
Medication
7 Ways to Manage IBS-D Symptoms
- Understand the Problem. There are three major areas of research into the causes of IBS. ...
- Identify Your Food Triggers. It can be so hard to try to figure out what foods are causing your symptoms. ...
- Consider the Low-FODMAP Diet. ...
- Don't Skip Meals. ...
- Keep Your System Calm. ...
- Try Psychotherapy or Hypnotherapy. ...
- Sip Some Tea. ...
Self-care
If the symptoms are mild, they can be managed by changing stress, lifestyle, and diet. On the other side, severe symptoms are treated with medication and counseling. Get Sample PDF Copy of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) Treatment Market at: Increasing Prevalence of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Associated Conditions
Nutrition
Caffeine can trigger the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) -- especially abdominal cramping and diarrhea -- as well as aggravate heartburn and dyspepsia. It does so by stimulating the gut directly; by stimulating the brain and heart, which contributes to anxiety; and by interfering with sleep.
What to try next for IBS-D?
Black, green, and white teas are all considered to be good beverage options for people with IBS-D because they are low in FODMAPs. Of the herbal teas, fennel and anise tea may be helpful for people with constipation-type IBS (IBS-C), but not for IBS-D. And chamomile tea is not low in FODMAPs, so it may not be appropriate for IBS sufferers.
How to cure IBS D?
Is caffeine bad for IBS-D?
Does tea help IBS-D?
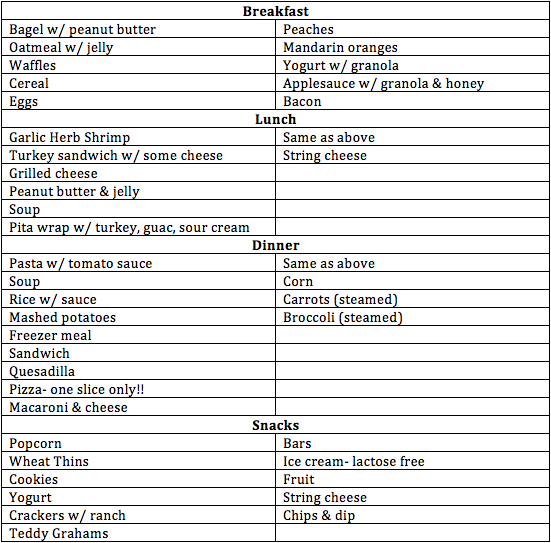
How do you treat IBS-D permanently?
There is no known cure for this condition, but there are many treatment options to reduce or eliminate symptoms. Treatment includes dietary modifications, lifestyle changes, and prescription medications. There is no specific diet for IBS, and different people react differently to different foods.
How do I live with IBS-D?
Tips for everyday life with IBS-DTry getting regular exercise or practicing meditation or other stress-reducing techniques.Keep a detailed journal of all of your symptoms.Eliminate trigger foods from your diet, such as foods that cause gas or contain gluten.More items...
How do I get rid of IBS diarrhea?
7 Ways to Manage IBS DiarrheaTake fiber. ... Take an antidiarrheal. ... Avoid trigger foods. ... Eat foods that can help solidify your stools. ... Manage stress. ... Try therapy. ... Ask your doctor about medications.
Is there any help for IBS-D?
Over-the-counter medications:Anti-diarrhea medications like loperamide (Imodium) may help. Peppermint oil supplements may reduce cramping. Some experts believe probiotics (“good” bacteria, which you can get in supplement form or from foods like pickles and sauerkraut) can help relieve IBS symptoms, including diarrhea.
How do you stop IBS-D flare ups?
An IBS flare-up can be frustrating and may cause a range of digestive symptoms. If you're experiencing a flare, there are several at-home remedies you can try, such as gut-directed hypnotherapy, removing high-FODMAP foods from your diet, heat therapy, avoiding caffeine, exercising, and reducing stress.
How serious is irritable bowel?
Only a small number of people with IBS have severe signs and symptoms. Some people can control their symptoms by managing diet, lifestyle and stress. More-severe symptoms can be treated with medication and counseling. IBS doesn't cause changes in bowel tissue or increase your risk of colorectal cancer.
What triggers IBS-D?
All types of IBS, including IBS-D, have similar triggers. Stress is a common trigger, although the symptoms are not psychological in nature. Certain foods, such as milk, wheat, and red wine, are more likely to cause reactions. Smoking and caffeine consumption may also trigger IBS symptoms.
Can I take Imodium every day for IBS?
For diarrhea-predominant IBS, 2 to 4 mg of loperamide up to four times a day can be effective.
What is the best over the counter medicine for IBS?
For gas, bloating, and abdominal painGas-X Extra Strength Softgel for Fast Gas Relief. ... IBgard for the Dietary Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. ... Iberogast Dietary Supplement to Support the Digestive System. ... Metamucil Fiber Supplement. ... Imodium Multi-Symptom Relief Anti-Diarrheal Medicine Caplets. ... Miralax Laxative Powder.More items...•
What is the best medicine for chronic diarrhea?
