In combination with these chemicals, proteinase K
Proteinase K
In molecular biology Proteinase K (EC 3.4.21.64, protease K, endopeptidase K, Tritirachium alkaline proteinase, Tritirachium album serine proteinase, Tritirachium album proteinase K) is a broad-spectrum serine protease. The enzyme was discovered in 1974 in extracts of the fungus Eng…
Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin is a digestive enzyme component of pancreatic juice acting in the duodenum, where it performs proteolysis, the breakdown of proteins and polypeptides. Chymotrypsin preferentially cleaves peptide amide bonds where the side chain of the amino acid C-terminal to the scissile amid…
What is the role of protease in DNA extraction?
If you are performing DNA extraction as a preliminary step in detecting bacteria and viruses in the environment or as a way of diagnosing disease/genetic disorders, you probably know that the removal of proteins in the sample via the appropriate protease is an important step.
What is the role of proteases in disease?
Consistent with these essential roles of proteases in cell behavior and survival and death of all organisms, alterations in proteolytic systems underlie multiple pathological conditions such as cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and inflammatory and cardiovascular diseases.
What is the role of protease inhibitors?
Protease inhibitors have been developed against proteases that viruses use to cleave nascent proteins for assembly of new virions, for example, in treatment or prevention of viral infection by HIV or hepatitis C viruses.
Why are there so many types of protease enzymes?
This outstanding diversity in protease functions directly results from the evolutionary invention of a multiplicity of enzymes that exhibit a variety of sizes and shapes.

Why are proteases added while isolating the DNA?
Proteases are added to degrade the proteins so that they do not interfere with the downstream DNA treatment.
What happens when protease is added to protein?
A protease (also called a peptidase or proteinase) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products.
What is the role of protease?
Proteolytic enzymes (proteases) are enzymes that break down protein. These enzymes are made by animals, plants, fungi, and bacteria. Proteolytic enzymes break down proteins in the body or on the skin. This might help with digestion or with the breakdown of proteins involved in swelling and pain.
Why do cells need proteases?
Intramembrane proteases (IMPRs) cleave transmembrane proteins inside the lipid bilayer. They regulate a growing number of biological processes, and our knowledge about the evolutionary and functional niches these unusual enzymes have filled is slowly unravelling.
Why is keratin associated with proteinase?
Why keratin is associated with proteinase is a very interesting story. The keratin is a hair protein and the hardest form of protein. Proteinase is the first enzyme isolated from the fungus Tritirachium album which can digest the hardest form of protein, “Keratin”. Therefore the K is given as suffix for the enzyme.
What chemicals are used in proteinase K?
The proteinase K gives the best results in the presence of several other chemicals. Chemicals such as Sodium dodecyl sulphate, EDTA, urea, CTAB and Nonidet P40 can be used for protein digestion. In combination with these chemicals, proteinase K increases the efficiency of the result by increasing the purity of the DNA.
What temperature does proteinase K digest?
Highest proteinase K activity is reported at the temperature 60ºC ranging from 37ºC to 70ºC.
What is proteinase K protocol?
Proteinase K DNA extraction protocol. There are many variations in proteinase K DNA extraction protocol. However, the variation depends on the requirement of the researcher and the type of tissue. I am describing the protocol for DNA extraction from the blood.
What is the best method for DNA extraction?
Proteinase K is one of the best DNA extraction methods to date. The method is accurate, reliable and fast. The proteinase K DNA extraction method is also called as an enzymatic method of DNA extraction because of the important role of proteinase K enzyme in the DNA extraction.
What is proteinase K?
Proteinase K is a member of the family subtilisin, typically a proteinase. The molecular mass of the proteinase K is ~28, 930kDa. The enzyme is typically a protein which is made up of the long chain of approximately 278 amino acids. As we all know every enzyme required a cofactor for performing a reaction.
What is DNA extraction?
