
Different types of activated carbon are suited for various specialized applications
- Granulated activated carbon dechlorinates water, adsorbs organic material and produces a chemical-reducing environment
- Granulated activated carbon impregnated with silver salts inhibits the growth of bacteria
- Catalytic activated carbon removes chloramines from drinking water
What will happen if activated carbon mixed with water?
How does the filter with Activated Carbon work? The effectiveness of activated carbon for water filtration is mostly due to its large surface area. Physical absorption serves as the prime method for filtering out any constituent from a given substance with the use of activated carbon. Apart from physical adsorption, activated carbon can also be used for the facilitation of chemical …
How effective is activated carbon for water purification?
Apr 15, 2016 · In general, access to the surface area improves with decreasing carbon particle size, thereby increasing the adsorption rate. Activated carbon is used by water treatment facilities to help improve water quality. Many home water treatment devices also employ activated carbon, especially to help reduce water odor and taste. Activated carbon can be prepared from many …
Does Activated Carbon Clear aquarium water?
Jun 11, 2020 · To summarize, Activated carbon is highly porous charcoal that removes impurities via adsorption. It can be formed by using a thermal or chemical method. It is used in water purification in the form of Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) or …
What is activated carbon and how is it made?
However, any organic material with a high carbon content can effectively be used to create activated carbons through physical modification and thermal decomposition. The most prevalent uses of activated carbon in today’s world revolve around the treatment of process water, industrial and commercial wastewater and air/odour abatement issues.

Why is activated carbon used in water treatment?
Activated carbon is used by water treatment facilities to help improve water quality. Many home water treatment devices also employ activated carbon, especially to help reduce water odor and taste. Activated carbon can be prepared from many common substances that are high in carbon, and bituminous coal is a typical starting point.
What is activated carbon after disinfection?
In conclusion, adsorption with activated carbon is an efficient and useful technology —one of several in the water treatment toolbox that can be applied to help provide the best quality drinking water possible.
How much surface area is activated carbon?
One gram (or about ½ teaspoon) of activated carbon contains about 5,400 square feet of surface area! That’s roughly twice the area of the average American home (see National Association of Home Builders website ).
What happens when a substance is absorbed?
1 When a substance is absorbed, on the other hand, it fills the empty spaces inside a solid (imagine a completely saturated sponge).
What is the second heating process?
The second heating process creates a pore structure that “activates” the carbon by greatly increasing the surface area of the carbon. A great environmental and economic advantage of activated carbon is that it is recyclable following a thermal treatment to drive off adsorbed compounds. That process is called reactivation.
What is activated carbon?
Activated carbon is essentially charcoal. It is full of pores that are ready to absorb a wide variety of impurities. However, absorb may not exactly be the right word. The actual process is adsorption. The basic working mechanism is that the impurities simply attach to the surface of the activated carbon. Charcoal has a highly porous surface area ...
How does activated carbon remove impurities?
All of these largely have to do with physical adsorption. Another way an activated carbon can remove impurities is through a chemical reaction. This reaction is most commonly seen during chlorine filtration. During this process, the incoming chlorine simply reacts with the carbon to form chloride ions.
What is the process of making charcoal?
Chemical Method. In the chemical method, the charcoal is made to react with certain chemicals before carbonization. Carbonization is the process where carbon is heated in the absence of air. The chemicals used are typically high-strength acids, bases, or salt. The end result is a solid and porous activated carbon.
How does charcoal work?
The basic working mechanism is that the impurities simply attach to the surface of the activated carbon. Charcoal has a highly porous surface area that makes it perfectly suited for purification. In fact, one gram of activated carbon can boast of a surface area of nearly 3000 square meters. This charcoal can be collected from sources ...
What is the condition of activated carbon?
This condition is crucial as the impurities will need to be trapped and accumulated inside these pores. All of these largely have to do with physical adsorption.
Why is adsorption important?
The adsorption process is aided by the fact that all molecules have an attractive property. This property helps the materials adhere to the carbon more readily. The carbon surface also carries a stronger attractive force than that of the impure water. Usually, organic impurities are more easily absorbed.
How to turn charcoal into carbon?
Thermal Method. This method utilizes steam to turn charcoal into activated carbon. It also requires an inert atmosphere, which is created by using gases like carbon dioxide, argon, or nitrogen. This process includes reducing the moisture present in charcoal.
Why are activated carbons used in water treatment?
Powdered Activated Carbons are used by water treatment plants for taste and odour control and to ensure the removal of organic chemicals. PACs are added early in the treatment process to enable a period of sole contact time before other treatment chemicals are added to the water stream.
