However, if the cyst is large and causes pain, your doctor may recommend the following treatments:
- Medication. Your doctor may inject a corticosteroid medication, such as cortisone, into your knee to reduce inflammation. ...
- Fluid drainage. Your doctor may drain the fluid from the knee joint using a needle. ...
- Physical therapy. Icing, a compression wrap and crutches may help reduce pain and swelling. ...
What to do when ganglion cyst ruptures?
Other symptoms of a ruptured ganglion cyst include:
- Redness or pus that’s leaking
- A painful area that’s painful to touch
- Warmth or swelling around the area
How to treat bakers cyst behind knee?
When a Baker’s cyst ruptures — or even before a rupture — you can reduce pain and swelling by:
- applying ice or a cold pack to the affected area
- keeping your calf elevated
- taking over-the-counter medications for pain and inflammation
- using an elastic wrap or brace to support your knee
- resting
- avoiding strenuous activity
Does Aspercreme help ganglion cysts?
You can reduce the discomforts associated with a ganglion cyst with regular use of warm compresses. It will increase blood circulation to the affected area and promote fluid drainage. It will also reduce pain and swelling. However, warm compresses will not prevent the growth of a cyst.
What happens when bakers cyst ruptures?
The cyst can rupture, leaking fluid down the inner leg and will sometimes cause the appearance of a painless bruise under the inner ankle. A baker's cyst rupture can mimic phlebitis - a swelling or inflammation of a vein that impairs the flow of blood - of the leg.

Do Baker's cysts need to be removed?
Most Baker cysts go away without surgery. Healthcare providers only rarely advise surgery. You might need surgery if your Baker cyst is causing you severe symptoms and no other treatments have worked. Your provider will check you carefully for other knee problems to treat before advising surgery.
Can a cyst behind the knee be removed?
In some cases, surgery is recommended. Baker's cyst surgery is usually performed as a minimally invasive, outpatient surgery to remove the cyst and repair the knee capsule or synovial lining. Even with surgical removal, Baker's cysts can reoccur if the underlying cause of the cyst is not controlled.
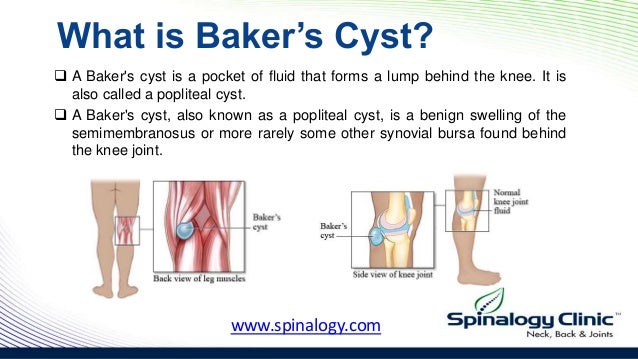
What does it mean when you have a cyst behind your knee?
A Baker's cyst, also called a popliteal cyst, is a fluid-filled swelling that develops at the back of the knee. Credit: It's caused when the tissue behind the knee joint becomes swollen and inflamed.
How long does it take to recover from Baker's cyst surgery?
It typically takes around four weeks after baker's cyst excision for the wound to completely heal. A firm bump of scar tissue will form in the incision. As the wound heals, the bump will slowly go away.
What happens if you leave a Baker's cyst untreated?
Baker's cysts aren't dangerous and they may go away on their own. But occasionally they burst, and if that happens, synovial fluid can leak into the calf below, causing pain, swelling, and reddening.
Will cortisone injection help Baker's cyst?
Sometimes a Baker's cyst will disappear on its own. However, if the cyst is large and causes pain, your doctor may recommend the following treatments: Medication. Your doctor may inject a corticosteroid medication, such as cortisone, into your knee to reduce inflammation.
When should I worry about a baker's cyst?
When to see the doctor for a Baker's cyst. Swelling that comes on quickly or doesn't go away may be a sign of infection. Other signs of infection include fever, tiredness, and severe knee pain. You should also call your doctor if you experience shortness of breath along with swelling in your leg.
Can you drain a Baker's cyst behind your knee?
Generally no. If you drain the cyst, it ususally comes back. Drainage is advised for cosmetic reasons or if you develop pain or discomfort at the back of the knee. However, we recommend you have your knee injected to reduce joint swelling and prevent a recurrence.
Does a knee brace help Baker's cyst?
Baker's cysts are most often caused by injuries such as a torn ACL / MCL or a torn meniscus. To treat it, our team will address the main injury with bracing. In rare cases, if the cyst is large enough, a physician may recommend that they aspirate or remove it.
