pH has a significant impact on the microbial makeup of a wastewater system. Most biological wastewater treatment is accomplished at pH range of 6.5 - 8.5, which is where a majority of our common environmental microbes thrive.
Does pH change immediately in wastewater treatment?
Aug 02, 2016 · Aug 02, 2016. The term “pH ” refers to the measurement of hydrogen ion activity in the solution. Determination of pH plays an important role in the wastewater treatment process. Extreme levels, presence of particulate matters, accumulation of toxic chemicals and increasing alkalinity levels are common problems in wastewater.
How does pH affect the quality of water?
Jun 24, 2014 · pH & Wastewater Microbes. pH has a significant impact on the microbial makeup of a wastewater system. Most biological wastewater treatment is accomplished at pH range of 6.5 - 8.5, which is where a majority of our common environmental microbes thrive. Today, I want to detail how (1) long run high or low pH can impact microbial populations and (2) what rapid …
What is the best pH range for biological wastewater treatment?
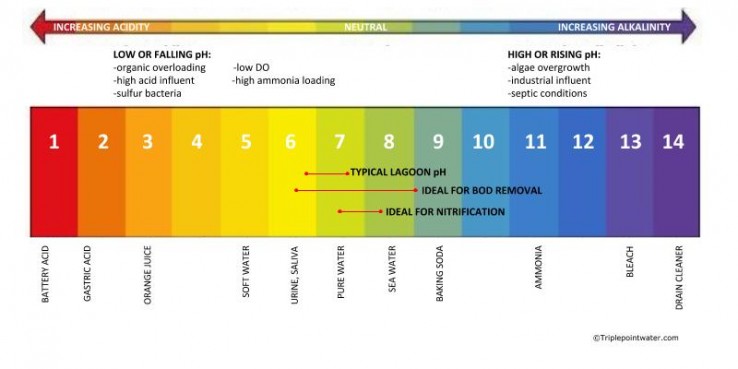
The bacteria and other organisms which play an active role in wastewater treatment are most effective at a neutral to slightly alkaline pH of 7 to 8. To maintain these optimal pH conditions for biological activity there must be sufficient alkalinity present in the wastewater to neutralize acids generated by the active biomass during waste treatment especially nitrification.
How do I implement a pH adjustment in a wastewater tank?
How do starting and ending pH values impact the treatment procedure? It takes residence or contact time during wastewater treatment for the pH to adjust appropriately. A very narrow pH range (i.e., 7.0 to 8.0) requires less contact or residence time as compared to a wider pH range (i.e., 7.0 to 10.0), so the procedure is affected by the required pH adjustment range. Why is …

How does pH affect water environment?
What is the pH value of wastewater?
How does pH increase in waste water?
- Calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide (as lime slurry)
- Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)
- Sodium carbonate (soda ash) or sodium bicarbonate.
- Magnesium hydroxide or magnesium bicarbonate.
What causes high pH in wastewater?
Why is pH important in wastewater?
But more than that, maintaining a pH in the neutral 6 to 8 range is critical to maintaining the biological treatment in your wastewater facility . Maintaining the alkalinity of your wastewater is particularly essential to the nitrification bacteria, which consume large quantities of alkalinity as they nitrify the ammonia in your wastewater.
What pH level is needed to remove phosphorus from wastewater?
Traditional phosphorus removal coagulants, using aluminum or iron-based salts, are strongly acidic with a pH level of 1.5 to 2.2. The impact of this low pH is amplified by the volume required to reduce phosphorus to low discharge limits.
What happens when the phosphorus limit is lowered?
As the phosphorus limit is lowered, the corresponding amount of these coagulants required increases to 4 or more molecules of coagulant for every molecule of phosphate removed. That is a lot of acid! Your pH tips strongly to the acidic side and if you don’t balance it out, your treatment is compromised. To pull your pH back into the neutral range ...
How to get pH back into neutral range?
To pull your pH back into the neutral range and restore alkalinity, you are probably adding caustic, and lots of it. So, you seesaw back and forth, using traditional coagulants then caustic. These strongly acidic and basic chemicals are also hazardous to your operators.