What is activated carbon?
Activated carbon is normally utilised to treat process water in two very different processes – powdered activated carbons and granular activated carbons. However, the dosage methods and use cases for each of these forms of activated carbons vary quite considerably. The selection of a specific type of activated carbons for water treatment will depend on the nature of the specific application, the result required and any process restrictions in place.
Why is activated carbon important?
Why activated carbon plays a critical role in water treatment. The versatility of activated carbon is endless, with over 1,000 known applications in use. From gold-mining to water purification, the production of food materials and more, activated carbon can be customised to meet a vast array of specific needs.
How effective is activated carbon?
During regular operation of any device, channels form within the carbon filter, allowing some water to bypass the filtering material, short-circuiting treatment. Since treatment depends on the carbon granules adsorbing the chemical contaminants, these channels decrease the contact time and the effectiveness of the carbon filter unit. A disadvantage of block carbon is that if it is unevenly compressed when manufactured, irregular flow patterns may affect the effectiveness of contaminant removal.
What is activated carbon filter?
Generally, an activated carbon filter is used with a pre-treatment filter to remove sediment or iron particles that may be present and can clog the carbon filter. Granular activated carbon (GAC) treatment is most common for private water systems. Granular activated carbon is an effective filter for removing organic chemicals ...
How to determine how much carbon a filter can adsorb?
There are two main procedures to determine how much a carbon filter can adsorb: the iodine test and the phenol test. The iodine number is defined as the amount of iodine (in milligrams) adsorbed by one gram of carbon under a certain set of conditions. The larger the number, the more the carbon filter can adsorb.
What is a treated water line?
is installed beneath the kitchen sink in the cold water supply line to treat water for drinking or cooking. If both hot and cold water come from a single faucet, the treated (cold) water can mix with the untreated (hot) water. Treated water is assured only when using cold water for drinking and cooking.
Can synthetic resin be used as a substitute for carbon?
These devices also clog easily if the water is cloudy or turbid. A synthetic resin may be a substitute for carbon. Although activated carbon is efficient in removing a variety of organic chemicals, a specially formulated synthetic resin may be a better absorber for a specific contaminant.
Do activated carbon filters need to be changed?
Most activated carbon filter units need to have the carbon changed periodically. For small specialty units, the entire unit is normally replaced. Cartridge filters are the easiest to change. Before purchasing a unit, consider the ease of opening the filter housing and the amount of space required to change the filter.
How does activated carbon work?
How it Works. Activated carbon water treatment is basically used for two water treatment purposes and each work in totally different ways. 1. Chlorine Removal: Activated carbon may be used to remove chlorine with little degradation or damage to the carbon. Dechlorination occurs rapidly and flow rates are typically high.
What is carbon activated by steam?
Carbon activated by steam generally has a fine pore structure, ideal for adsorbing both liquid phase and vapor phase compounds. Chemical Activation – With chemical activation the carbon is first filled with a powerful dehydrating agent, typically a paste form of phosphoric acid (P 2 O 5) or zinc chloride (ZnCl 2 ).
What are the physical properties of an AC filter?
Physical Properties: Pore size and distribution have the greatest impact on the effectiveness of AC filtration. The best filtration occurs when carbon pores are barely large enough to allow for the adsorption of contaminants (Figure 1). The type of contaminants an AC filter attracts will depend on the pore size of the filter, which varies based on the type of carbon used and the activation method. AC filters tend to work best for removing organic chemicals with larger molecules.
Why do you need to replace an activated carbon filter?
Ultimately, the activated carbon filter will need to be replaced as its ability to dechlorinate the water will slowly decline.
What is activated carbon filter?
Activated carbon filters are generally employed in the process of removing organic compounds and/or extracting free chlorine from water, thereby making the water suitable for discharge or use in manufacturing processes. Eliminating organics in potable water, such as humic and fulvic acid, prevents chlorine in the water from chemically reacting ...
What is the purpose of removing organics from water?
Eliminating organics in potable water, such as humic and fulvic acid, prevents chlorine in the water from chemically reacting with the acids and forming trihalomethanes, a class of known carcinogens. Activated Carbon (AC) filtration, as with any water treatment method, is not capable of removing every possible type of contaminant.
Why do you backwash carbon beds?
Carbon beds should be backwashed to help remove trapped silt, prevent packing and head loss, and to remove carbon fines produced by friction between granules. As described above, there are a host of variables that must be considered in designing a filtration system and selecting the best carbon for the application.
Why is activated carbon used in water treatment?
