How long do the effects of ECT last?
There is considerable variability in the trajectories, but most commonly there is progressive symptomatic improvement within the first week and complete remission within 3 to 4 weeks.May 11, 2010
What mental illnesses does ECT treat?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What does ECT do to the brain?
It may promote changes in how brain cells communicate with each other at synapses and it may stimulate the development of new brain cells. ECT may flood the brain with neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to be involved in conditions like depression and schizophrenia.
How often do ECT treatments make you feel better?
HOW MANY TIMES WILL I NEED TO BE TREATED? People undergoing ECT need multiple treatments. The number needed to successfully treat severe depression can range from 4 to 20, but most people need a total of 6 to 12 treatments.Apr 7, 2021
Does ECT change your personality?
ECT does not change a person's personality, nor is it designed to treat those with just primary “personality disorders.” ECT can cause transient short-term memory — or new learning — impairment during a course of ECT, which fully reverses usually within one to four weeks after an acute course is stopped.
What does ECT feel like?
On the days of an ECT treatment, some people experience nausea, headache, jaw pain or muscle ache. These generally can be treated with medications. Medical complications. As with any type of medical procedure, especially one that involves anesthesia, there are risks of medical complications.Oct 12, 2018
Does ECT reset the brain?
ECT has been referred to as a “reset button for the brain,” which not only directly improves depressive symptoms, but also allows current medications to work more effectively.
Do they shave your head for ECT?
During surgery prep, you'll have your head shaved. You may be kept unconscious throughout brain surgery with general anesthesia or stay awake with a local anesthetic used on your scalp. A sturdy frame will hold your head to prevent movement during surgery.Feb 21, 2021
Can ECT make you worse?
ECT may have a role in people who have comorbid depression and anxiety. The concern of some psychiatrists is that while ECT may help with depressive symptoms, it could worsen anxiety symptoms, including obsessional thoughts or panic attacks.Mar 22, 2020
Does ECT increase serotonin?
Conclusion. Altogether, our results showed that serum serotonin levels significantly increase following ECT in MDD patients.
Does ECT cause weight gain?
During ECT, all patients increased their caloric intake (280 +/- 180 to 1,510 +/- 60 kcal/day, mean +/- SEM) to exceed their basal energy expenditure; major improvements in their depressive symptoms and weight gain were seen in five of the six patients.
Does ECT wear off?
The duration of improvement (how long recovery lasts). The benefits of ECT may last for years or they may disappear in a matter of weeks. After a series of ECT treatments, your doctor may prescribe medication to help prevent symptomsfrom returning.
What is ECT therapy?
What is Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT)? Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment most commonly used in patients with severe major depression or bipolar disorder that has not responded to other treatments. ECT involves a brief electrical stimulation of the brain while the patient is under anesthesia.
What are the side effects of ECT?
The most common side effects of ECT on the day of treatment include nausea, headache, fatigue, confusion, and slight memory loss, which may last minutes to hours.
What is consent process?
In situations where a person is too ill to make decisions for him or herself, the consent process is governed by state law (for example, a court-appointed guardian). Patients and their families should discuss all options for treatment with the psychiatrist before making a specific treatment decision.
How long does a seizure last after ECT?
This causes a seizure within the brain that lasts for approximately a minute. The patient is asleep for the procedure and awakens after 5-10 minutes, much as from minor surgery. Most insurance plans offering coverage for psychiatric disorders at least partially reimburse the cost of ECT.
How often is TMS given?
TMS is usually administered four or five times a week for four-to-six weeks. Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) was developed as a treatment for seizure disorders but can also be used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies.
Is ECT a cure for mental illness?
Although ECT can be very effective for many individuals with serious mental illness, it is not a cure. To prevent a return of the illness, most people treated with ECT need to continue with some type of maintenance treatment. This typically means psychotherapy and/or medication or, in some circumstances, ongoing ECT treatments.
What is TMS in medical terms?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is used to treat depression that has not responded to other therapies. It involves the use of rapidly alternating magnetic fields to stimulate specific areas of the brain. Unlike ECT, TMS does not cause a seizure and the patient remains awake through the noninvasive process.
