In children over 5 years old (reasonably mature eustachian tube anatomy) with nonrecurrent (no AOM in past month), nonsevere (no otalgia or high fever) AOM, 5 days is enough. But 2- to 5-year-olds (less mature anatomy) need 7 days and those <2 years old (least mature plumbing) need 10 days. Likewise, severe AOM usually warrants 10 days.
What is the age range for management of otitis media?
Management of acute otitis media in children six months of age and older Nicole Le Saux, Joan L Robinson, and Canadian Paediatric Society, Infectious Diseases and Immunization Committee
When is amoxicillin/clavulanate indicated in the treatment of acute otitis media (AOM)?
Amoxicillin remains first line therapy for children who have not received amoxicillin within the past 30 days. Amoxicillin/clavulanate is recommended if amoxicillin has been taken within the past 30 days, if concurrent purulent conjunctivitis is present, or if the child has a history of recurrent AOM unresponsive to amoxicillin.
How is acute otitis media (AOM) diagnosed?
To diagnose AOM, there must be acute onset of symptoms such as otalgia (or nonspecific symptoms in nonverbal children), signs of a middle ear effusion associated with inflammation of the middle ear (ie, a TM that is bulging and, usually, very erythematous or hemorrhagic, and yellow or cloudy in colour) or a TM that has ruptured.
When to give amoxicillin to a 2 year old with otalgia?
AnswerCurrent Canadian guidelines recommend all children younger than 2 years of age with otalgia due to AOM and fever greater than 39°C be considered for treatment with amoxicillin. Watchful waiting is indicated only for children older than 6 months with mild-to-moderate AOM.
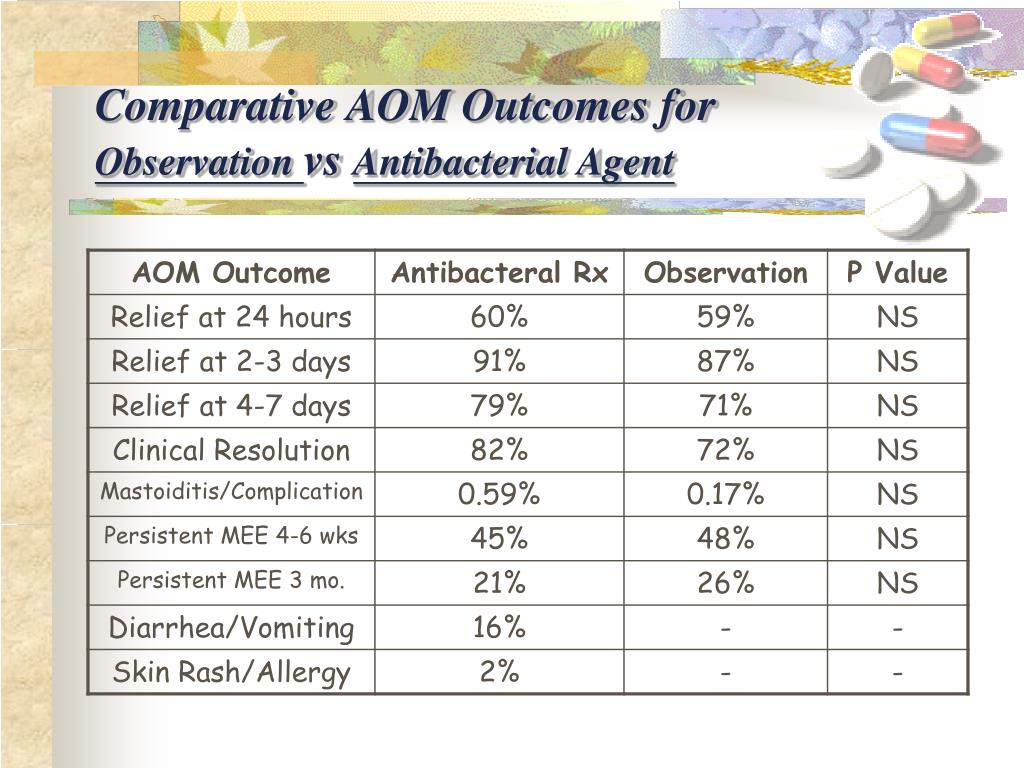
When should AOM be treated in children?
Children with AOM (defined by a bulging TM) who are highly febrile (≥39°C) and moderately to severely systemically ill, or children who have severe otalgia or have been significantly ill for 48 h should be treated with antimicrobials (Figure 1).
How is otitis media treated in toddlers?
