What happens when ferric chloride is added to water?
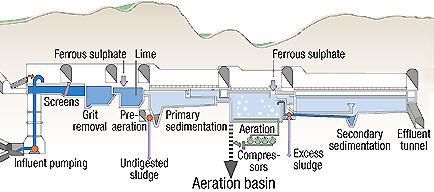
Ferric Chloride or Iron (III) Chloride (FeCl3) is used as a flocculant in sewage treatment and drinking water production. When small quantities of ferric chloride are added to the raw water, iron(III) hydroxide precipitates and adsorbs finely divided solids and colloids.
How does ferric chloride clean water?
As a flocculant, chemicals that help small particles in water clump together so they can be removed, Ferric Chloride is dissolved in solution, where it forms an aqueous brown tinted solution. The solution is used to clear water of particles.
What is ferric chloride solution used for?
It is used to treat sewage, industrial waste, to purify water, as an etching agent for engraving circuit boards, and in the manufacture of other chemicals. Ferric chloride, solution appears as a colorless to light brown aqueous solution that has a faint hydrochloric acid odor.
What is ferric sulfate used for in water treatment?
ALAR recommends Ferric Sulfate for pH adjustment, coagulation and dissolved heavy metal precipitation. Ferric Sulfate starts out as a dissolved solid, but falls out of solution and becomes a suspended solid at multiple pH levels for easy filtration.
Does ferric chloride dissolve in water?
WaterEthanolMethanolAcetoneDiethyl etherIron(III) chloride/Soluble in
Does alum remove smell from water?
Alum addition was effective in reducing odors in anaerobically digested biosolids. Addition of 4% alum to anaerobically digested liquid biosolids prior to dewatering resulted in a 60% reduction in the peak odor concentration in the laboratory dewatered cake, relative to the control sample.Dec 1, 2017
Why does ferric chloride stop bleeding?
In order to stop the bleeding during the injury ferric chloride is used because ions coagulate and they are negatively charged solutions and the ions coagulate since they are positively charged in nature.
What is the pH of ferric chloride?
1.8Ferric Chloride Properties (Theoretical)Compound FormulaCl3FeBoiling Point315° C (599° F)Density2.90 g/cm3Solubility in H2O480 g/l (20 °C)pH1.8 (6 g/l, 20 °C)5 more rows
Is ferric chloride toxic?
Ferric chloride can react with metals to form flammable and potentially explosive hydrogen gas. Carcinogenicity: None of the components of this material are listed as a carcinogen by IARC, NTP, OSHA, or ACGIH. Ingestion – Toxic by ingestion. May cause irritation to the mouth and stomach.
Where is ferric sulphate used?
It is a mechanic hemostatic agent used directly on the damaged tissue. In dentistry, ferric sulfate is used as a pulpotomy medicament to control pulpal bleeding, as an antibacterial agent and as a hemostatic reagent for restorative dentistry, for postextraction hemorrhage and for periradicular and endodontic surgery.Dec 3, 2015
What is the difference between ferrous sulphate and ferric sulphate?
Ferric and ferrous sulphate are sulphates of iron. The key difference between ferric and ferrous sulphate is that ferric sulphate has iron in the +2 oxidation state, whereas ferrous sulphate has iron in the +3 oxidation state.Nov 10, 2019
Is ferrous also known as iron?
Outside chemistry, "ferrous" means generally "containing iron". The word is derived from the Latin word ferrum ("iron"). Ferrous metals include steel and pig iron (with a carbon content of a few percent) and alloys of iron with other metals (such as stainless steel).
What is ferric chloride?
In the laboratory, ferric chloride is commonly used as a Lewis acid for catalyzing reactions, such as Friedel-Crafts reaction of aromatics and chlorination of aromatic compounds. Ferric chloride, also called iron chloride, is a chemical compound with a chemical formula of FeCl3. It has a relatively low melting point, ...
What percentage of ferric chloride is sold in municipal bids?
This is one of the few water treatment chemicals that can sequester odors. In the U.S., more than 80 percent of all ferric chloride is sold in municipal bids, with 65 percent sold for municipal wastewater applications, and 18 percent for potable water treatment applications. ADVERTISEMENT.
What is the best replacement for ferric chloride?