What is ECT therapy?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure that deliberately applies electric current to the brain, through the scalp, to cause a short seizure. It is used to treat people with severe mental illnesses, like depression, that did not respond to other treatments. Appointments 866.588.2264. Appointments & Locations.
When to use ECT?
ECT is generally used as a later treatment option when severe depression is unresponsive to other forms of therapy, or when the patient is so ill that his or her life is in danger. It also is used when these patients pose a severe threat to themselves or others, and it is dangerous to wait until medications take effect.
Why is electroconvulsive therapy used?
Why is electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) used? ECT is one of the fastest ways to relieve symptoms in severely depressed or suicidal patients, in patients who suffer from mania, and in other mental illnesses.
What is ECT in medical terms?
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is a procedure in which a brief application of electric current to the brain, through the scalp, induces a seizure. It is typically used to treat a patient who is suffering from severe depression. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Is ECT a quick fix?
There also is a misconception that ECT is used as a "quick fix" instead of long-term therapy or hospitalization. Unfavorable news reports and media coverage have added to the controversy of this treatment. In fact, ECT is safe and among the most effective treatments available for depression.
What is the effect of ECT on the brain?
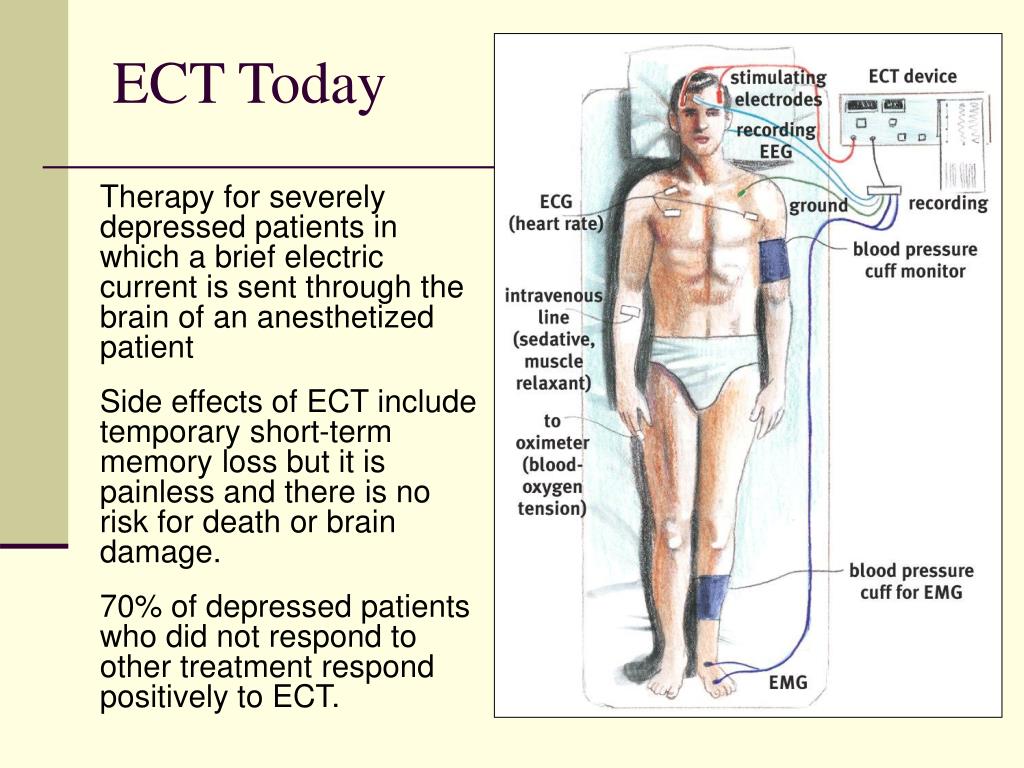
ECT causes the patient to have a seizure. Electrodes are placed on the patient’s scalp and a finely controlled electric current is applied, which causes a brief seizure in the brain. Because the muscles are relaxed, the seizure will usually be limited to slight movement of the hands and feet. Patients are carefully monitored during the treatment.
