Stylecraze.com
1. Drumstick Leaves...
2. Vitamins B12 And Folate...
3. Blackstrap Molasses...
4. Green Veggies...
5. Vitamin C...
6. Probiotics...
7. Figs...
8. Beetroot...
Learn More...Top10homeremedies.com
1. Inculde Beetroot in Your Diet...
2. Consume Probiotics...
3. Eat Fermented Foods...
4. Drink Blackstrap Molasses in Water...
5. Drink Spinach Juice...
6. Drink Pomegranate Juice...
7. Eat a Concoction of Sesame Seeds...
8. Chow Down on Dates...
Learn More...Rapidhomeremedies.com
1. Beetroot-Apple Juice...
2. Sesame Seeds...
3. Blackstrap Molasses...
4. Spinach...
5. Tomatoes...
6. Pomegranate...
7. Parsley...
Learn More...How can I increase my erythropoietin levels naturally?
how can I increase my erythropoietin levels naturally? Manipulating diet for protein and total calorie adequacy, monitoring hydration, using supplements, timing food combinations, adding weekly hypoxic exercise followed by easy or rest days all increases the release of natural EPO for healthy maximal oxygen carrying capacity.
What causes high erythropoietin levels?
The risk factors for secondary polycythemia (erythrocytosis) are:
- obesity
- alcohol abuse
- smoking
- high blood pressure (hypertension)
How is EPO administered?
The other factors playing a role in the detection are follows:
- It is difficult to discriminate between the endogenous EPO and recombinant exogenous hormone.
- EPO has a relatively short half-life in serum (the half-life of rhEPO-a is 8.5 ± 2.4 hours when administered IV and 19.4 ± 10.7 hours when administered SC).[62]
- EPO is undetectable in urine after 3–4 days of injection.
What stimulates production of erythropoietin?
- Heart disease
- High blood pressure
- Porphyria (a group of diseases that are caused by enzyme deficiencies)
- Seizures
- An allergy to epoetin alfa or any other part of this medicine
- Uncontrolled high blood pressure
What is erythropoietin used to treat?
Epoetin is used to treat severe anemia in patients on kidney dialysis or for those not on dialysis. Epoetin may also be used to prevent or treat anemia that is caused by surgery or medicines (eg, zidovudine) that are used for other conditions, such as HIV or cancer.
In which disease erythropoietin is widely used?
Human recombinant erythropoietin (rEPO) has been widely used to treat CKD-associated anemia and is known to possess organ-protective properties that are independent from its well-established hematopoietic effects.
How does erythropoietin affect anemia?
EPO tells your body to make red blood cells. When you have kidney disease, your kidneys cannot make enough EPO. Low EPO levels cause your red blood cell count to drop and anemia to develop.
What is erythropoietin deficiency anemia?
When your kidneys are damaged, they produce less erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone that signals your bone marrow—the spongy tissue inside most of your bones—to make red blood cells. With less EPO, your body makes fewer red blood cells, and less oxygen is delivered to your organs and tissues.
What four conditions cause the release of erythropoietin?
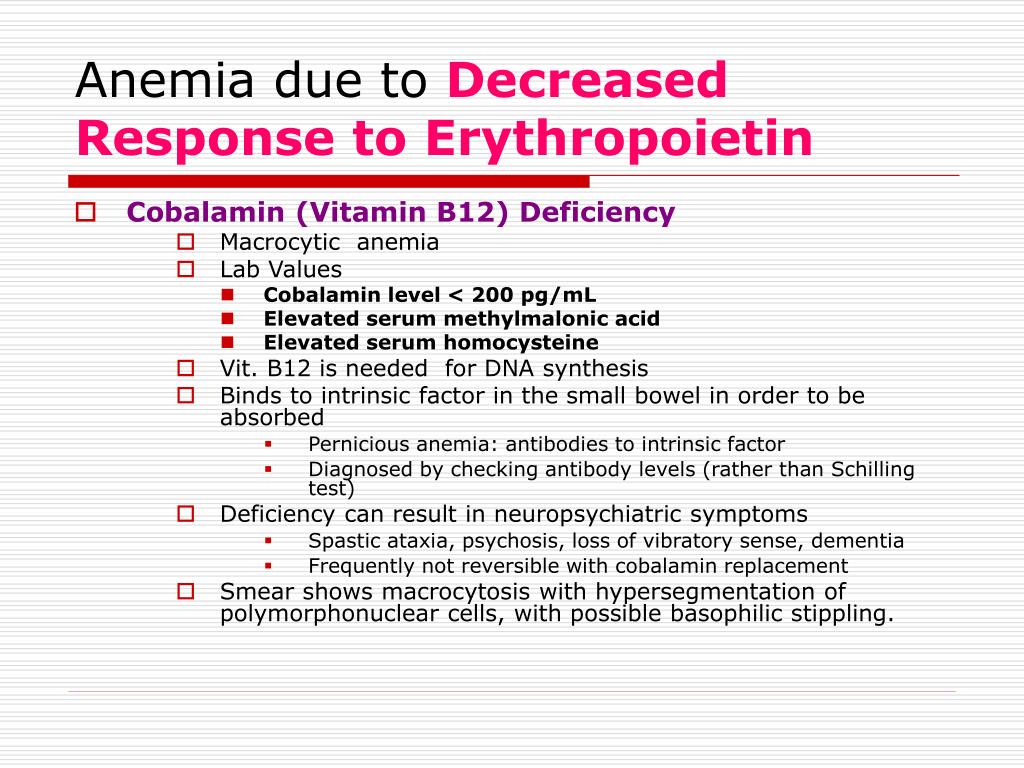
An erythropoietin (EPO) test may be ordered when you have anemia that does not appear to be caused by iron deficiency, vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, decreased lifespan of red blood cells (RBCs; hemolysis), or by excessive bleeding.
