Medication
Twelve drugs doctors commonly prescribe for migraine include:
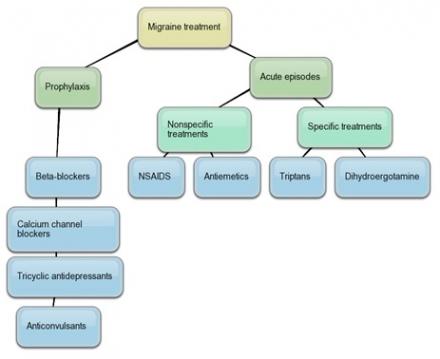
- Amitriptyline (Elavil) is an antidepressant. ...
- Divalproex sodium extended-release (Depakote ER) is an anticonvulsant. ...
- Eletriptan (Relpax) is a triptan. ...
- Metoprolol ( Lopressor, Toprol XL) is a beta blocker. ...
- Propranolol extended-release (Inderal, Inderal LA, Inderal XL) is another beta blocker. ...
Therapy
You can get magnesium from foods that include:
- almonds
- sesame seeds
- sunflower seeds
- Brazil nuts
- cashews
- peanut butter
- oatmeal
- eggs
- milk
Self-care
- Pain relievers. Simple pain relievers available without a prescription are usually the first line of treatment for reducing headache pain. ...
- Combination medications. Aspirin or acetaminophen (Tylenol, others) or both are often combined with caffeine or a sedative drug in a single medication. ...
- Triptans and narcotics. ...
Nutrition
Here are some common ones to know:
- Throbbing head pain, typically on one side
- Light or sound sensitivity
- Trouble concentrating
- Blurred vision
- Blind spots or vision loss
- Nausea and vomiting
- Overwhelming fatigue
What is the best medicine for a migraine headache?
What is the best product for natural migraine relief?
Which treatment is best for your headaches?
How to cure a migraine?

Can you permanently cure migraines?
A: Although there's no permanent migraine cure, many people with chronic migraine use a combination of treatments to find long-lasting, effective relief. Some treatments help ease the pain and shorten attacks in progress. Others work to prevent or reduce future attacks.
What is the fastest way to cure a migraine?
In this ArticleTry a Cold Pack.Use a Heating Pad or Hot Compress.Ease Pressure on Your Scalp or Head.Dim the Lights.Try Not to Chew.Hydrate.Get Some Caffeine.Practice Relaxation.More items...•
What triggers a migraine headache?
Migraine triggers. Many possible migraine triggers have been suggested, including hormonal, emotional, physical, dietary, environmental and medicinal factors. These triggers are very individual, but it may help to keep a diary to see if you can identify a consistent trigger.
What are the four stages of a migraine?
Migraines, which affect children and teenagers as well as adults, can progress through four stages: prodrome, aura, attack and post-drome. Not everyone who has migraines goes through all stages.
What is the best medicine for migraines?
Ginger Root: Ginger contains more than 200 substances that have anti-inflammatory, anti-nausea and antihistamine properties to help users address their migraine symptoms. Peppermint Oil: Peppermint oil has a cooling effect on the skin, and as such, may help relieve migraine pain in the temples and forehead.
What is the Migraine Institute?
Committed to helping patients find relief, The Migraine Institute is the first center in Los Angeles solely dedicated to alleviating pain from the dreaded migraine. Our team of migraine specialists are pioneers in the field of migraine surgery, and are highly respected by surgeons from around the world. From the first moment you step into The Migraine Institute, our top priority is to take care of you so you can start enjoying life again!
What is the best treatment for migraine headaches?
Migraines can be treated with two types of drugs: abortive and preventive. Abortive: The goal of abortive treatment is to stop a migraine once it starts. Abortive medications stop a migraine ...
How to stop migraines?
Abortive medications can be taken by self-injection, mouth, skin patch, or nasal spray. These forms of medication are especially useful for people who have nausea or vomiting related to their migraine, and they work quickly.
What is the best medication for migraines?
Preventive treatment medications include the following: Medications used to treat high blood pressure: beta-blockers ( propranolol, timolol, metoprolol) calcium channel blockers ( verapamil)
What is the name of the device that sends electrical pulses through the forehead to stimulate a nerve linked with migraine
These include: Cefaly , a small headband device that sends electrical pulses through the forehead to stimulate a nerve linked with migraines. Spring TMS or eNeura sTM, a device for people who have an aura before migraine headaches.
Can triptans help with headaches?
The triptans are used only to treat headache and do not relieve pain from back problems, arthritis, menstruation, or other conditions. People with certain medical conditions should not take these medications. The following drugs are sometimes used for nausea related to migraine headaches, in addition to migraine treatment: ...
An update on new options for effective migraine treatment
This is an exciting time for people with migraine. New, promising treatment options are coming out, and these breakthroughs offer hope for better migraine symptom relief and prevention.
New Treatment Options
In this webinar, Dr. Jessica Ailani, the director of the MedStar Georgetown Headache Center in the Washington, D.C., area, and Dr. Stewart Tepper, a professor of neurology at Dartmouth in New Hampshire and director of the Headache Center at Dartmouth Hitchcock Medical Center, shared updates on new migraine treatments. Drs.
New Acute Migraine Treatments
Triptans are commonly used for immediate migraine relief, but advancements in migraine research have led to the discovery of other oral medications, such as gepants, which are medications that target and reduce CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide, a protein that causes inflammation in the brain).
Preventive Treatments
Anti-CGRP treatments include injections specifically designed to bind to or block CGRP to prevent migraine attacks. There are currently three available as a self-administered injection and an intravenous infusion called eptinezumab (VYEPTI™.) Eptinezumab is a monoclonal antibody infusion that targets CGRP.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- If you have migraines or a family history of migraines, a doctor trained in treating headaches (neurologist) will likely diagnose migraines based on your medical history, symptoms, and a physical and neurological examination. If your condition is unusual, complex or suddenly becom…