
Stem Cell Treatment for Cancer A stem cell transplant helps to restore the blood-forming cells in the patient. It happens that the stem cells are destroyed due to the high doses of chemotherapy or radiotherapy. Hence, in such cases, stem cell treatment contributes to regenerating the new blood cells.
What are stem cells and how do they treat cancer?
These cells help replace cells damaged by the cancer. They also let your body recover faster from intense chemotherapy and radiation treatments. For some, it may be the best -- or only -- approach. What Are Stem Cells?
Who can benefit from stem cell therapies?
People who might benefit from stem cell therapies include those with spinal cord injuries, type 1 diabetes, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, heart disease, stroke, burns, cancer and osteoarthritis.
What is the best way to use stem cells?
Corneal and skin grafts are the only other recognised stem cell-based medical treatments. Stem cells make cells that can then be transplanted to help a patient recover following severe burns or injury. How are stem cells used in research?
What are stem cells and how do they work?
Stem cells possess unique biological actions, including self-renewal, directional migration, differentiation, and modulatory effects on other cells, which can be utilized as regenerative medicine, therapeutic carriers, drug targeting, and generation of immune cells.
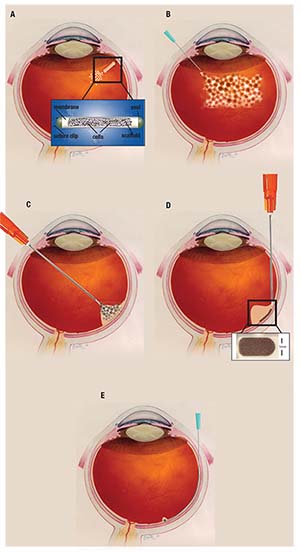
How could stem cells be used to treat cancer?
Stem cell transplants are used to replace bone marrow cells that have been destroyed by cancer or destroyed by the chemo and/or radiation used to treat the cancer. There are different kinds of stem cell transplants. They all use very high doses of chemo (sometimes along with radiation) to kill cancer cells.
How do stem cells prevent cancer?
The pluripotent stem cells can generate infinite (or unlimited) numbers of patient-specific immune cells, persuading the body's immune system to help fight cancer.
How are stem cells used in treatment?
In stem cell transplants, stem cells replace cells damaged by chemotherapy or disease or serve as a way for the donor's immune system to fight some types of cancer and blood-related diseases, such as leukemia, lymphoma, neuroblastoma and multiple myeloma. These transplants use adult stem cells or umbilical cord blood.
Can stem cell therapy be used for cancer?
Stem cell or bone marrow transplants are treatments for some types of cancer including leukaemia, lymphoma and myeloma. You have them with high dose chemotherapy and sometimes radiotherapy. They are sometimes called stem cell rescue, or bone marrow rescue, or intensive treatment.
How are stem cells administered?
How are stem cells administered? Stem cells can be administered in a variety of fashions; IV Stem Cell Therapy (Intravenous administration), Intrathecal (directly into the spinal canal), Site injections into problem areas (Knee, hips, hands, etc.)
Why cancer stem cells are resistant to chemotherapy?
Recent studies suggest that CSCs are enriched after chemotherapy because a small subpopulation of cells remaining in tumor tissue, so-called CSCs, can survive and expand though most chemotherapeutic agents kill bulk of tumors [12–14].
How might stem cells be used to treat patients in the future?
Decades of research has allowed us to glimpse the potential of stem cells to treat disease. It is possible they will give us life-changing therapies for multiple sclerosis, type 1 diabetes, Parkinson's disease and macular degeneration, amongst others.
Who Cannot donate stem cells?
Most diseases which may be defined as autoimmune disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, systemic lupus, chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia, will prevent you from donating marrow or blood-forming cells.
How do they do a stem cell transplant?
To prepare for a stem cell transplant, you receive chemotherapy to kill the diseased cells and malfunctioning bone marrow. Then, transplanted blood stem cells are put into your bloodstream. The transplanted stem cells find their way to your marrow, where — ideally — they begin producing new, healthy blood cells.
Where do cancer stem cells come from?
Cancer stem cells might be derived from tissue-specific stem cells and bone marrow stem cells. They might also be derived from somatic cells that undergo transdifferentiation processes. Furthermore, cancer stem cells might be initiated as a result of cell fusion or horizontal gene-transfer processes.
Does cancer have stem cells?
Cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a subpopulation of tumor cells that can drive tumor initiation and can cause relapses. At the time point of tumor initiation, CSCs originate from either differentiated cells or adult tissue resident stem cells.
Can stem cells turn into cancer?
What about the type of stem cells that more and more scientists are using instead of embryonic ones? Those are called induced pluripotent stem cells; they come from the cells of already-born people. Unfortunately, any such cells that grow in the lab long enough can accumulate cancer-causing mutations, Loring said.
Why are pluripotent stem cells important?
Stem cell research has long been respected as valuable for studies and treatment, but the use of pluripotent stems cells offers major advantages, without ethical issues or restrictions. Pluripotent stem cells reproduce quickly, can multiply over and over again indefinitely, and are resilient during the research process, making ongoing study, research, and, eventually, treatment promising. Cells can be reproduced from adult skin or blood cells or excised tumors and can be genetically reprogrammed to repair damaged tissues in the human body. Because these cells do not come from embryos, they don’t carry ethical issues or restrictions, providing scientists and researchers with increased opportunities for important research into immunotherapy and regenerative medicine.
What is the role of pluripotent stem cells in cancer?
“Immunotherapy is revolutionizing cancer care. Pluripotent cells share many features with cancer cells, and that can help researchers investigate and understand the development and changes in cells that are caused by the disease,” he says. The pluripotent stem cells can generate infinite (or unlimited) numbers of patient-specific immune cells, persuading the body's immune system to help fight cancer.
What is immunotherapy for cancer?
Immunotherapy uses certain parts of a person’s immune system as a treatment to fight diseases such as cancer. That’s what these new studies with iPSCs are hoping to prove. Headed by Dr. Ito, a team of researchers from Roswell Park, the University of Michigan and Kyoto University has recently demonstrated that human pluripotent stem cells can be ...
Why are T lymphocytes important?
This type of cell may play a major role in encouraging immunity response, and in fighting cancer because the T lymphocytes generated from pluripotent stem cells have been shown to be stronger in anti-tumor activity.
What is the name of the cell that can self-renew?
Yamanaka discovered a new way to turn adult, dividing cells into pluripotent stem cells. Pluripotent stem cells, often called master cells, have the ability to self-renew, or make copies of themselves, and multiply indefinitely. These cells are also able to reproduce cells from all three basic body layers, giving them the ability ...
Does Roswell Park use pluripotent stem cells?
"Roswell Park is one of the few academic institutions that has shown successful use of pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) for treatment in cancer immunotherapy,” says Fumito Ito, MD, PhD, and Assistant Professor of Oncology in the Department of Surgical Oncology at Roswell Park. Immunotherapy uses certain parts of a person’s immune system as a treatment to fight diseases such as cancer. That’s what these new studies with iPSCs are hoping to prove.
Does Roswell Park have T-cell therapy?
Since melanoma has been found to respond well to T-cell therapy, Roswell Park plans to target melanoma first in clinical trials, but trials for other cancers such as lymphoma, leukemia, sarcoma and ovarian cancer are scheduled to follow.
Why are stem cells important?
Some day, stem cells will be enlisted to help repair or replace damaged tissues and organs. They will rescue us from diseases for which drugs can only treat the symptoms. But they may have another role in our lives, one that is not so beneficial. They may in fact be the source of some, and possibly most cancers.
What do embryonic stem cells do?
Embryonic stem cells produce the progenitors and patterns that determine how our organs, muscles, sinews, and skeletons are formed and how they are arranged in the body. After their work is done, they leave behind a guardian population of stem cells that repair each tissue as the need arises.
What happens when a stem cell divides into two?
When the stem cell divides into two, it creates one progenitor and renews itself. The progenitor continues its path of differentiation into mature, specialized cells, while the new stem cell waits for the next round when it is called upon to replenish tissue. Stem cells survive much longer than ordinary cells, increasing the chance ...
What is the name of the cell that initiates melanomas?
A recent study completed by Markus Frank, Assistant Professor at Harvard Medical School, and Associate Faculty member of HSCI, identified a class of stem cells that initiate melanomas (skin cancer) in an animal model, and identified an antibody that slowed tumor growth by specifically targeting these stem cells.
What is the rationale for a new treatment strategy?
A rationale for a new treatment strategy is emerging that specifically targets the cancer stem cells, which may only be a very small percentage of the total tumor mass. In combination with current treatments, however, these new treatments may lead to a more complete and durable response.
Who discovered that tumors are linked to embryonal tissue growth?