How is a Baker's cyst surgically removed?
There are some patients where the cyst is very large, or causing swelling further down the calf, and the cyst needs to be removed. Removing the cyst requires an open incision on the back of the knee. It is usually performed along with an arthroscopic surgery to address what's damaged inside the knee itself.
What is the average size of a Baker's cyst?
The average size of a Bakers cyst is 3cm.
Can a bakers cyst cause a blood clot?
DVT associated with Baker's cyst is rather common and these two conditions are thought to be causally related. Baker's cyst is the most frequent mass lesion in the popliteal region. We suggest that Baker's cyst is a risk factor for PE as well as surgery and trauma.
What is the procedure for Baker's cyst?
Surgical options for Baker’s cysts can include: Cyst draining: Your healthcare provider can drain the fluid out of the cyst with a needle. Arthroscopic Knee Surgery: This procedure can be used to both diagnose and correct knee damage.
What causes a Baker's cyst in the knee?
A Baker’s cyst is the result of joint damage that causes swelling in the knee. Examples of damage can include: Arthritis (osteoarthritis or rheumatoid). Direct damage to the knee (meniscus tear or ligament tear). Inflammation.
What is a popliteal cyst?
A Baker’s cyst, also known as a popliteal cyst or synovial cyst, is a soft, fluid-filled lump that forms on the back of your knee. Like many diseases and disorders, this cyst is named after the doctor who first described it.
What happens if you leave a Baker's cyst untreated?
However, there are other complications that can happen if a Baker’s cyst is left untreated, including: The pain getting worse. The cyst increasing in size. The cyst bursting, causing bruising in the lower leg. If the cyst doesn’t go away, reach out to your healthcare provider.
How to tell if you have a Baker's cyst?
Pain. Stiffness of your knee. Limited range of motion and ability to bend your knee. Swelling of your knee and/or leg .
What to do if a Baker's cyst doesn't go away?
If the cyst doesn’t go away, reach out to your healthcare provider. It’s important to get the right diagnosis and make sure it is a Baker’s cyst. This condition could be mistaken for something more serious like a tumor or artery aneurysm, which is a medical emergency.
How to stop knee pain after knee surgery?
Avoiding strenuous activities. Keeping your knee propped up for a few days after surgery to decrease swelling or any pain you may feel. Taking all of your pain and antibiotic medications as instructed by your healthcare provider. Going to your follow up appointment with your provider several days after your surgery.
What is a Baker's cyst?
A Baker's cyst is a swelling that can develop behind the knee. It is filled with synovial fluid which is the lubricating fluid that is usually found inside the knee joint. It most commonly occurs if there is an underlying problem with your knee such as osteoarthritis. Symptoms can include pain, swelling and tightness behind the knee. Rarely, a Baker's cyst can split open (rupture) and cause similar symptoms to a deep vein thrombosis (DVT). A Baker's cyst often gets better and disappears by itself over time. However, there are various treatments that may help if you do have symptoms associated with it.
What is the name of the swelling behind the knee?
A Baker's cyst is a fluid-filled swelling that can develop behind the knee. It is one cause of knee pain. It is named after a doctor called William Baker who first described this condition in 1877. It is also sometimes called a popliteal cyst, as the medical term for the area behind your knee is the popliteal fossa.
Why does my knee ache when I bend it?
Some people feel an ache around the knee area. It may be difficult to bend your knee if you have a large Baker's cyst and the area behind your knee may feel tight, especially when you are standing up. Less commonly, you may feel a sensation of clicking or locking of your knee.
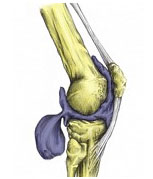
What happens when you stretch your knee capsule?
As a result of this, the pressure inside the knee increases. This has the effect of stretching the joint capsule. The joint capsule bulges out into the back of the knee, forming the Baker's cyst that is filled with synovial fluid.
What is the membrane that lines the knee?
It is lined by a special membrane called the synovium. The synovium produces a fluid called synovial fluid. This fluid acts as a lubricant within your knee joint and helps to cushion it during movement. There are also various tissue pouches called bursae next to the knee.
How common is a Baker's cyst?
A Baker's cyst most commonly occurs in children aged 4 to 7 years and in adults aged 35 to 70 years. However, Baker's cysts are much more common in adults than in children. You are more likely to develop a Baker's cyst if you have an underlying problem with your knee.
What is the cartilage on the knee called?
