
- Clot-busting drugs, such as tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) to dissolve coronary artery clots.
- Anticlotting medicines – such as aspirin, clopidogrel or heparin – to prevent new clots.
- Drugs to increase the heart's pumping ability, such as dobutamine, dopamine and norepinephrine.
Medication
- Coronary artery bypass surgery. This surgery uses a healthy blood vessel in your leg, arm or chest to create a new pathway for blood so it can flow around a ...
- Surgery to repair an injury to your heart. ...
- Ventricular assist device (VAD). ...
- Heart transplant. ...
Procedures
These can include:
- Blood pressure: Cardiogenic shock usually causes low blood pressure.
- Cardiac catheterization: A long, thin tube called a catheter is inserted in an artery through a small incision, usually near your groin or wrist. ...
- Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG): A recording of your heart’s electrical activity.
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound of your heart.
Self-care
Cardiogenic shock is the leading cause of death after acute myocardial infarction (MI). In the absence of aggressive highly experienced technical care, mortality rates among patients with cardiogenic shock are exceedingly high (up to 70–90%).
Nutrition
Symptoms:
- Heart rate:
- In cardiogenic shock heart rate can either be increased or decreased.
- In hypovolemic shock heart rate is always increased owing to the fact that body tries to compensate for the low fluid volume.
- Jugular venous pressure:
- In cardiogenic shock, jugular venous pressure in neck is high.
- In hypovolemic shock, jugular venous pressure is low.
How does one prevent cardiogenic shock?
What do you need to know about cardiogenic shock?
What are the mortality rates for cardiogenic shock?
How to recognize cardiogenic shock?
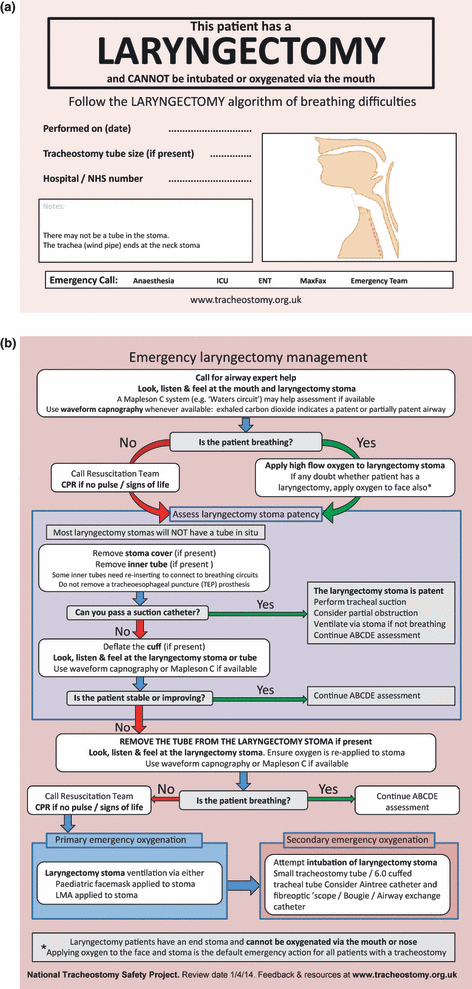
What is the treatment of cardiogenic shock?
Medications to treat cardiogenic shock are given to increase your heart's pumping ability and reduce the risk of blood clots. Vasopressors. These medications are used to treat low blood pressure. They include dopamine, epinephrine (Adrenaline, Auvi-Q), norepinephrine (Levophed) and others.
What is the treatment priority for cardiogenic shock?
The appropriate nursing interventions for a patient with cardiogenic shock includes: Prevent recurrence. Identifying at-risk patients early, promoting adequate oxygenation of the heart muscle, and decreasing cardiac workload can prevent cardiogenic shock.
What treatment should be used cautiously in patients with cardiogenic shock?
Aspirin should be given to symptomatic patients. Beta blockers should be used cautiously in the acute setting because they may increase the risk of cardiogenic shock and death.
What are the treatment of shock?