Is caustic acidic coagulant dangerous?
The acidic coagulant is extremely irritating to skin, eyes and lungs, and the caustic is just as dangerous. If you mix caustic yourself from bags, it is a very hazardous operation. Once you have it mixed, even the most dilute solution has a high freezing point, which means you must keep the tank and pipes heat traced.
Does wastewater have acid?
Almost every wastewater system has enough excess alkalinity so that this little bit of acid doesn’t even cause a significant dip in the pH. In fact, wastewater plants with limits as low as 0.07 mg/L of total P have switched to Neo WaterFX and eliminated their caustic feeds. Less chemical feeds, no more seesawing back and forth.
Can you seesaw back and forth on pH?
But you don’t have to operate like this, seesawing back and forth on pH, driving it down to remove phosphorus then adjusting it back up to remove ammonia, or just maintain your biomass, constantly balancing your chemical feeds.
What pH is needed for wastewater treatment?
The bacteria and other organisms which play an active role in wastewater treatment are most effective at a neutral to slightly alkaline pH of 7 to 8. To maintain these optimal pH conditions for biological activity there must be sufficient alkalinity present in the wastewater to neutralize acids generated by the active biomass during waste treatment especially nitrification. This ability to maintain the proper pH in the wastewater as it undergoes treatment is the reason why alkalinity is so important to the wastewater process. If all alkalinity in the wastewater process is consumed, an alkaline solution such as caustic soda or magnesium hydroxide can be added to maintain the system pH between 7-8 as the denitrifying bacteria generate acid but this adds cost and complexity to the system.
Why is alkalinity important in wastewater treatment?
This ability to maintain the proper pH in the wastewater as it undergoes treatment is the reason why alkalinity is so important to the wastewater process. If all alkalinity in the wastewater process is consumed , an alkaline solution such as caustic soda or magnesium hydroxide can be added to maintain the system pH between 7-8 as ...
What is the difference between acid and pH?
Acid – An acid is anything that will donate a proton (a proton is the same thing as a hydrogen ion H+) in solution. A lower pH acid is simply a higher concentration of protons in solution. A pH of 1 is the lowest number on the scale and therefor the most acidic measurement on the pH scale.
Why does acidic water react with alkalinity?
The acid molecules react with the alkalinity which results in the acid molecules being neutralized, therefor when adding acid to a solution with alkalinity, the pH stays constant until the alkalinity is consumed . This is the reason adding acidic water treatment chemicals consumes alkalinity.
What is the pH range of a solution?
It ranges from 1 to 14 with 7 considered neutral. The pH scale is logarithmic which means that every integer change results in a 10x higher acid or base concentration. Example; pH 6 is 10 times more acidic than pH 7 and pH 4 is 1,000 times more acidic than 7. Alkalinity – Alkalinity is the ability of a solution to resist pH changes ...
What are the factors that contribute to alkalinity?
Factors which contribute to alkalinity include the type of dissolved inorganic and organic compounds present in the water, the amount of suspended organic matter in the water, and the amount of bicarbonate in the water. Acid – An acid is anything that will donate a proton (a proton is the same thing as a hydrogen ion H+) in solution.
Why is pH 14 important?
A pH of 14 is the most basic measurement on the scale. Acids and bases are linked because when you combine them in equal amounts the H+ bonds with the OH- to create water H2O. Bases are used in water treatment to adjust the pH if the water becomes acidic.
Why is pH important in wastewater treatment?
As a chemical component of the wastewater, pH has direct influence on wastewater treatability — regardless of whether treatment is physical/chemical or biological. Because it is such a critical component of the makeup of the wastewater, it is therefore critically important to treatment.
Why is chemical selection important in controlling pH?
Why is chemical selection an important consideration in controlling pH? Different chemicals have varying reaction times, which in turn have a major effect on pH adjustment and control . Therefore, the equipment residence or contact time is very relevant in relation to the chemical used for treatment.
Can you control pH manually?