Over-the-counter anti-diarrheal medications, such as loperamide and bismuth subsalicylate, might help reduce the number of watery bowel movements and control severe symptoms.
Do probiotics help with IBS-D?
Probiotics may relieve symptoms of IBS In a clinical trial published in Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics, once-daily Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 significantly improved overall IBS symptoms, as well as individual IBS symptoms including abdominal pain, bloating, and fecal urgency.
What is the best prescription medication for diarrhea?
What is the best medication for diarrhea?Best medications for diarrheaImodium AD (loperamide)Over-the-counter antidiarrhealOralLomotil (diphenoxylate / atropine)Rx AntidiarrhealOralXifaxan (rifaximin)Rx Antibiotic/AntibacterialOralAlinia (nitazoxanide)Rx AntiprotozoalsOral3 more rows•Oct 5, 2020
How to treat IBS?
Treatment of IBS focuses on relieving symptoms so that you can live as normally as possible. Mild signs and symptoms can often be controlled by managing stress and by making changes in your diet and lifestyle. Try to: Avoid foods that trigger your symptoms.
What are the different types of IBS?
Type of IBS. For the purpose of treatment, IBS can be divided into three types, based on your symptoms: constipation-predominant, diarrhea-predominant or mixed.
How to get rid of constipation and cramps?
Try slowly increasing the amount of fiber in your diet over a period of weeks with foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables and beans. A fiber supplement might cause less gas and bloating than fiber-rich foods.
How long does abdominal pain last?
These criteria include abdominal pain and discomfort lasting on average at least one day a week in the last three months, associated with at least two of these factors: Pain and discomfort are related to defecation, the frequency of defecation is altered, or stool consistency is altered. Type of IBS. For the purpose of treatment, IBS can be divided ...
How to get rid of diarrhea?
Eliminate foods that trigger your symptoms. Eat at regular times. Don't skip meals, and try to eat at about the same time each day to help regulate bowel function. If you have diarrhea, you may find that eating small, frequent meals makes you feel better.
What is the procedure to check for abdominal pain?
Diagnostic procedures can include: Colonoscopy. Your doctor uses a small, flexible tube to examine the entire length of the colon. X-ray or CT scan. These tests produce images of your abdomen and pelvis that might allow your doctor to rule out other causes of your symptoms, especially if you have abdominal pain.
What tests are done to check for malabsorption?
Your doctor may recommend several tests, including stool studies to check for infection or problems with your intestine's ability to take in the nutrients from food (malabsorption). You may also have a number of other tests to rule out other causes for your symptoms. Diagnostic procedures can include: Colonoscopy.
What anti-inflammatory drugs are used for IBS-D?
Two anti-inflammatory agents have been used for this subset of patients: mast cell stabilizers such as disodium cromoglycate and ketotifen, and 5-ASA, which has shown mixed results for IBS-D in four small trials.
What are the causes of IBS?
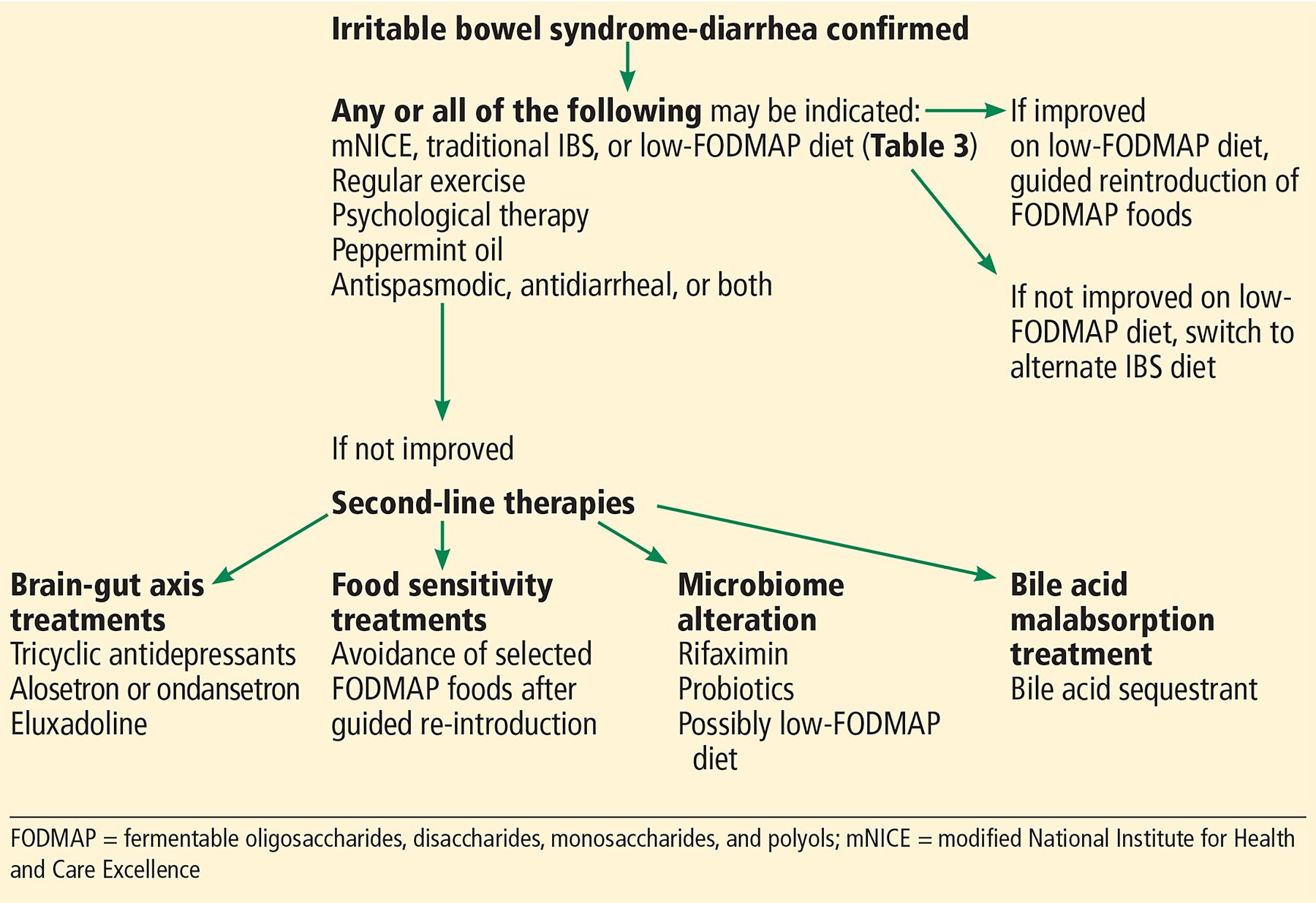
Certain factors that alter gastrointestinal function can contribute to IBS symptoms, including stress, prior gastroenteritis, changes in the gut microbiome, and bile acids and short-chain fatty acids, which may stimulate serotonin (5-HT) release and increase colonic permeability and motility. Still, the underlying cause ...