Which patients are eligible to receive erythropoiesis stimulating agents?
The two primary FDA-approved indications for ESAs are anemia secondary to chronic kidney disease and chemotherapy-induced anemia in patients with cancer.
What type of anemia is CKD?
Anemia of chronic renal disease, also known as anemia of chronic kidney disease (CKD), is a form of normocytic, normochromic, hypoproliferative anemia. It is frequently associated with poor outcomes in chronic kidney disease and confers an increased mortality risk.
What causes normocytic anemia?
The most common cause of the acquired form of normocytic anemia is a long-term (chronic) disease. Chronic diseases that can cause normocytic anemia include kidney disease, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis and thyroiditis. Some medicines can cause you to have normocytic anemia, but this does not happen often.
What are the different types of anemia?
Many types of anemia exist, such as iron-deficiency anemia, pernicious anemia, aplastic anemia, and hemo- lytic anemia. The different types of anemia are linked to various diseases and conditions. Anemia can affect people of all ages, races, and ethnici- ties.
Is haemolytic anaemia normocytic?
Normocytic anemias can be further classified as hemolytic when there's increased destruction of RBCs, or hemolysis, and non-hemolytic when there's decreased production of RBCs from the bone marrow.
What is absolute anemia?
Absolute iron deficiency was defined as transferrin saturation (TSAT) less than 20% with ferritin levels below 40 micrograms per litter, and functional iron deficiency was defined as TSAT less than 20% with ferritin levels above 40 micrograms per litter.
What is Hypoproliferative anemia?
INTRODUCTION. Anemia of central origin, or hypoproliferative anemia, broadly refers to anemia resulting from underproduction of red blood cells by the bone marrow.
What does it mean when you have erythropoietin in your blood?
An abnormal level of erythropoietin in the blood can indicate bone marrow disorders, (such as polycythemia, or increased red blood cell production) kidney disease, or erythropoietin abuse.
What is the purpose of measuring erythropoietin levels?
Measurement of the blood erythropoietin level can be used to detect certain medical conditions. Erythropoietin can be synthesized and used as a treatment of some forms of anemia.
What happens when you replace erythropoietin with synthetic erythropoiet
Therefore, by replacing the erythropoietin with an injection of synthetic erythropoietin, anemia related to kidney disease may be treated.
What is EPO in the blood?
What is erythropoietin (EPO)? Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone produced by the kidney that promotes the formation of red blood cells by the bone marrow. The kidney cells that make erythropoietin are sensitive to low oxygen levels in the blood that travels through the kidney. These cells make and release erythropoietin when ...
What is the meaning of EPO?
Erythropoietin (EPO) definition and facts. Measuring blood levels of erythripoietin, a hormone involved in red blood cell production, can diagnose some medical conditions. Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone produced by the kidney. Erythropoietin promotes the formation of red blood cells by the bone marrow. The erythropoietin hormone level can be ...
Can erythropoietin be used as a performance enhancer?
Yes. For example, erythropoietin has been misused as a performance-enhancing drug in athletes such as cyclists (in the Tour de France), long-distance runners, speed skaters, and Nordic (cross-country) skiers.
Is erythropoietin normal?
Sometimes, the erythropoetin level may be inappropriately normal when it should be elevated (such as when there is an anemia), indicating a problem with the kidneys.
What is erythropoietin in the kidney?
Erythropoietin is a hormone synthesized in the kidney responsible for red blood cell maturation in the bone marrow. It is deficient in the majority of patients with advanced kidney disease thereby predisposing to anemia.
Which organ is the primary source of erythropoietin?