This is how activated carbon is used to remove pollutants from water. Despite the range of activated carbons available, they can be too expensive for large-scale water treatment. Also, new types of porous carbons are needed. This is not just for water treatment, but for applications such as batteries or fuel cells.
What is activated carbon made of?
Activated carbon is normally made from various biological materials such as wood, nut shells, peat or coal. If these are heated in an inert atmosphere (no oxygen), they will turn into carbon.
How to make a carbon cylinder?
Weigh 1 g of activated carbon into a beaker (make sure you label the beaker). Measure 100 mL of a dye solution into the cylinder and add to the beaker. Stir for 5 minutes and observe any colour loss. You may need to filter the mixture to remove any carbon powder. But beware; some dyes are adsorbed onto filter paper. Repeat this using 1 g of crushed charcoal and compare the two solutions.
What is the best way to remove pollutants from water?
Some countries struggle with water-borne diseases. Others face natural pollutants such as arsenic or man-made pollutants like textile dyes or pharmaceuticals. One way to remove pollutants from water is to use activated carbon.
What is the name of the compound that is used to color carbon?
In scientific research, a compound called methylene blue is often used. However, food dyes such as E102 or E133 can also be used.
How does steam make carbon?
The steam reacts with the carbon to make carbon dioxide and very tiny holes are left behind in the carbon. Another option for making activated carbon is to use chemical treatment. In this case, the biological material is soaked in acid, base or a strong salt solution before being heated. This also makes small pores in the carbon.
What is left behind from carbon nanotubes?
What is left behind is essentially a carbon nanotube and so the result of the process is a solid material that looks a lot like charcoal, but is full of very tiny hollow tubes, each one over 1000 times smaller than a human hair. We can see these tiny tubes using a technique called electron microscopy.
What chemicals are used in potable water?
PAC Application in the Potable Water Industry 1 Atrazine: A herbicide used to prevent weeds in crops such as corn and sugarcane, Atrazine is an endocrine disruptor. 2 Geosmin: Geosmin creates a musty taste and smell in drinking water. 3 Methylisoborneol (MIB): A common taste and odor compound, MIB is most recalcitrant against treatment.
What is PAC in water?
Powdered Activated Carbon (PAC) is a high performance absorbent engineered to remove harmful contaminants in the air, gas, and liquid phases. The potable water industry has long used PAC products to effectively remove taste and odor compounds, and provide clean water that is safe to drink.
What is activated charcoal?
Activated charcoal (also known as activated carbon) consists of small, black beads or a solid black porous sponge. It is used in water filters, medicines that selectively remove toxins, and chemical purification processes. Activated charcoal is carbon that has been treated with oxygen. The treatment results in highly porous charcoal.
How does adsorption work?
Since adsorption works by chemically binding the impurities to the carbon, the active sites in the charcoal eventually become filled. Activated charcoal filters become less effective with use and have to be recharged or replaced.
How long does it take to heat activated charcoal beads?
Also, you can heat activated charcoal beads to 200 C for 30 minutes. This will degrade the organic matter in the charcoal, which can then be rinsed away, but it won't remove heavy metals. For this reason, it's generally best to just replace the charcoal.
Does charcoal affect filtration?
Adsorption tends to increase as pH and temperature decrease. Contaminants are also removed more effectively if they are in contact with the activated charcoal for a longer time, so flow rate through the charcoal affects filtration.
Does charcoal filter water?
What Activated Charcoal Will and Won't Filter. The most common everyday use of activated charcoal is to filter water. It improves water clarity, diminishes unpleasant odors, and removes chlorine. It's not effective for removing certain toxic organic compounds, significant levels of metals, fluoride, or pathogens.
Can charcoal be used in water filters?
While the contaminants on a full filter aren't released back into the gas or water, used activated charcoal is not effective for further filtration. It is true that some compounds associated with certain types of activated charcoal may leach into the water.
Is charcoal effective?
Activated Charcoal Effectiveness. Several factors influence the effectiveness of activated charcoal. The pore size and distribution varies depending on the source of the carbon and the manufacturing process. Large organic molecules are absorbed better than smaller ones.
What is activated carbon treatment?
Activated carbon treatment generally consists of one or more columns or tanks filled with GAC. Contaminated water or vapors are usually pumped through a column from the top down, but upward flow is possible. As the contaminated water or air flows through the GAC, the contaminants sorb to the outer and inner surfaces of the granules.
What is activated carbon?
Activated carbon is a material used to filter harmful chemicals from contaminated water and air. It is composed of black granules of coal, wood, nutshells or other carbon-rich materials. As contaminated water or air flows through activated carbon, the contaminants sorb (stick) to the surface of the granules and are removed from the water or air.
How big is a carbon tank?
