Kaiser?
HAART accepts Kaiser and other insurance. Be sure to check with your insurance carrier to see if you are covered for Methadone Maintenance Treatment.
How does treatment help prevent HIV?
Having an undetectable viral load may also help prevent transmission from injection drug use.
How long does it take to get rid of HIV?
There is no effective cure for HIV. But with proper medical care, you can control HIV. Most people can get the virus under control within six months. Taking HIV medicine does not prevent transmission ...
What to do if your treatment makes you sick?
Talk to your health care provider if your treatment makes you sick. Your health care provider may prescribe medicines to help manage the side effects or may change your treatment plan.
Is there a drug interaction between HIV and hormone therapy?
There are no known drug interactions between HIV medicine and hormone therapy.
What Is Antiretroviral Therapy?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) involves using two or more antiretroviral drugs to suppress the virus to undetectable levels in the blood. This treatment can slow the progression of the disease to a point at which you can live a long, healthy life. 4
How It Works
Antiretroviral drugs do not kill HIV. Rather, they prevent the virus from making copies of itself by blocking stages in the virus's life cycle (also known as the replication cycle ). Antiretrovirals are so named because HIV is a type of virus known as a retrovirus. 4
Side Effects
While all drugs can cause side effects, current antiretrovirals tend to cause far fewer side effects than drugs of the past. Even so, side effects can occur and, in rare cases, be severe.
Tests
Once you have been diagnosed with HIV, your doctor will advise to you start treatment immediately to bring the virus under control. You will not only be counseled on how to take your drugs correctly (including dietary restrictions) but also advised on ways to maintain optimal adherence .
Other Treatments
There are no other medications other than antiretrovirals that can control HIV.
Talk to Your Doctor
The choice of ART relies heavily on the results of a genetic resistance test that helps determine which antiretrovirals work best based on your virus's genetic profile. But it is not the sole factor involved in the selection of ART. 17
Summary
Antiretroviral therapy is used to control HIV. It relies on drugs that inhibit points of the viral replication cycle so the virus cannot make copies of itself and infect immune system cells. Antiretroviral drugs are usually given daily in the form of a pill, which may contain a combination of drugs. These medications may have side effects.
How does HIV treatment affect the body?
By reducing the amount of HIV in the body, HIV medicines also reduce the risk of HIV transmission. A main goal of HIV treatment is to reduce a person’s viral load to an undetectable level. An undetectable viral load means that the level of HIV in the blood is too low to be detected by a viral load test.
What is the treatment for HIV called?
The treatment for HIV is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART involves taking a combination of HIV medicines (called an HIV treatment regimen) every day. ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV. People with HIV should start taking HIV medicines as soon as possible.
Can HIV be treated with ART?
People with HIV should start taking HIV medicines as soon as possible. ART can’t cure HIV, but HIV medicines help people with HIV live longer, healthier lives. ART also reduces the risk of HIV transmission. A main goal of HIV treatment is to reduce a person’s viral load to an undetectable level.