The kidney is the primary site of erythropoietin production in adults (Ratcliffe et al 1995). Studies utilizing transgenic mice suggest that a population of interstitial fibroblasts (also known as the type I interstitial cell) are the major source of renal erythropoietin synthesis (Maxwell et al 1993).
When was epoetin alfa approved?
Since the approval of recombinant human erythropoietin (epoetin alfa) by the US FDA in 1989 , epoetin alfa and similar agents now collectively known as erythropoietin stimulating agents (ESA) have become the standard of care for the treatment of the erythropoietin-deficient anemia that occurs in most patients with CKD.
Is epoetin alfa marketed as Procrit?
In the US, epoetin alfa is also marketed as Procrit®(Ortho Biotech) primarily in pre-ESRD patients. In Europe epoetin alfa (Eprex®, Ortho Biotech) and epoetin beta (Neorecormon®, Roche), different only in glycosylation were approved for the treatment of anemia of CKD.
Is recombinant human erythropoietin a substitute for CKD
Although recombinant human erythropoietin is a substitute for the deficiency observed in CKD, therapy of anemia often involves many other issues detailed below that need to be considered in order to effectively correct anemia, reduce costs and minimize side effects. Impact of anemia on health.
What tests are used to diagnose hemolysis?
Tests of hemolysis such as total bilirubin, lactate dehyrogenase, urine hemosiderin, urine hemoglobin, haptoglobin, and a peripheral smear should be performed to diagnose the presence of hemolysis. By far, haptoglobin is the most specific of these tests and a depressed value indicates significant hemolysis.
Can iron deficiency cause blood draw?
Iron deficiency may result from nutritional deficiency as well as blood losses from occult gastrointestinal hemorrhage, menstruation, and blood draws. Blood draws are particularly significant in hemodialysis patients in whom up to 2 g of iron can be lost per year (KDOQI 2006).
How often is erythropoietin injected?
before each injection of erythropoietin during the first 2 weeks of treatment, every week until the 12th week, every other week until the end of the first six months of treatment, and every month thereafter.
When is erythropoietin measured?
Serum levels of erythropoietin were measured before the start of therapy and after six weeks of treatment. If the therapeutic attempt was considered a failure before six weeks had elapsed, the serum sample obtained on the day of the decision to terminate therapy was used instead.
Is multiple myeloma anemia?
Since myeloma-associated anemia represents a specific form of chronic anemia of cancer, the excellent response rate observed in our patients with multiple myeloma must not be indiscriminately generalized to results in all patients with cancer.
Does histocompatibility reduce platelet transfusion?
Sensitization to histocompatibility antigens may reduce the efficacy of concomitant platelet transfusions. With the introduction of genetically engineered recombinant human erythropoietin into clinical use, the treatment of chronic anemias may improve substantially.
Is anemia a complication of multiple myeloma?
Anemia is a common complication of multiple myeloma. It resolves early in the disease if chemotherapy induces a complete remission, but persists if the disease progresses, causing disabling symptoms and often requiring blood transfusions. We treated 13 patients with myeloma-associated anemia by administering recombinant human erythropoietin three ...
Abstract
Until 1990, erythropoietin (EPO) was considered to have a single biological purpose and action, the stimulation of red blood cell growth and differentiation. Slowly, scientific and medical opinion evolved, beginning with the discovery of an effect on endothelial cell growth in vitro and the identification of EPO receptors (EPORs) on neuronal cells.
Introduction
The presence of a circulating hemopoietic factor controlling the red blood cell (RBC) production was first suggested in 1906 ( 1 ). This humoral factor was experimentally confirmed almost half a decade later and the name erythropoietin was given ( 2 ).
Action of EPO on Non-Hematopoietic Cells
EPO and its receptor have been identified in several non-hematopoietic cells and tissue types like central nervous system, heart, kidney, gastrointestinal system, reproductive tract, endothelium, and others [reviewed in Ref. ( 11, 12, 61 )]. In these tissues, EPO was shown to be tissue protective in an anti-apoptotic and/or mitogenic manner.
Conclusion
A plethora of scientific evidence demonstrates a growth-promoting, anti-apoptotic action of EPO and other ESAs on non-hematopoietic cells, both normal and malignant, and this is supported by numerous clinical observations showing adverse effects of EPO administration on the clinical management of tumor growth and progression.
Author Contributions
Nataša Debeljak outlined the work. All authors designed and drafted the work. Arthur J. Sytkowski critically revised the work. All authors approved final version of the work and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Nataša Debeljak was supported by the J3-0124 grant to ND and P1-0104 to Radovan Komel, both from the Slovenian Research Agency. Peter Solár was partly supported by Scientific Grant Agency of the Ministry of Education of the Slovak Republic under contract no. VEGA 1/0733/12. Arthur J.