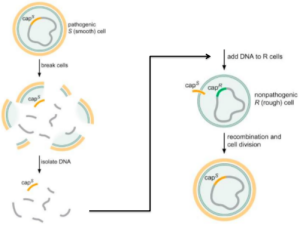
DNA extraction is an important step in any genomic technique ranging from the polymerase chain reaction to microarray and from real-time PCR to next-generation sequencing. For extracting DNA or isolating DNA from the cell we have to break cell membrane (or cell wall in case of Plant cell) and nuclear membrane.
What is the purpose of protease?
A protease will destroy the DNAses that would attack the DNA. EDTA is also usually added since it will bind Mg ions needed for most DNAases. In order to isolate DNA from a cell we have to first isolate DNA. In other words we have to remove everything else in the cell excluding the DNA.
Why is DNA extraction important?
It is also useful for the detection of bacteria and viruses and from the environment and it also provides chance to diagnose diseases and other genetic disorders which cannot be identified through any other means. 2.7K views. ·.
What happens after DNA is centrifuged?
After centrifugation or elution, ethanol or isopropanol is added and the DNA becomes insoluble. After this step centrifugation is necessary to pellet the DNA. In some cases when working with genomic DNA you have enough material to spool it, but this. Continue Reading.
How to isolate DNA from a cell?
In order to isolate DNA from a cell we have to first isolate DNA. In other words we have to remove everything else in the cell excluding the DNA. So we use digestive enzymes such as protease , lipase , cellulase .etc in order to lyse the unwanted protiens , fats , cellulose .etc such that only DNA remains in the cell.
What buffer is used for DNA extraction?
The commonest buffer used in DNA extractions is Tris-HCl which operates round neutrality. Other buffers exist that operate at acid and alkali conditions. Practically all biochemical work involves using buffers, so it is a good idea to find out which ones are available and at what range they operate.
Why do proteins lose their structure?
Because of loss of confirmation the protein loses its structure. The proteins from the cell membrane get damaged and cell gets broken. This will help the cell membranes and nuclear envelopes to break down and expose the chromosomes that contain the DNA. . .
Why do cells need buffers?
Buffers keep the pH stable. When cells are lysed open they release many types of compounds that can change pH which could alter the properties of the target molecule. Including a buffer prevents this and keeps the pH to something similar to that in the cell.
Do drugs change DNA?
Most drugs act on proteins - the molecules in our cells that do particular jobs - so they don't change your underlying DNA. But some can act on DNA - for example many chemotherapy drugs, such as cisplatin, damage DNA and make cancer cells die.
Can cancer drugs damage DNA?
But they can also damage DNA in healthy cells too, causing side effects. Some other new cancer drugs in development are designed to change the molecular 'tags' on your DNA, known as methylation and acetylation, affecting how genes are switched on or off.
When was recombinant DNA first used?
The first recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecules were generated in 1973 by Paul Berg, Herbert Boyer, Annie Chang, and Stanley Cohen of Stanford University and University of California San Francisco. In 1975, during “The Asilomar Conference” regulation and safe use of rDNA technology was discussed.
What is the tumor suppressor gene?
Inserting tumor suppressor genes to immunotherapy, oncolytic virotherapy and gene directed enzyme prodrug therapy are different strategies that have been used to treat different types of cancers. The p53, a commonly transferred tumor suppressor gene, is a key player in cancer treating efforts.
What was the first protein expressed in tobacco plants?
Human growth hormone was the first protein expressed in tobacco plants [41, 42]. Besides insulin, several new drugs related to recombinant DNA technology have undergone developmental improvements and a number of protein production systems have been developed.
Can CRISPR be used to study human diseases?
Mouse models can be managed for studying human diseases with CRISPR, where individual genes study becomes much faster and the genes interactions studies become easy by changing multiple genes in cells [25]. The CRISPR ofH. hispanicagenome is capable of getting adapted to the nonlytic viruses very efficiently.