How are radioisotopes used for treatment? Radioisotope therapy is a procedure in which a liquid form of radiation is administered internally through infusion or injection. RIT’s ultimate purpose is to treat cancerous cells with minimal damage to the normal surrounding tissue.
What is radioisotope therapy used to treat?
Radioisotope therapy, also known as targeted radionuclide therapy, uses a radioactive drug that seeks out and destroys cancer cells while minimizing damage to neighboring healthy cells. Lutathera ® is a radioisotope therapy that is targeted for cancers affecting the neuroendocrine cells of the pancreas and gastrointestinal tract. The FDA approved Lutathera in January 2018.
How do radioisotopes kill cancer cells?
Radioisotope therapy is a procedure in which a liquid form of radiation is administered internally through infusion or injection. RIT's ultimate purpose is to treat cancerous cells with minimal damage to the normal surrounding tissue. These therapies are not normally the first approach used to fight a patient's cancer.
What types of radiation are used to kill cancer cells?
Mar 27, 2022 · Radioisotope therapy is a procedure in which a liquid form of radiation is administered internally through infusion or injection. RIT’s ultimate purpose is to treat cancerous cells with minimal damage to the normal surrounding tissue. These therapies are not normally the first approach used to fight a patient’s cancer.
What is the most common radioisotope used in nuclear medicine?
RADIOISOTOPES IN THE TREATMENT OF CANCER In the treatment of cancer, radiation can be administered to the malignant tissues in several dif ferent ways: for example, needles of radium or cobalt-60 can be implanted directly into the tumor, or (in a rather limited number of cases) a radioisotope in liquid form (e.g. gold-198) can be injected, know

Which radioisotopes is used in the radiation treatment of cancer?
Radioactive iodine (Iodine-131) has been used to treat thyroid cancer for almost 80 years. This is done to treat some patients after thyroidectomy to destroy any remaining cancer cells and prevent the thyroid cancer returning. It is also used to treat patients with metastatic thyroid cancer.
How are radioactive isotopes used in treatment?
Radioisotope therapy uses radioisotopes to destroy cancer cells. Radioisotope therapy can be used to treat several different kinds of cancer, including thyroid cancer, bile duct cancer, liver cancer, bone metastases, and neuroblastoma.
Where are radioactive isotopes used?
The most widely used radioactive pharmaceutical for diagnostic studies in nuclear medicine. Different chemical forms are used for brain, bone, liver, spleen and kidney imaging and also for blood flow studies. Used to locate leaks in industrial pipe lines…and in oil well studies.
What are some radioisotopes used in medicine?
Specific Diagnostic Applications of Radioisotopes The most common radioisotopes used in the medical industry are Technetium-99m, Iodine-131, and Molybdenum-99. 85% of all nuclear medical examinations use Mo/Tc generators for diagnosing problems with the liver, bones, or lungs [6].Jun 14, 2021
What is radioisotope therapy?
Radioisotope therapy is a procedure in which a liquid form of radiation is administered internally through infusion or injection. RIT's ultimate purpose is to treat cancerous cells with minimal damage to the normal surrounding tissue. These therapies are not normally the first approach used to fight a patient's cancer.
What are the side effects of radioisotope therapy?
The most common side effect from radioisotope therapy is a feeling of tiredness for a few weeks. Radioisotope therapy can treat a wide variety of cancers, including bone metastases, brain cancer, thyroid cancer, bile duct cancer, liver cancer, and neuroblastoma.
How long does radiation last after a radiotherapy injection?
These injections or infusions can often be followed by a short period of radiation application, normally around one week. While the amount of radiation in a patient's body following radioisotope therapy will be higher than normal, those levels will recede with time, usually no more than a few days.
Can radioisotopes be used after other therapies?
Instead, they are more likely to be used after other therapies . Initial radioisotope therapy is relatively brief, as many forms of the therapy are administered via a series of injections or single infusions.
Is radioisotope therapy a cancer treatment?
Radioisotope therapy can also be useful as an adjuvant, or assisting, therapy when combined with other forms of cancer therapy.
How is radiation used to treat cancer?