Throughout the mid-19th century, theories and observations accumulated that tumors were linked to embryonal tissue growth, culminating in a comprehensive “embryonal rest” theory put forward by Julius Cohnheim in 1875.
Who discovered stem cells in breast cancer?
In 2003, Michael Clarke of the University of Michigan and now at Stanford, found cancer stem cells in breast tumors and demonstrated that most other cells in the tumor were incapable of seeding growth on their own. Others followed with similar discoveries in brain cancer, colon cancer, bone cancer and melanoma.
What happens when you get stem cells from a donor?
When you get stem cells from a donor or cord blood, there’s a risk of something called graft-versus.-host disease. It’s when your body fights to get rid of the new cells, or the cells launch an attack against you. It could happen right after the transplant or not until a year later.
Where do stem cells grow?
What Are Stem Cells? They grow inside your marrow, the soft tissue of your bones. They’re also in your blood, as well as blood from umbilical cords. As they mature, blood stem cells change into three types of cells your body needs: Platelets that help your blood clot.
How do you get thawed stem cells back?
After your treatment ends, your thawed stem cells are returned to your bloodstream through an IV. They’ll find their way back to your bone marrow. Once there, they can help your body make healthy blood cells again. In an allogeneic (ALLO) transplant, you get healthy stem cells from a donor.
What is the best treatment for cancer?
Stem Cell Treatments for Cancer. Medically Reviewed by Kumar Shital, DO on July 17, 2020. If you have leukemia or lymphoma, you may need a stem cell transplant. These cells help replace cells damaged by the cancer. They also let your body recover faster from intense chemotherapy and radiation treatments.
Do stem cells keep cancer alive?
Now, there’s reason to believe that special, fast-growing cancer stem cells keep your disease alive by reproducing. If that’s true, in the next few years, the focus of treatments could shift from trying to shrink tumors to trying to kill this type of cell. Pagination.
Can you get stem cells from someone you don't know?
You can also get stem cells from someone you don’t know. Before an ALLO transplant, you’ll get chemotherapy, radiation, or both. This wipes out your own stem cells and gets your body ready for the new ones soon after your treatment is done. If your doctor can’t find a donor,they may use cells from donated umbilical cord blood.
What are stem cells used for?
You may wonder what stem cells are, how they're being used to treat disease and injury , and why they're the subject of such vigorous debate.
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy, also known as regenerative medicine, promotes the repair response of diseased, dysfunctional or injured tissue using stem cells or their derivatives. It is the next chapter in organ transplantation and uses cells instead of donor organs, which are limited in supply.
What are the master cells of the body?
Stem cells are the body's master cells. All other cells arise from stem cells, including blood cells, nerve cells and others. Stem cells are the body's raw materials — cells from which all other cells with specialized functions are generated. Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called ...
Why are adult stem cells more likely to contain abnormalities?
Adult stem cells also are more likely to contain abnormalities due to environmental hazards, such as toxins, or from errors acquired by the cells during replication.
What are perinatal stem cells?
Perinatal stem cells. Researchers have discovered stem cells in amniotic fluid as well as umbilical cord blood. These stem cells also have the ability to change into specialized cells. Amniotic fluid fills the sac that surrounds and protects a developing fetus in the uterus.
What type of cells are used to test for drugs?
Test new drugs for safety and effectiveness. Before using investigational drugs in people, researchers can use some types of stem cells to test the drugs for safety and quality. This type of testing will most likely first have a direct impact on drug development first for cardiac toxicity testing.
What is the name of the cell that divides to form more cells?
Under the right conditions in the body or a laboratory, stem cells divide to form more cells called daughter cells. These daughter cells either become new stem cells (self-renewal) or become specialized cells (differentiation) with a more specific function, such as blood cells, brain cells, heart muscle cells or bone cells.

Stem Cells and Immunotherapy
Avoiding Ethical Issues
- Stem cell research has long been respected as valuable for studies and treatment, but the use of pluripotent stems cells offers major advantages, without ethical issues or restrictions. Pluripotent stem cells reproduce quickly, can multiply over and over again indefinitely, and are resilient during the research process, making ongoing study, research, and, eventually, treatment promising. Cell…
Stem Cell Research and Treatment
- Dr. Ito believes that pluripotent stem cell research results show much promise. “Immunotherapy is revolutionizing cancer care. Pluripotent cells share many features with cancer cells, and that can help researchers investigate and understand the development and changes in cells that are caused by the disease,” he says. The pluripotent stem cells can generate infinite (or unlimited) n…