Both large and small plants will see cost savings; the more ATS 806 is used to replace ferric chloride, the larger the savings. It should be noted that both ATS 835 and 806 are potentially excellent replacements for alum or ferric chloride—it’s all dependent on the chemistry.
What is a good substitute for alum?
Proprietary products, instead of commodities, may offer a better solution. For example, a few products from ATS Innova’s ATS 800 line are excellent substitutes for alum and ferric chloride: ATS 835 is a great replacement for alum because it does an amazing job, but with a much, much smaller dose. For example, a water treater who feeds 25 parts ...
What is a coagulant in water treatment?
As every water treater knows, coagulants are used in the first step of water treatment; they destabilize the water so micro flocks can begin to form. This is followed up by a polymer, which turns it into a larger flock by creating a bigger charge. Alum and ferric chloride are two widely-used “commodity chemical” coagulants ...
Why is sludge not easy to de-water?
It produces a lot of sludge. Plus, the sludge it creates is not very easy to de-water because it becomes very gelatinous. For example, let’s say a small plant runs at a million gallons a day, feeding 25 parts of alum on a wet basis.
Is ATS 806 better than ferric chloride?
This product is not only a successful replacement but also offers a much better quality of water for the same dollars spent. ATS 806 removes much more total organic carbon than either alum or ferric chloride. And while it may be a bit more expensive than the ferric, the amount needed is roughly only 25% of the amount of ferric required, ...
Is ATS 835 soluble in water?
And because ATS 835 is completely soluble, it will hardly increase solids due to the coagulant. Alternatively, if a water treatment plant is using ferric chloride, a recommended replacement product is ATS 806.
Is ferric chloride a competitor for alum?
Some water treaters simply aren’t aware of alternative products. The companies that supply alum and ferric chloride aren’t advertising competing products, and the companies that do sell alternative products struggle to get the word out.
What is the best way to store ferric chloride?
For safe storage, we recommend a high-density crosslinked polyethylene tank. Ferric chloride is also a high fuming chemical. These fumes can potentially defoliate surrounding trees and plants. When storing Ferric Chloride in a chemical storage tank, a fume-tight manway lid cover prevents fumes from escaping the tank.
What is flocculant in water?
A flocculant is a substance that promotes the clumping of particles so that they may be removed from water. Flocculants are essential in proper water treatment. One particularly popular flocculant is Ferric Chloride.
Is ferric chloride a coagulant?
Ferric Chloride offers versatility in the water treatment industry, by working as a flocculant and coagulant, as well as a reactant. It promotes faster sedimentation in general and specifically, better sedimentation in cold water, making it an ideal choice for the industry.
Is ferric chloride a pure iron?
As one of the purest and most concentrated forms of iron commercially available for water treatment, Ferric Chloride has a unique distinction. In order to produce Ferric Chloride, Ferrous Chloride must be used. It is the oxidation of Ferrous Chloride with Chlorine that creates this new compound.
What is ferric chloride?
Ferric chloride is a configuration of iron that can be used for treating drinking water in the water treatment process. Ferric chloride can purify water of many different PH balances and can help remove any discoloration present in the water. Ferric chloride can also work to purify drinking water at a lower dose than comparable sulfate-based ...
What happens if you store ferric chloride?
If stored improperly, ferric chloride can cause a reaction known as defoliation, the process of leaf removal, to any plant matter within range. To help prevent this unfortunate side-effect, it is highly recommended that you purchase tank lids that are fume-tight.
What is a belding tank?
Belding Tank offers a wide range of features for you to choose from, such as the option of adding a U.V. inhibitor to the exterior resin layer, as well as the optional addition of a gel coat. These features can be beneficial if you are looking to store your tank outside. Belding Tank also offers plumbing solutions that can allow for lateral ...
Is ferric chloride safe to drink?
Ultimately, ferric chloride can be an effective and low-cost option for purifying drinking water. However, it is important to store ferric chloride securely and safely. Ferric chloride is what is known as a high fuming chemical.
Does ferric chloride purify water?
Ferric chloride can also work to purify drinking water at a lower dose than comparable sulfate-based coagulants. Interestingly, when used to purify drinking water, ferric chloride produces a by-product substance that has a very high iron content.