However, by far the most important therapeutic technique is teletherapy (or beam therapy) in which the source of radiation remains outside the body and the beam of radiation is directed at the tumor through the overlying tissue. The source of radiation may be an X-ray tube, a "supervoltage" machine such as a betatron or a linear accelerator, or a radioisotope which emits high energy gamma-rays. The two isotopes commonly used for this purpose are cobalt-60 and cesium-137.
What is the most important item of dosimetric data?
One of the most important items of dosimetric data is the isodose chart , a kind of contour map which shows how the dose of radiation varies from point to point under stated conditions. Hundreds of such charts have been measured or computed in advanced radiotherapy institutes, but the task is beyond the capacity of the majority of centers. Obviously there is a need for this kind of material to be collected, systematiz ed, catalogued and redistributed on a world wide scale. The problem was examined in detail by an international panel of experts which met in Vienna in November 1960. Prior to this meeting a standard questionnaire was sent (through the co-operation of several national associations of medical physicists) to a large number of radiotherapy centers in many countries. Not only the answers to the questionnaire, but examples of isodose charts from different centers were brought to the Vienna meeting by the participants. The recommendations of the panel have recently been published by the Agency under the title "Therapeutic Dose Distributions with High Energy Radiation". It was suggested that the Agency should publish atlases of isodose charts under 3 main divisions, viz: single fields, multiple fields and moving beams. The preparation of these publications is now well advanced, material having been collected from all over the world, and they should be available in 1962. Associated with the atlases there is to be an "international Catalogue of Single Field Isodose Charts" and provisional copies of this have already been sent out, for comment and correction, to the contributing radiotherapy centers.
What are the problems with teletherapy?
Dosimetry is only one of many problems in teletherapy. There are many other questions of a more general nature, including those of organization, staff (medical, physical and auxiliary), training, the selection of suitable equipment and radiation protection. These were some of the problems considered by an international Study Group on the "Use of Radioisotope Teletherapy Units and Supervoltage Radiation in Radiotherapy" which met in Vienna in August 1959. It was convened jointly by the Agency and the World Health Organization. The report of this group, which was published in 1960, not only reviewed the existing situation but provided a practical guide both for practising radiotherapists and radiation physicists and for those considering the establishment of radiotherapy centers. The recommendations of this group have been widely reported and acted upon. Indeed, much of the subsequent activity of the Agency in the dosimetric field, already detailed in this article, stemmed from suggestions made by the 1959 group. According to present plans, the work of this group is to be followed up and extended, with special reference to the needs of the less developed countries, by a Study Group which is to meet in the autumn of 1962.
What is radioisotopes used for in medicine?
(Updated April 2021) Nuclear medicine uses radiation to provide diagnostic information about the functioning of a person's specific organs, or to treat them. Diagnostic procedures using radioisotopes are now routine.
Why are radioisotopes important?
In combination with imaging devices which register the gamma rays emitted from within, they can study the dynamic processes taking place in various parts of the body.
How many people use radioisotopes in a year?
There is widespread awareness of the use of radiation and radioisotopes in medicine, particularly for diagnosis (identification) and therapy (treatment) of various medical conditions. In developed countries (a quarter of the world population) about one person in 50 uses diagnostic nuclear medicine each year, and the frequency ...
What is short range radiotherapy?
This is radionuclide therapy (RNT) or radiotherapy. Short-range radiotherapy is known as brachytherapy , and this is becoming the main means of treatment. Although radiotherapy is less common than diagnostic use of radioactive material in medicine, it is nevertheless widespread, important, and growing.
How many hospitals use radioactive tracer?
Five Nobel Laureates have been closely involved with the use of radioactive tracers in medicine. Over 10,000 hospitals worldwide use radioisotopes in medicine, and about 90% of the procedures are for diagnosis.
How many nuclear procedures are performed annually?
Over 40 million nuclear medicine procedures are performed each year, and demand for radioisotopes is increasing at up to 5% annually. Sterilization of medical equipment is also an important use of radioisotopes.
What is the most common radioisotope used in nuclear medicine?
The most common radioisotope used in diagnosis is technetium-99 (Tc-99), with some 40 million procedures per year, accounting for about 80% of all nuclear medicine procedures and 85% of diagnostic scans in nuclear medicine worldwide. In developed countries (about one-quarter of world population) the frequency of diagnostic nuclear medicine is 1.9% ...
