What are gold nanoparticles in chemotherapy and radiotherapy?
Gold nanoparticles in chemotherapy and radiotherapy is the use of colloidal gold in therapeutic treatments, often for cancer or arthritis. Gold nanoparticle technology shows promise in the advancement of cancer treatments.
Can nanogold nanoparticles be used to treat cancer?
The possibility to modify the surface of nanogold particles with different targeting and functional compounds significantly broadens the range of their potential biomedical applications, with particular emphasis on cancer treatment.
Can gold nanorods be used to detect cancer cells?
In addition, gold nanorods, as appealing TPL imaging substrates, can strongly scatter to detect cancer cells under excitation in the near-infrared region where biological tissues exhibit slight extinction coefficients (Zhang W. et al., 2018).
What makes ultrasmall gold nanoparticles suitable for clinical application?
In order to improve this concern for clinical application, ultrasmall gold nanoparticles are designed to be coated with the pH-sensitive polymer and encapsulated within ∼150 nm of polymeric micelle.

What is the cost of gold nanoparticles?
However, a single milligram of gold nanoparticles currently costs about $80 (depending on the size of the nanoparticles). That places the price of gold nanoparticles at $80,000 per gram while a gram of pure, raw gold goes for about $50.
How gold nanoparticles can be used to cure cancer?
Gold nanoparticles absorb incident photons and convert them to heat to destroy cancer cells. Due to their unique optical properties as a result of LSPR, gold nanoparticles absorb light with extremely high efficiency (cross section at ~10 9 M−1 cm−1), which ensures effective PTT at relatively low radiation energy.
What is Nano gold cancer therapy?
Nanoparticles of gold can be injected into a tumor. The patient is then exposed to a specific wavelength of light that harmlessly passes through the skin and body tissue but gets absorbed by the nano-gold, which heats up and destroys the surrounding tumor cells.
Which nanoparticles are used in cancer treatment?
mAb Nanoparticles Monoclonal antibodies are widely used in cancer treatment for their particular targeting abilities [65]. These mAb are now combined with NPs to form antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs). These are proved to be highly specific and compelling than cytotoxic drugs or mAb alone.
Does gold cure cancer?
Tiny flecks of gold could be used in the fight against cancer, new research has suggested. Scientists at Edinburgh University found the precious metal increased the effectiveness of drugs used to treat lung cancer cells. Minute fragments, known as gold nanoparticles, were encased in a chemical by the research team.
How do nanoparticles help in chemotherapy?
The technique involves storing a cancer drug inside tiny objects called nanoparticles. Using this method, researchers were able to shrink tumors in mice while using smaller doses of the drug to reduce harmful side effects. The chemotherapy drug cisplatin is an effective cell killer.
Can nanoparticles cure cancer?
Nanoparticles are a promising treatment option for cancers that are resistant to common therapies. In a new study that demonstrates an innovative and non-invasive approach to cancer treatment, Northwestern Medicine scientists successfully used magnetic nanoparticles to damage tumor cells in animal models.
Why is nanotechnology better than chemotherapy?
Nanotechnology targets cancer cells more exactly to spare healthy tissues. In theory, it should cause fewer side effects than current treatments like chemotherapy and radiation. Current nanotechnology-based treatments such as Abraxane and Doxil do cause side effects like weight loss, nausea, and diarrhea.
What is Nano surgery?
Nanosurgery is the term that refers to surgery that uses fast laser beams which are focused by an objective microscope lens to exert a controlled force to manipulate organelles and other subcellular structures.
Is nanotechnology expensive?
Nanotech is an expensive area of research, and largely confined to developed nations with strong infrastructure. Many social scientists are concerned that underdeveloped countries will fall further behind as they cannot afford to develop a nanotechnology industry.
Why nanomaterials are used in cancer treatment?
Nanotechnology can provide rapid and sensitive detection of cancer-related molecules, enabling scientists to detect molecular changes even when they occur only in a small percentage of cells. Nanotechnology also has the potential to generate entirely novel and highly effective therapeutic agents.
How do you destroy cancer cells?
Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells. Radiation therapy. Radiation therapy uses high-powered energy beams, such as X-rays or protons, to kill cancer cells. Radiation treatment can come from a machine outside your body (external beam radiation), or it can be placed inside your body (brachytherapy).
Can colloidal gold cure cancer?
Colloidal gold-bound tumor necrosis factor is made in the laboratory by binding a cancer-killing protein called tumor necrosis factor (TNF) to the surface of very tiny particles of gold. These TNF-gold particles may kill cancer cells without harming healthy tissue. Also called Aurimmune and TNF-bound colloidal gold.
What are the uses of gold nanoparticles?
Gold nanoparticles are used in resonance scattering dark-field microscopy for the detection of microbial cells and their metabolites [37], the bio-imaging of tumor cells [38], and for the detection of receptors on their surface [39], and for the study of endocytosis [40].
Why are gold nanoparticles used in biomedical applications?
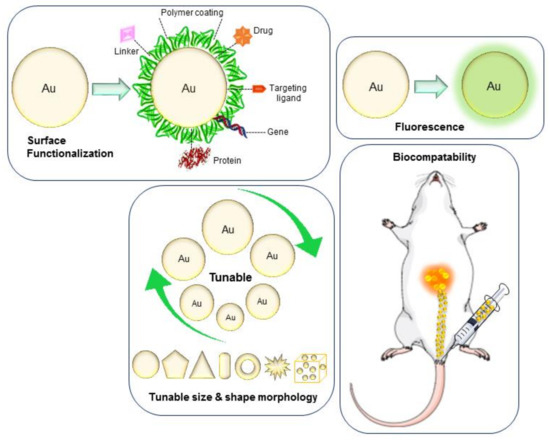
They have suitable properties for controlled drug delivery, cancer treatment, biomedical imaging, diagnosis and many others, due to their excellent compatibility with the human organism, low toxicity and tunable stability, small dimensions, and possibility to interact with a variety of substances.