Medicines. In many cases, acute otitis media will resolve without antibiotics, so they are not always needed for treatment. For these children Tylenol® or Motrin® may be given for the fever, pain, and irritability. For some children with severe acute otitis media, antibiotics will be prescribed.
Can adults get AOM?
AOM is seen frequently in children but is less common in adults. This is because children are more prone to viral infections, and have shorter and more horizontal Eustachian tubes. The incidence of otitis media in adults is widely quoted as 0.25% per annum. Smoking is a recognised risk factor.
What is AOM in children?
Acute otitis media (AOM) is characterized by the presence of middle ear effusion together with an acute onset of signs and symptoms caused by middle ear inflammation. The most common pathogens in AOM are Streptococcus pneumoniae, nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis.
What can I give my 2 year old for ear infection?
For an uncomplicated ear infection, children between 6 months and 2 years usually take an antibiotic for 10 days. Children over 2 years of age will take an antibiotic for 5 days. The doctor might suggest acetaminophen or ibuprofen to reduce the child's pain.
What can I do for a 5 year old earache?
Five tips for ear infection treatment at homeFever and pain medicine: based it on age, consult with doctor. Over-the-counter medications can help reduce pain and fever in your child. ... Place a cold pack or warm compress over your child's ear. ... Keep child hydrated. ... Elevate your child's head. ... Watch for ear discharge.
How do you treat serous otitis media in adults?
Chronic Serous Mastoiditis and Idiopathic Hemotympanum The condition is commonly treated with antibiotics, ear drops, and regular ear cleanings, but may require surgery to remove the infected bone in serious cases.
How are middle ear infections treated in adults?
A middle-ear infection may be treated with: Antibiotics, taken by mouth or as ear drops. Medication for pain. Decongestants, antihistamines, or nasal steroids....They can lead to:Infection in other parts of the head.Permanent hearing loss.Paralysis of a nerve in your face.
Why do adults get otitis media?
Otitis media is another name for a middle ear infection. It means an infection behind your eardrum. This kind of ear infection can happen after any condition that keeps fluid from draining from the middle ear. These conditions include allergies, a cold, a sore throat, or a respiratory infection.
How is recurrent otitis media treated in children?
Treatment with systemic antibiotics is required in recurrent episodes of acute otitis media. A cautious attitude is recommended due to antibiotic resistance. Antibiotics also provide effective prophylaxis for rAOM. Topical treatment with ear drops is recommended in rAOM with otorrhea from tympanostomy tubes.
Which of the following children is at risk of recurrent otitis media OM )?
Although OM can occur at any age, 80-90% of cases occur in children younger than 6 years. Children who are diagnosed with AOM during the first year of life are much more likely to develop recurrent OM and chronic OME than children in whom the first middle ear infection occurs after age 1 year.
How is AOM diagnosed?
Your child's doctor may use one or more of the following methods to diagnose AOM:Otoscope. Your child's doctor uses an instrument called an otoscope to look into your child's ear and detect:Tympanometry. ... Reflectometry. ... Hearing test.
How long does amoxicillin help with otitis media?
Among children 6 to 23 months of age with acute otitis media, treatment with amoxicillin–clavulanate for 10 days tended to reduce the time to resolution of symptoms and reduced the overall symptom burden and the rate of persistent signs of acute infection on otoscopic examination.
What is acute otitis media?
Introduction. Acute otitis media is the most frequently diagnosed illness in children in the United States 1 and the most commonly cited indication for antimicrobial therapy in children 2; in the United States, most children with acute otitis media have routinely been treated with antimicrobial drugs.
How long does it take for atypical disease to improve?
Usually patients worsen between 3-5 days, followed by improvement.
How long can you wait to take amoxicillin for a child?
Mild cases with unilateral symptoms in children 6-23 months of age or unilateral or bilateral symptoms in children >2 years may be appropriate for watchful waiting based on shared decision-making. Amoxicillin remains first line therapy for children who have not received amoxicillin within the past 30 days.
How long does it take to treat bacteriuria in a child?
Duration of therapy should be 7-14 days in children 2-24 months. Antibiotic treatment of asymptomatic bacteriuria in children is not recommended.
Can prophylactic antibiotics be used for AOM?
Prophylactic antibiotics are not recommended to reduce the frequency of recurrent AOM. For further recommendations on alternative antibiotic regimens, consult the American Academy of Pediatrics guidelines. 3. Pharyngitis 4, 6. Recent guidelines aim to minimize unnecessary antibiotic exposure by emphasizing appropriate use ...