Depending on the amount of groundwater or vapors that need to be treated, tanks of activated carbon can range in size from a 55-gallon drum to a tank that is 20 feet tall and 10 feet or more in diameter.
Why is water and air cleaner?
The water and air exiting the container will be cleaner. Regular testing of exiting water or air is conducted to check contaminant levels. If testing shows that some contaminants remain, the water or air may need to be treated again to meet the treatment levels.
How is treated groundwater pumped?
Depending on the site, treated groundwater may be pumped into a nearby stream or river or back underground through injection wells or trenches. At some sites, a sprinkler system can distribute the water over the ground surface so that it seeps into soil.
How to regenerate GAC?
To regenerate spent GAC, it is usually sent to an offsite facility where it is heated to very high temperatures to destroy the contaminants. If a lot of GAC needs to be regenerated, equipment to heat the GAC and remove the sorbed contaminants can be brought to the site.
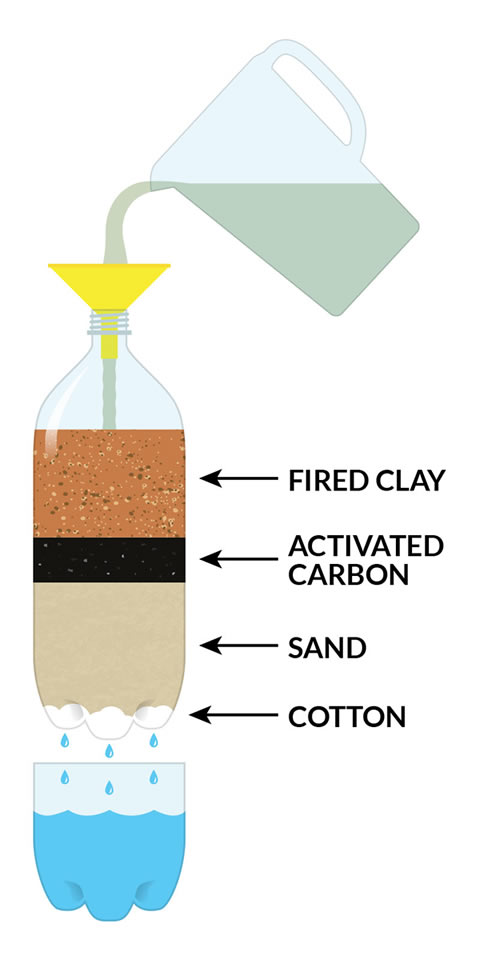
How Activated Carbon Treatment Works
- Activated carbon filters are used to remove unwanted tastes, odors, radon, and some man-made volatile organic contaminants from drinking water. The efficiency of the unit depends on the type of activated carbon installed, the filter bed depth, the type of contaminants in the water and their concentration, and the contact time between the water and ...
Types of Units
- Activated carbon filters come in both pointof- entry (POE) units and point-of-use (POU) units. POE and POU devices refer to the location where the device is installed. POE units treat all the water coming into the house. POU units treat water at specific areas, i.e. below the kitchen sink to treat only tap water in the kitchen. POU units include pour through, faucet mount, in-line, and line bypa…
Unit Effectiveness
- The effectiveness of an activated carbon unit depends on the extent of contact between the carbon and the untreated water. During regular operation of any device, channels form within the carbon filter, allowing some water to bypass the filtering material, short-circuiting treatment. Since treatment depends on the carbon granules adsorbing the chemical contaminants, these channel…
Maintenance
- Regardless of the quality of the equipment purchased, it will not perform satisfactorily unless maintained in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations for maintenance, cleaning, and part replacement. Keep a logbook to record equipment maintenance and repairs. Most activated carbon filter units need to have the carbon changed periodically. For small specialty un…
Other Considerations
- Ensure the system you choose is installed and operated according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After installation, retest both the raw water (prior to treatment) and the treated water at a state certified laboratory to ensure it is working properly and removing the contaminants. You should continue to test the quality of both the raw and treated water annually or more frequentl…
Questions to Ask Before You Buy
- Before purchasing a water treatment device, have your water tested at a state certified laboratory to determine the contaminants present and their concentration. This will help you determine if activated carbon is an effective treatment method for your situation. See the factsheet Questions to Ask When Purchasing Water Treatment Equipment for more information. Consumers should i…
Product Certification
- NSF International is a non-profit organization that sets performance standards for water treatment devices. Because companies can make unsubstantiated statements regarding product effectiveness, the consumer must evaluate test results of the device to determine if claims are realistic. Products that have been tested or evaluated by NSF and meet their minimum requirem…