What is the bowel disorder?
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a multifactorial disorder marked by recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort and altered bowel function. It affects between 10 and 20 percent of people in the developed world, about one-third of whom have IBS associated with diarrhea (IBS-D). Certain factors that alter gastrointestinal function can contribute ...
Does bile sequestration help with cholerrheic disease?
Roughly 30 percent of people with IBS-D have diagnosed bile acid malabsorption, and for this subset of patients, bile acid sequestration may relieve the cholerrheic effect of bile acids. Some evidence suggests that certain genetic variants may influence response to the bile sequestrant colesevelam, a medication that may be preferable to cholestyramine.
Is asimadoline safe for IBS?
Asimadoline, a kappa-opioid agonist, is being evaluated in clinical trials. So far, it has shown a good safety profile and reduced pain, urgency and stool frequency in IBS-D patients.
Can probiotics help with IBS?
Of increasing interest in many gastrointestinal disorders, single or combination probiotics have been investigated for IBS-D in several small trials. In these studies, bloating and distension improved but not diarrhea.
Does loperamide help with constipation?
In a small, placebo-controlled study, loperamide improve d pain, stool consistency, urgency and overall subjective response, but it must be carefully titrated for individual patients to avoid constipation.
How Is IBS-D Treated?
Getting relief from your IBS-D may take some detective work. You’ll probably need to try several strategies and use many different techniques at a time. Make sure your doctor is in the picture. They can work with you to find an effective plan.
What is the best medicine for IBS?
Prescription medications:There are several options your doctor can prescribe. Anticholinergic dicyclomine(Bentyl) slows bowel contractions that lead to diarrhea. Hyoscyamine(Levsin) acts in much the same way. An antidepressantmay be an option if your IBS-D causes a lot of pain or if you’re feeling depression or anxiety.
What Causes IBS-D?
We do know that women are more likely to have it than men, and it’s more common in adults under 50. If you have a family member with IBS, your odds of getting IBS or IBS-D go up.
What is IBS D?
WebMD explains the causes, symptoms, and treatment of IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D), a long-lasting condition that affects your digestive system. Skip to main content .
How does IBS-D affect diarrhea?
How Is IBS-D Treated? IBS that causes increased diarrheais often called IBS-D. If you have IBS-D, you have belly pain and other IBS symptoms plus frequent bowel movements. Your stool might be loose, though not always. You also might have sudden urges to use the bathroom.
How to get rid of diarrhea?
But they can make symptoms like diarrhea worse. That’s why it’s important to try to find effective ways to manage your mood. Exercisecan help you feel better and improve the way your bowel functions, too. Massage, yoga, hypnotherapy, and forms of talk therapy can help with stress, which may lessen your symptoms.
What tests are done to check for celiac disease?
These can include a blood test to check for celiac diseaseand a colonoscopy to check for abnormal growths and signs of cancer. (During a colonoscopy, doctors use medication to sedate you, then insert a tube with a tiny camera into your rectum and your large intestine to see if it’s healthy.)
Diagnosis
Treatment
Clinical Trials
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Specialist to consult
Alternative Medicine