Can you use fibreglass in ferric chloride tanks?
Though fibreglass can be a potentially effective storage solution for your ferric chloride storage tanks needs, it is always important to take the proper precautions and use the correct protective measures when working with, or around, a chemical like ferric chloride. When looking for ferric sulfate storage tanks, consider Belding Tank.
What is a Coagulant for Water Treatment?
Ferric sulfate, aluminum sulfate, or ferric chloride, classed as aluminum or iron salts, are common coagulants for water treatment.
How Does Coagulation Treatment Work?
Coagulation treatment is usually carried out before sedimentation and filtration. During the process, a coagulant is added to water, and its positive charge neutralizes the negative charge of suspended contaminants.
What Is Removed During Coagulation?
Coagulation is most effective at removing suspended solids and natural organic matter like gravel, sand, algae, clay, iron, protozoa, and even bacteria. Many of these contaminants can give water an unpleasant taste when present in large quantities, and can also give water a brown or orange color.
What Are the Most Common Types of Coagulants?
The most commonly used chemical for coagulation is aluminum sulfate. Ferric sulfate, ferric chloride, or sodium aluminate are also popular types of coagulants.
How to Choose a Coagulant for Water Treatment
The type of coagulant used by your local water treatment facility will usually depend on availability and affordability. With aluminium sulfate being available, affordable and highly effective, it is the preferred choice for public water treatment around the world.
About the author
Brian Campbell is the founder of WaterFilterGuru.com, where he blogs about all things water quality. His passion for helping people get access to clean, safe water flows through the expert industry coverage he provides. Follow him on twitter @WF_Guru or contact him by email [email protected]
What is ferrous chloride used for?
Mainly used for water treatment . Its quality is steady. Its inexpensive, It's the best, most suitable economy industrial waste water treatment on the market at present. As proven in hundreds of plants in the US and Canada. As it pertains to odor Control Problems, Ferrous Chloride reduces H2S odors to a harmless iron compound, controlling odors and lessening corrosion. With General Plant Operation Problems, improving the removal of solids and heavy metals and augment the efficiency of digesters with the addition Ferrous Chloride. FeCl2 greatly enhances the fertilizer value of wastewater sludge.
What is a nuiron?
NuIron is a custom blend of metal salts designed especially for each customer’s specific needs and specifications. Ferrous chloride is the base product for most of our blends. This can be neutralized and blended to provide a specific solution for each individual customer’s process. NuIron is traditionally blended to a pH of <2. The product can be blended to a non-hazardous pH of 2-10 reducing the cost of hauling a hazardous material. NuIron offers customers effective solutions for the following needs: Odor control our blend is an improvement over traditional ferrous chloride with an added advantage of less free acid. Ph adjustable allows for reduced alkalinity demands on the plant providing a potential cost saving on additional chemicals. Phosphorus Removal accelerated removal rate depending on the blend of product. Non-hazardous available in a custom blended form for those clients unwilling or unable to handle a hazardous product. Corrosion Control, improved over traditional ferrous chloride’s lower Ph.
Inorganic coagulants
Inorganic compounds do not have carbon elements in their molecular structure. As such, they are considered to be “artificial” or unnatural. However, just because a coagulant is inorganic does not mean it is environmentally unfriendly, provided it is handled correctly. This also applies to organic coagulants, which are not necessarily eco-friendly.
Organic coagulants
As well as the inorganic coagulant compounds listed above, there are a number of different organic coagulants available on the market. These include substances such as polymers, amines, and acrylamides, all of which can be used to achieve effective coagulation at your facility.
Disadvantages to Ferric Chloride
As with any chemical, there are advantages and disadvantages. Here are some other disadvantages to using ferric chloride:
Ferric Chloride Advantages
Even with the disadvantages, ferric chloride still has its place as a wastewater treatment chemical with approximately 60% usage in wastewater facilities. Its application in industrial water makes up about 8% and 20% in drinking water treatment, as well.
The Key is Balance
Up until now, we’ve been discussing the problems with using the wrong chemicals in the wrong place but haven’t touched on the real problem: chemicals in general. It’s not enough to just throw in a bunch of chemicals and hope they treat sewage and drinking water.