Lay the Person Down, if Possible. Elevate the person's feet about 12 inches unless head, neck, or back is injured or you suspect broken hip or leg bones. ... Begin CPR, if Necessary. If the person is not breathing or breathing seems dangerously weak: ... Treat Obvious Injuries.Keep Person Warm and Comfortable. ... Follow Up.
What are the nursing management of shock?
Monitor daily weight for sudden decreases, especially in the presence of decreasing urine output or active fluid loss. Monitor vital signs. Monitor vital signs of patients with deficient fluid volume every 15 minutes to 1 hour for the unstable patient, and every 4 hours for the stable patient. Oxygen administration.
What is cardiogenic shock nursing?
By Paul Martin, BSN, R.N. Cardiogenic shock is a condition caused by the inability of the heart to pump blood sufficiently to meet the metabolic needs of the body due to the impaired contractility of the heart. Clients usually manifest signs of low cardiac output, with adequate intravascular volume.
Which drug is most commonly used to treat cardiogenic shock?
Medication Summary Sympathomimetic amines with both alpha- and beta-adrenergic effects are indicated for persons with cardiogenic shock. Dopamine and dobutamine are the drugs of choice to improve cardiac contractility, with dopamine the preferred agent in patients with hypotension.
Why is dobutamine used for cardiogenic shock?
In patients with cardiogenic shock due to decompensated heart failure, dobutamine decreases left ventricular end-diastolic pressure and raises blood pressure by increasing cardiac output.
Which vasopressor is the drug of choice for cardiogenic shock?
A recent RCT and a meta-analysis on individual data suggested that norepinephrine may be preferred over epinephrine in patients with cardiogenic shock . For inotrope agents, when norepinephrine fails to restore perfusion, dobutamine represents the first-line agent.
What is the management of hypovolemic shock?
Three goals exist in the emergency department treatment of the patient with hypovolemic shock as follows: (1) maximize oxygen delivery - completed by ensuring adequacy of ventilation, increasing oxygen saturation of the blood, and restoring blood flow, (2) control further blood loss, and (3) fluid resuscitation.
Is cardiogenic shock obstructive shock?
Obstructive shock is similar to cardiogenic shock in that the impaired heart function is the primary abnormality. In cardiogenic shock, the contractility is impaired; but in obstructive shock, the heart is prevented from contracting appropriately.
What is the immediate treatment for victim in hypovolemic shock?
How is hypovolemic shock treated? Once at a hospital, a person suspected of having hypovolemic shock will receive fluids or blood products via an intravenous (IV) line, to replenish the blood loss and improve circulation.
Emergency and short-term treatments
Emergency treatments may include delivering enriched oxygen via a tube or mask; breathing assistance, using a ventilator; and intravenous (IV) fluids and medications to support blood pressure or heart function.
Longer-term treatments
Once doctors have determined the cause of a patient's cardiogenic shock, they may recommend various procedures or devices to address the underlying problem.
What is cardiogenic shock?
Cardiogenic shock is an emergency involving acute hemodynamic instability that necessitates immediate resuscitative therapy before shock irreversibly damages vital organs. The key to a good outcome in patients with cardiogenic shock is an organized approach, with rapid diagnosis and prompt initiation of pharmacologic therapy to maintain blood ...
What does 5 mg/kg/min do to your heart?
A dosage of less than 5 mcg/kg/min causes vasodilation of renal, mesenteric, and coronary beds. At a dosage of 5-10 mcg/kg/min, beta1-adrenergic effects induce an increase in cardiac contractility and heart rate.
What are the complications of a left ventricular distention?
However, complications can include left ventricular distention and pulmonary edema, distal limb ischemia, hemorrhage, and thromboembolism, [ 28, 29] as well as hemolysis, infection, acute kidney injury, and upper body hypoxia.
Is IABP a definitive therapy?
However, an IABP is not definitive therapy; the IABP stabili zes patients so that definitive diagnostic and therapeutic interventions can be performed. [ 40, 41] The IABP also may be a useful adjunct to thrombolysis in acute MI for initial stabilization and transfer of patients to a tertiary care facility.
Is a pulmonary artery catheter necessary for cardiogenic shock?