How long does it take for short term memory loss to go away?
Short-term memory loss is the major side effect, although this usually goes away 1 to 2 weeks after treatment. You should be educated and informed about ECT and any treatment prior to receiving it. Ask for educational literature, videos, and an honest discussion with your doctor about the potential benefits and side effects.
How does ECT work?
ECT uses electric currents to stimulate a person’s brain to induce a controlled seizure. Researchers do not exactly know how ECT works, but one theory is that it could regulate neurotransmitter activity. This article looks at how ECT works, whether it is an effective treatment, and its controversial history. It also discusses some alternative ...
How long does an ECT last?
An ECT session may last for about 1 hour, which includes 15–20 minutes for the procedure and 20–30 minutes of recovery time. A person may receive ECT two or three times a week for a total of between six and 12 sessions. The frequency and number of sessions will differ among individuals depending on the severity of the condition and ...
What is electro shock therapy?
Electroshock therapy, also known as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), is a treatment for severe major depression, bipolar depression, and other mental health conditions. Psychiatrists may recommend ECT when a person does not respond well to other treatments. ECT uses electric currents to stimulate a person’s brain to induce a controlled seizure.
Is ECT a good treatment for schizophrenia?
ECT can be an effective therapy for treatment-re sistant mental health conditions , including depression, schizophrenia, and catatonia. It is a very old psychiatric treatment and has a controversial history. However, doctors recommend ECT for some people because it is low risk and carries few side effects.
Why was the VNS developed?
Researchers originally developed VNS to treat seizure conditions. However, they realized that it was also an effective treatment#N#Trusted Source#N#for depression. Before stimulating the vagus nerve, a doctor places an electrode under the skin of a person’s chest.
Is TMS better than ECT?
However, TMS is the only technique that researchers have directly compared with ECT, and ECT produced better outcomes for people with depression.
How long is a brief pulse?
The stimulus usually consists of a brief electrical pulse, which is one in the range of 0.5–2.0 milliseconds (ms) Trusted Source. . Doctors may sometimes use ultra-brief pulses, which are under 0.5 ms. The pulse reaches the brain through electrodes on the head and induces a controlled seizure.
How does ECT work?
With ECT, an electric current is briefly applied through the scalp to the brain, inducing a seizure. In addition, alternative therapies such as yoga and hypnosis sometimes work for mild depression.
When is ECT used?
ECT is generally used when severe depression is unresponsive to other forms of therapy. Or it might be used when patients pose a severe threat to themselves or others and it is too dangerous to wait until medications take effect. Although ECT has been used since the 1940s and 1950s, it remains misunderstood by the general public.
What are the treatments for depression?
Some experimental therapies currently being investigated for treatment of depression include: 1 Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in women: Depression is more common in women than in men. Changes in mood with premenstrual syndrome ( PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), post- childbirth, and postmenopause are all linked with sudden drops in hormone levels. Hormone replacement is a treatment currently used to relieve symptoms of menopause such as night sweats and hot flashes. HRT can also help prevent bone-thinning osteoporosis. However, the true contribution of hormones to depression is not known. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have had depression before and are considering HRT. 2 Intravenous ketamine: The anesthetic agent ketamine has been approved for treatment of severe depression. It has been shown in preliminary studies to produce a rapid (within hours) improvement in depression for and is recognized as effective in some patients. 3 Riluzole: ( Relutek, Tiglutik) This medicine, originally used to treat motor neuron disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS, or Lou Gehrig's Disease), has been shown also to affect neurotransmitters involved in depression, and in early studies has begun to show promise in treating depression that is unresponsive to more traditional medicines.
Why does TMS work?
The current is caused by the magnetic field created by an electromagnetic coil that delivers the pulses through the forehead. Approved by the FDA in 2008 for treatment-resistant depression, TMS works best in patients who have failed to benefit from one, but not two or more, antidepressant treatments.
What is electroconvulsive therapy?
When medication fails to ease the symptoms of clinical depression, there are other options to try. Brain stimulation techniques such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), for example, can be used to treat major depression that hasn't responded to standard treatments.