Each knee joint also contains a medial and a lateral meniscus. These are thick rubber-like pads of cartilage tissue. The menisci cartilage sit on top of, and are in addition to, the usual thin layer of cartilage which covers the top of one of the bones of the lower leg, called the tibia.
What are the symptoms of a lump behind the knee?
Behind knee lump may accompany other localized symptoms including: Bleeding or bruising. Deformity of the joint. Instability of the joint. Limited ability, or inability, to move the knee or leg. Muscle weakness or spasm.
Why do I have a lump in my knee?
Other possible causes of a lump behind the knee include abscesses (infections); tumors of the skin, soft tissue, or bones; bleeding; or deformity of the joint accompanying a fracture or other injury to your knee. A lump behind your knee may be associated with injury and may be accompanied by more serious injuries to the joint.
Why does my knee feel swollen?
A swollen area or lump that can be felt behind your knee can be caused by several different conditions. The lump may create an unsightly appearance, limit knee flexibility, or generate discomfort. A Baker’s cyst is a collection of synovial fluid (the fluid that is present within joint spaces) that bulges out through the back ...
What does it mean when you have a lump in your knee?
A lump behind your knee may be associated with injury and may be accompanied by more serious injuries to the joint. Seek immediate medical care (call 911) for serious symptoms, such as paralysis or inability to move a body part, loss of sensation, absent pulses in the feet, uncontrolled or heavy bleeding, or uncontrollable pain.
Can a Baker's cyst be found on the knee?
Knee injuries, arthritis, damage to the cartilage of the knee, and other problems can all result in the development of a Baker’s cyst. The majority of individuals with Baker’s cyst experience no symptoms. The cyst may be found during radiologic imaging for other joint complaints. A lump behind the knee may be painful or may not produce any other ...
Can a cyst in the knee be seen on radiology?
The cyst may be found during radiologic imaging for other joint complaints. A lump behind the knee may be painful or may not produce any other symptoms. In some cases, you may experience tenderness, warmth, difficulties with movement of your knee joint, or bleeding or bruising.
How to heal a cyst in the knee?
These can help lessen inflammation. Exercise. A physical therapist can teach you gentle exercises , to help improve your range of motion, and strengthening moves, to build up the muscles around your knee. This could ease your symptoms. Aspiration. Your doctor can drain the cyst.
How to treat Baker's cyst?
You may not need any treatment for a Baker's cyst. They aren’t dangerous and tend to go away on their own. But there are things you can do at home to ease your pain and make yourself more comfortable: 1 Keep it cold. Apply a cold pack to the affected area. It’ll help keep the swelling down. A compression wrap might also help. 2 Take medication. For pain (and to ease inflammation ), take an over-the-counter medication like ibuprofen. 3 Rest your leg. Keep it raised above your heart level when possible. This will keep down swelling. You may want to use a compression bandage, and a cane or crutch when you walk, to keep pressure off your leg.
Why does my knee swell?
Swelling in the knee. This happens when the fluid that lubricates your knee joint increases. When pressure builds up, fluid squeezes into the back of the knee and creates the cyst. Arthritis. People with all forms of arthritis often have Baker’s cysts. Injury.
How to prevent knee injury?
Possibly -- by preventing knee injuries in the first place. Wear the right shoes when you work out. Be sure to warm up before you exercise. And if you do get a knee injury, take care of it right away. See your doctor if it doesn’t get better. Baker’s Cyst Complications. Sometimes, the cysts break open.
Can you move your knee with a Baker's cyst?
Surgery. If you’re in serious pain or if the cyst makes it hard for you to move your knee, this might be an option. But it’ll work only if your doctor also treats the issue that caused the Baker’s cyst to begin with, such as arthritis. If your leg turns red or darker and starts to swell, see your doctor right away.
Can Baker's cysts get worse?
See your doctor if it doesn’t get better. Baker’s Cyst Complications. Sometimes, the cysts break open. This can cause pain, swelling, and bruising on the back of your knee and calf. The pain might get worse when you fully extend your knee or when you’re active.
What causes a Baker's cyst in the knee?
But sometimes the knee produces too much synovial fluid, resulting in buildup of fluid in an area on the back of your knee (popliteal bursa), causing a Baker's cyst. This can happen because of: 1 Inflammation of the knee joint, such as occurs with various types of arthritis 2 A knee injury, such as a cartilage tear
What is Baker's cyst?
A Baker's cyst is a fluid-filled cyst that causes a bulge and a feeling of tightness behind your knee. The pain can get worse when you fully flex or extend your knee or when you're active.