Rigorous precision of pH control is often required for treatment, and it seldom occurs by attempting to control pH manually. There are multiple interferences when attempting to control pH manually, so automation is recommended.
Does pH change after wastewater treatment?
Actually, pH virtually never changes immediately. The rate of change depends on chemical reaction times, which are directly associated with tank volume, the amount of mixing, and all other aspects of the treatment procedure. Often, the pH can change after wastewater leaves the treatment tank. In those instances, the reaction time exceeds residence ...
What is buffering pH?
Buffering refers to how the pH tends to remain stable once adjusted. Organisms such as AOB & Nitrite Oxidizing Bacteria (NOB) like a slightly alkaline pH while also consuming significant alkalinity (usually expressed as calcium carbonate). Additional alkalinity is required to buffer against organic acids, carbon dioxides (from respiration), ...
What acid is used to lower pH?
Now for pH adjustment - most systems use strong chemistry: To lower pH acids such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4) can be used. A newer technology is to use carbon dioxide to adjust pH without the chance to over shoot your target. The correct choice all stems from how much adjustment is required.
What is the pH range of bioaugmentation?
Biological wastewater treatment usually works best in a pH range from 7.0 - 8.0. Remember that this is the "best" range in a general sense. In making bioaugmentation products, we have used strains with pH ranges from 3.0 (Thiobacillus) to 11.0 (alkanophilic Bacillus). The most pH sensitive process tends to be ammonia removal or nitrification.
What pH does sodium bicarbonate have?
Sodium bicarbonate - soluble, tends to max out pH at 8.3 - so low overdosing potential. So remember that you have choices in adjusting pH and buffering the system. Alkalinity or buffering capacity is a key consideration in wastewater treatment especially if you require ammonia oxidation.
What is the pH of ammonia?
The most pH sensitive process tends to be ammonia removal or nitrification. Ammonia Oxidizing Bacteria (AOB) do best at a pH of 7.2 - 8.2 where the free ammonia (NH3-N) is present but is still soluble in water.
Does sodium hydroxide raise pH?
Raising pH is usually done using sodium hydroxide (caustic soda) (NaOH). As with sulfuric acid, sodium hydroxide immediately raises pH. It does not buffer the solution & buffering is a key concept that we need to consider in biological systems. Buffering refers to how the pH tends to remain stable once adjusted.
Why is pH important in wastewater treatment?
The pH is the controlled parameter because it has direct influence on wastewater treatability — regardless of whether treatment is physical/chemical or biological. Because it is such a critical measure of wastewater makeup , it is critically important to treatment.
How to control pH in wastewater?
In taking control of pH, first identify the constituents — the pollutants or impurities — that are actually in the wastewater. Once those pollutants are identified, determine the starting and the ending pH values, along with a specific treatment procedure. Then select the chemicals best suited to the prescribed treatment.
What is the advantage of batch system?
The advantage of a batch system is that no effluent is removed from the tank until the effluent meets the control-discharge criteria. Batch systems are far more suitable for smaller treatment volumes and effluents that may be characterized by large swings in influent pH, concentrated discharges or erratic flow rates.
Can pH be changed?
The pH cannot be changed instantly. The change rate depends on chemical reaction times, in turn associated with tank volume, the amount of mixing, and other treatment aspects. Often, the pH can change even after the wastewater leaves the treatment tank. In those instances, the reaction time exceeds residence or contact time.
What pH does biodegradation occur at?
Together these processes can neutralize the water so the biodegradation can occur at neutral pH.
Does biological treatment reduce TDS?
The biological treatment is not effective for reducing TDS or EC. The chemical addition for pH neutralization will also increase the TDS content of the wastewater. Therefore, you need to account such increase when evaluating TDS content of the treated water.
Can a well be used as a pH equilibration tank?
Because of the small volume of wastewater, a well can be used as the pH equilibration tank. For the conductivity reduction by sedimentation, flotation etc in the same well, you must know the composition of TDS. Alternatively, you can dilute the high conductivity treated water by mixing with irrigation water before use. Cite.