Is colloidal gold real gold?
Colloidal gold is a sol or colloidal suspension of nanoparticles of gold in a fluid, usually water. The colloid is usually either wine-red coloured (for spherical particles less than 100 nm) or blue/purple (for larger spherical particles or nanorods).
What is gold nanoparticle?
Gold nanoparticles are emerging as promising agents for cancer therapy and are being investigated as drug carriers, photothermal agents, contrast agents and radiosensitisers. This review introduces the field of nanotechnology with a focus on recent gold nanoparticle research which has led to early-phase clinical trials.
Is GNP oxidized or nonoxidized?
GNPs, however, exist in a non-oxidised state (Au [0]). GNPs are not new; in the 19th century, Michael Faraday [7] published the first scientific paper on GNP synthesis, describing the production of colloidal gold by the reduction of aurochloric acid by phosphorous.
What is the best stabilizer for blood circulation?
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) (Huckaby and Lai, 2018) is another commonly used stabilizer prolonging the blood circulation time in vivo. Clinically, PEG is approved for intravenous application (Rafiei and Haddadi, 2017).
What are the intrinsic limits of cancer?
The intrinsic limits of conventional cancer therapies prompt the increasing interests in the applying of nanotechnology in the diagnosis and therapy assessments for cancer, which fight cancer cells more accurately with fewer potential side effects .
What is gold nanoparticle?
Gold nanoparticles (AuNPS) represent one of the most studied classes of nanomaterials for biomedical applications, especially in the field of cancer research . In fact, due to their unique properties and high versatility, they can be exploited under all aspects connected to cancer management, from early detection to diagnosis and treatment.
What is the purpose of nanomedicine?
Human health was not an exception, and the term “nanomedicine” [ 2] was coined to describe the application of nanoscience and nanotechnology to the therapy, diagnosis and prevention of diseases, especially cancer, for which the superiority of nanomedicine over conventional treatments was immediately recognized.
What is gold nanoparticle?
Gold nanoparticles in chemotherapy and radiotherapy is the use of colloidal gold in therapeutic treatments, often for cancer or arthritis. Gold nanoparticle technology shows promise in the advancement of cancer treatments. Some of the properties that gold nanoparticles possess, such as small size, non-toxicity and non-immunogenicity make these ...
What are the advantages of gold nanoparticles?
Gold nanoparticles have their advantages in drug vectorization. They can pack several different sizes and types of dendrimers and several different types of ligands in order to effectively treat different types of cancers. For example, research shows that 80~90% of breast cancer ’s tumor cells have estrogen receptors and 60~70% ...
How many nanoparticles of gold are in a cell?
The concentrations of gold nanoparticles in biological systems for practical usage range from 1-100 nanoparticles per cell. High concentrations may lead to adverse effects for cell structure and function, which may not appear non-toxic in assays but preparation of the particles have been found to produce abnormal effects in the cell. If large concentrations quickly clear the blood vessels, the nanoshells may accumulate in major organs (mainly the liver and spleen ). Residual concentrations of these particles were also found in kidneys, lungs, muscle, brain, and bone of mice after 28 days. The concentration of the solution injected intravenously 2.4*10 11 nanoshells/mL. Even without complete clearance from the system, the nanoshells did not cause any physiological complications in the mice. Su et al observed a correlation with the concentration of Au 3 Cu and cell damage. Cells were incubated in concentrations of 0.001 and 200 mg mL −1 Au 3 Cu. They concluded a 15% cell viability and dose dependent cell damage. Reduction in cell viability was detected in vivo experiments; also related to dosage. Cytotoxicity is not a major concern in the usage of AuNPs, as they localize in the vesicles and cytoplasm as opposed to the nucleus. Thus, no complications spawned due to their aggregation in these parts of the cell.
How are AuNPs used in cancer?
Another way in which AuNPs can be used in cancer therapy is as agents for targeted drug delivery. Research shows that AuNPs can be easily functionalized and conjugated with a variety of molecules, including chemotherapeutic drugs such as Doxorubicin. One major complication with the current methods of treating cancer with chemotherapy is that treatment is not optimized to specifically target cancer cells and the widespread distribution of chemotherapeutic drugs throughout the body can cause harmful side effects such as naseua, hair loss, and cardiotoxicity. Since many of the characteristics of AuNPs allow them to target cancer cells specifically and accumulate within tumor cells, these molecules can act as tumor-targeting drug delivery systems. Once within the tumor microenvironment, these complexes dissociate and release the chemotherapeutic, allowing the drug to take effect and eventually cause apoptosis .
How does nanotechnology affect DNA?
In today’s biological fields, the use of nanotechnology has allowed for the indirect use of AuNPs to deliver DNA to mammalian cells; thereby reducing tumor agents and increasing efficiency of electron transfer by modulating the activity of glucose oxidase.
How do anti-estrogen molecules with thiolated PEG bind to gold nanoparticles?
Then, anti-estrogen molecules with thiolated PEG are bound to gold nanoparticles via Au-S bonds, forming thiolate protected gold nanoparticles.
Why are gold nanoparticles good absorbers of x-rays?
Gold nanoparticles are excellent absorbers of x-rays, due to its high atomic number of 197 Au. This allows for a higher mass of the element, providing for a greater area of x-ray absorption.