Why does my back of my knee feel tight?
Overview. Swelling on the back of one knee may be a Baker's cyst. A Baker's cyst can form when joint-lubricating fluid fills a cushioning pouch (bursa) at the back of your knee. A Baker's cyst is a fluid-filled cyst that causes a bulge and a feeling of tightness behind your knee. The pain can get worse when you fully flex or extend your knee ...
How do you know if you have a Baker's cyst?
If you do have signs and symptoms, they might include: Swelling behind your knee, and sometimes in your leg. Knee pain. Stiffness and inability to fully flex the knee.
What fluid is used to help your leg swing?
A lubricating fluid called synovial ( sih-NO-vee-ul) fluid helps your leg swing smoothly and reduces friction between the moving parts of your knee. But sometimes the knee produces too much synovial fluid, resulting in buildup of fluid in an area on the back of your knee (popliteal bursa), causing a Baker's cyst.
How to treat pain behind knee?
Generally, the first step is to reduce any swelling, then work on knee exercises to improve the strength and stability of the knee to reduce the force that goes through the knee joint .
What causes a tear in the cartilage at the back of the knee?
A tear in the cartilage aka meniscus at the back of the knee. Causes: Sudden twisting, a force through the knee or gradual wear and tear. Symptoms: Swelling, locking and pain behind the knee with knee extension, walking, running, squatting & going up stairs. Find Out More: Meniscus Tears.
What causes swelling in the back of the knee?
This fluid fills the semimembranosus bursa and causing swelling behind the knee. It often feels like there is a squashy orange behind the knee which can be really painful. Other possibilities of back of knee swelling include a calf tear, popliteal aneurysm and a synovial sarcoma.
Why does my knee hurt behind my knee?
1. Bakers Cyst. Swelling develops in the popliteal bursa at the back of the knee. Bakers Cyst is the most common cause of pain behind the knee. 2.
Why is my knee tight?
Tightness behind the knee is often caused by tightness in the hamstring or calf muscles. The hamstring muscles run down the back of the thigh attaching behind the knee, and one of the calf muscles, gastrocnemius, starting from the back of the knee, travels down to the heel. Tightness in these muscles is a common problem, particularly in men, ...
Why does my kneecap hurt?
Pain behind the kneecap is usually caused by a problem with the cartilage that lines the back of the kneecap. It may be Runners Knee, where a problem with how the kneecap glides causes friction and pain behind the kneecap.
What causes a knee ligament to tear?
Causes: Sudden twisting movements or a large force through the knee. Symptoms: Knee instability, back of knee pain, swelling, bruising, decreased knee movement. Find Out More: Knee Ligament Sprains.
What is the best way to diagnose a meniscus cyst?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or ultrasound may be necessary to diagnose a meniscal cyst. Treatment involves lancing and draining the cyst, although it will commonly return unless the underlying meniscus tear is also treated. 2 . Verywell / Tim Liedtke.
What is a meniscal cyst?
Diagnosis. Treatment. A meniscal cyst is a collection of joint fluid caused by a tear within the meniscus cartilage, the joint pad over the knee. It may have no symptoms, or it may cause pain, swelling, or mechanical issues with the knee. Meniscal cysts are most commonly reported in 20- to 30-year-old males and are usually associated ...
How to tell if you have a meniscal cyst?
Symptoms. Meniscal cyst symptoms may not always appear, but when they do, the most common symptoms are: 3 . Pain in the knee when standing. Tenderness directly over the joint line of the knee. A bump or lump at the cyst site: Cysts are usually found near the lateral meniscus (outside of the knee)
Where are meniscal cysts located?
Meniscal cysts are similar to popliteal or Baker's cysts, but the latter are located in the back of the knee joint . In addition, a popliteal cyst is seen with many types of knee joint problems that lead to fluid accumulation or knee swelling.
What causes a breakdown of the menisci?
Participation in contact sports or any sports in which there's a frequent twisting of the knee joint, such as football, soccer, rugby, or tennis. Increasing age or osteoarthritis, both of which cause a breakdown in menisci.
Can cartilage tear cause meniscal cysts?
Because of this, the cyst will continue to collect fluid. Risk factors for meniscal cysts include: Previous knee injury or meniscal injury.
Is a meniscal cyst a tumor?
It is important to understand that while called a cyst, a meniscal cyst is really just a pouch of dislocated joint fluid. It is not an abnormal growth and it is not a tumor. It is simply a collection of normal synovial fluid that has escaped to an abnormal location.