What radioisotopes are used for pain?
For example, Strontium-89 (Metastron) and samarium-153 (Quadramet) are beta-emitters that are taken up like calcium into bone and were approved to decrease pain.
What are the two types of radiation used to kill cancer cells?
The two main categories of radiation particles used to kill cancer cells are alpha and beta particles. Several radioisotopes – using both alpha and beta particles — have been approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for clinical use in cancer treatment.
What is the best way to kill cancer cells?
Using Alpha and Beta Radioisotopes to Kill Cancer Cells. Radionuclides, also known as radioisotopes, are particles that emit energy. The different particles they emit vary and some types emit damaging radiation (also called ionizing particles). This is a good thing when we’re using radiation as a way to kill cancer cells.
What is radioligand therapy?
Radioimmunotherapy or radioligand therapy involves the practice of attaching a radioactive isotope to a cancer-targeting antibody or small molecule that binds only to a specific cancer-related molecule on a tumor cell. This is similar to a “lock and key” scenario, where the antibody or molecule resembles the key that will only recognize ...
What is the lock on prostate cancer cells?
As it turns out, essentially all prostate cancer cells have a specific “lock” called prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA). This lock sits on the surface of each prostate cancer cell. We have engineered very specific monoclonal antibodies and molecules that will bind only to PSMA, leading to the opportunity for “molecularly targeted” ...
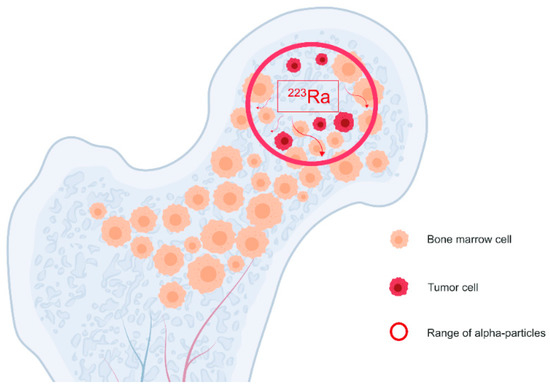
Is Radium 223 FDA approved?
However, unlike the previous beta-emitting agents, radium-223 was FDA-approved because it leads to longer overall survival rather than just symptom relief. Radium-223 is an alpha particle that mimics calcium and is delivered and taken up by the bone cells. This generally occurs near tumor cells, and while we don’t know the exact mechanism ...
How does radioisotope therapy work?
Radioisotope therapy. Radioisotope therapy uses radioactive liquid (known as radioisotopes or radionuclides) to destroy cancer cells. The liquid can be given: by mouth as a drink or capsules. as an injection into a vein. Cancer cells take in the radioisotope more than normal cells do.
What radioisotopes are used to treat metastatic bone cancer?
Strontium-89 and Samarium-153. These radioisotopes can be used to treat some types of cancer that have spread to the bones ( metastatic bone cancer ). This treatment can help reduce bone pain and improve quality of life. You can usually go home soon after having this treatment.
What is brachytherapy?
Brachytherapy. Brachytherapy uses radioactive implants such as seeds, pellets, wires or plates that are put near or inside the tumour. The radioactivity only affects tissue that is very close to the implant. This means the tumour is treated, but healthy areas around it get much less radiotherapy. Areas of the body that are further away are not ...
What is SIRT in cancer?
Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) is a type of internal radiotherapy that uses radioactive beads. It is used to treat some types of liver cancer. For example, it may be used to treat cancer that spreads to the liver from the bowel. SIRT is not widely available and is not always funded by the NHS.
What is brachytherapy for prostate?
This may also involve external beam radiotherapy or other treatments such as chemotherapy , hormonal therapy or targeted therapy. Brachytherapy is mainly used to treat cancers in the prostate , cervix and womb.
What is internal radiation therapy?
Internal radiotherapy is treatment with a radioactive material that is put inside the body to treat cancer. There are different types of internal radiotherapy. We have information about the following types: selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT).
What is the treatment for cancer?
Internal radiotherapy . Internal radiotherapy is treatment with a radioactive material that is put inside the body to treat cancer.