Although not necessary for the diagnosis of cardiogenic shock, invasive monitoring with a pulmonary artery catheter may be helpful in guiding fluid resuscitation in situations in which left ventricular (LV) preload is difficult to determine.
Is revascularization a CABG?
An early revascularization strategy with either PCI or CABG, in collaboration between cardiologists and surgeons, is recommended for appropriate patients with suspected cardiogenic shock related to acute coronary syndrome (eg, those with uncertain neurologic status, those who received previous fibrinolysis), regardless of the time delay from MI onset. [ 1, 24] Radial arterial access is preferred for angiography and PCI, when feasible. When it is not possible to promptly complete an early invasive approach, consider fibrinolysis in STEMI-associated cardiogenic shock. [ 1, 24]
What are the best medications for cardiogenic shock?
There is an array of medications that may be given to treat cardiogenic shock. These vary depending upon the cause of the shock and may include: 1 Thrombolytic drugs to dissolve coronary artery clots ("clot-busting" drugs such as tPA) 2 Anticlotting agents to prevent new clots (e.g., aspirin, clopidogrel, heparin) 3 Drugs to increase the heart's pumping ability (e.g., dobutamine, dopamine, epinephrine) 4 Other possible therapies include: oxygen to protect heart tissue; nitroglycerin to widen coronary vessels; drugs to decrease the heart's workload and pain, relieve anxiety or regulate heart rhythm
What is cardiogenic shock?
The goal of cardiogenic shock treatment is to quickly restore blood pressure and heart function. This often requires a series of emergency treatments that are given in an ambulance or the Emergency Department. Other treatments may include medications or temporary support devices to restore blood flow.
What is the pump used for in the heart?
Intra-aortic balloon pump is placed in the aortic artery (the main artery of your heart) and provides an extra push to help move blood coming out of your heart. Other short term devices that are used to treat cardiogenic shock include: Impella, Tandem heart and extra corporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
What is the procedure to restore heart rhythm?
In some cases, a stent (small mesh tube) is inserted to keep the artery open. One of the following procedures may be used to restore normal heart rhythm: Cardioversion is like a quick “reset” of the heart and is very effective for getting the heart back to its normal rhythm.
What are some drugs that help the heart pump?
Drugs to increase the heart's pumping ability (e.g., dobutamine, dopamine, epinephrine ) Other possible therapies include: oxygen to protect heart tissue; nitroglycerin to widen coronary vessels; drugs to decrease the heart's workload and pain, relieve anxiety or regulate heart rhythm.
What is a 3 wire pacemaker?
Sometimes a special 3-wire pacemaker system is used to re-coordinate a heart that is beating in an uncoordinated way. A new type of extra small pacemaker is being studied, which does not have any wires but instead is a small metal capsule that is implanted inside the heart itself.
Treatment
Management
Clinical significance
Prevention
Specialist to consult
Uses
- Cardiogenic shock is an emergency necessitating immediate resuscitative therapy before shock irreversibly damages vital organs. The key to a good outcome in patients with cardiogenic shock is an organized approach, with rapid diagnosis and prompt initiation of pharmacologic therapy to maintain blood pressure and cardiac output and respiratory suppo...
Diagnosis
- Early and definitive restoration of coronary blood flow is the most important intervention for achieving an improved survival rate. At present, it represents standard therapy for patients with cardiogenic shock due to myocardial ischemia.
Emergency Medical Treatment
- Correction of electrolyte and acid-base abnormalities, such as hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, and acidosis, is essential in cardiogenic shock.
Medications
- Cardiogenic shock may be prevented with early revascularization in patients with myocardial infarction (MI) and with required intervention in patients with structural heart disease.
Temporary Support Devices
- Placement of a central line may facilitate volume resuscitation, provide vascular access for multiple infusions, and allow invasive monitoring of central venous pressure. Central venous pressure may also be used to guide fluid resuscitation.
Procedures, Devices & Surgery
- Although not necessary for the diagnosis of cardiogenic shock, invasive monitoring with a pulmonary artery catheter may be helpful in guiding fluid resuscitation in situations in which left ventricular (LV) preload is difficult to determine.