What is brain stimulation?
Brain stimulation techniques such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), for example, can be used to treat major depression that hasn't responded to standard treatments. The least invasive of these techniques is called transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), in which a magnetic field is created by a device held above the head, ...
How often is ECT given?
The confusion typically lasts for only a short period of time. ECT is usually given up to three times a week for a total of two to four weeks.
What are the risks of ECT?
Risks and Side Effects of ECT. The most common side effect of ECT is short-term memory loss. However, some people report that they have long-term memory loss, as well. ECT also causes a brief rise in heart rate and blood pressure during the procedure, so it may not be recommended in people with unstable heart problems.
How does electroconvulsive therapy work?
How Electroconvulsive Therapy Works. With ECT, an electrical stimulation is delivered to the brain and causes a seizure. For reasons that doctors don't completely understand, this seizure helps relieve the symptoms of depression. ECT does not cause any structural damage to the brain.
What is the best treatment for depression?
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) for Depression. For some people with severe or hard-to-treat depression, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) is the best treatment. This treatment, sometimes referred to as "electroshock therapy," is often misunderstood and incorrectly portrayed by popular media as a harsh, cruel treatment.
Does ECT work for depression?
Studies have shown that ECT works for many people who have treatment-resistant depression. One study of 39 people with treatment-resistant depression compared the effects of an antidepressant with ECT. After two to three weeks, 71% of people who received ECT had a positive response to treatment.
Does ECT cause brain damage?
ECT does not cause any structural damage to the brain. The procedure itself typically requires a stay in the hospital, although more and more it is being performed on an outpatient basis. During the procedure, you will be put to sleep under general anesthesia. You won't feel anything.
Is ECT a life saving medication?
It can be lifesaving. ECT works quickly, which is why it's often the treatment of choice for people with highly severe, psychotic, or suicidal depression. For these people, waiting for antidepressants or therapy to work might be dangerous. However, the drawback is that the effects of ECT usually don't last, and further treatments will likely be ...
How does ECT work?
Why does ECT work? No one is sure how ECT helps certain psychiatric disorders. It may promote changes in how brain cells communicate with each other at synapses and it may stimulate the development of new brain cells. ECT may flood the brain with neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to be involved in conditions like ...
How long does an ECT last?
A single ECT session usually lasts one hour. This includes the time the patient will be in the treatment room (approximately 15-20 minutes) and the time spent in the recovery room (approximately 20-30 minutes). Typically, ECT (whether inpatient or outpatient) is given two to three times a week for a total of six to twelve sessions.
What are the side effects of a syringe?
The immediate side effects of the procedure which may last for about an hour include: 1 Headaches 2 Nausea 3 Muscle aches and soreness 4 Disorientation and confusion

Why It's Done
- Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can provide rapid, significant improvements in severe symptoms of several mental health conditions. ECT is used to treat: 1. Severe depression,particularly when accompanied by detachment from reality (psychosis), a desire to c…
Risks
- Although ECT is generally safe, risks and side effects may include: 1. Confusion.Immediately after treatment, you may experience confusion, which can last from a few minutes to several hours. You may not know where you are or why you're there. Rarely, confusion may last several days or longer. Confusion is generally more noticeable in older adults. 2. Memory loss.Some people hav…
How You Prepare
- Before having your first ECT treatment, you'll need a full evaluation, which usually includes: 1. Medical history 2. Complete physical exam 3. Psychiatric assessment 4. Basic blood tests 5. Electrocardiogram (ECG) to check your heart health 6. Discussion of the risks of anesthesia These exams help make sure that ECT is safe for you.
What You Can Expect
- The ECT procedure takes about five to 10 minutes, with added time for preparation and recovery. ECT can be done while you're hospitalized or as an outpatient procedure.
Results
- Many people begin to notice an improvement in their symptoms after about six treatments with electroconvulsive therapy. Full improvement may take longer, though ECT may not work for everyone. Response to antidepressant medications, in comparison, can take several weeks or more. No one knows for certain how ECT helps treat severe depression and other mental illness…