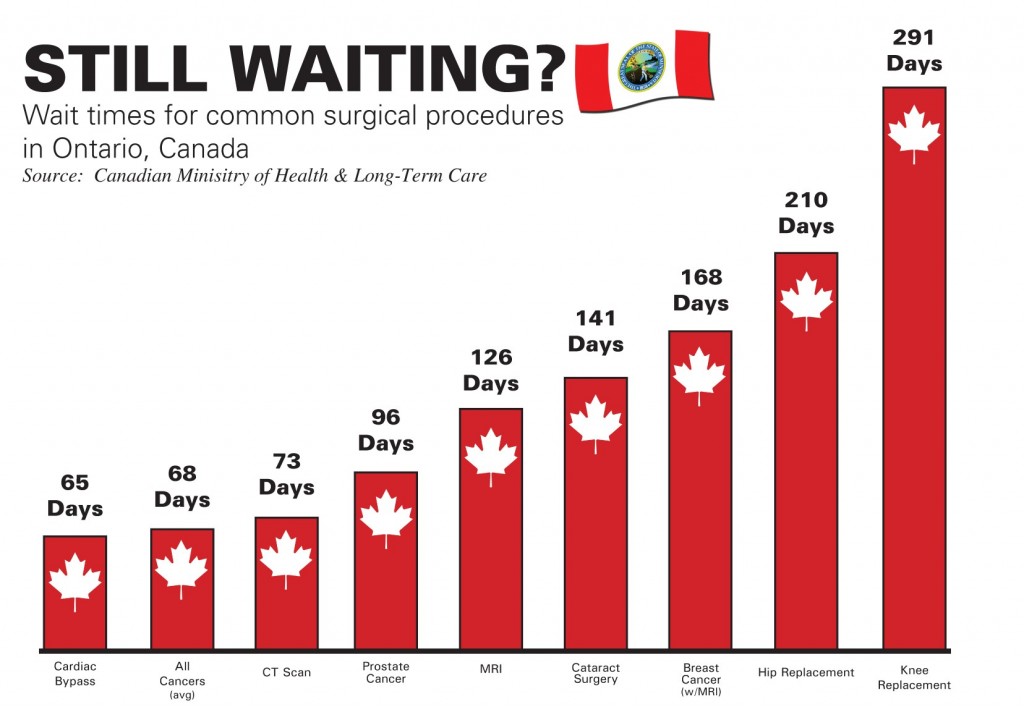
Canadian citizens and legal, long-term residents receive medical services through Medicare. Medicare is paid for through taxes, and there is no cost when you use medical care. This basic medical insurance provided by the government is governed by the provincial governments; the provinces have different regulations.
What is Medicare in Canada?
Medicare is a term that refers to Canada's publicly funded health care system. Instead of having a single national plan, we have 13 provincial and territorial health care insurance plans. Under this system, all Canadian residents have reasonable access to medically necessary hospital and physician services without paying out-of-pocket.
How do I get free health care in Canada?
To access free health care, you need to apply for a provincial health card. Once you are approved, you will receive your provincial health card. The health card proves that you are covered by a provincial health care program. You will have to show your health card each time you visit a doctor or receive any medical care.
Can a Canadian get medical care outside of Canada?
Receiving medical care outside Canada Travellers from Canada may access medical care in other countries due to a medical emergency as a result of an injury or illness. However, they may also travel to receive specific medical care, known as “medical tourism.”
How long do I have to declare medical treatment outside Canada?
For at least 12 months after returning, tell any health care professional you may consult that you have received medical treatment outside of Canada. Thank you for your help! You will not receive a reply.

Can I use my Medicare card in Canada?
In general, Medicare only covers recipients while in the United States. This means that if you have Medicare and you travel to Canada, your healthcare costs will not be covered, even if the services or medications provided would normally be covered in the United States.
Can I use my Medicare if I live in Canada?
Remember, you can have Medicare while you live abroad, but it will usually not cover the care you receive. Most people qualify for premium-free Part A, meaning you will pay nothing for coverage. If you must pay a premium for Part A, be aware of the high monthly cost for maintaining Part A coverage.
Will Medicare cover me if I move to Canada?
Yes. Because Medicare has limited coverage of health care services outside the U.S., you can choose to buy a travel insurance policy to get more coverage. An insurance agent or travel agent can give you more information about buying travel insurance.
Does Medicare cover emergencies in Canada?
Medicare will pay for emergency services in Canada if you are traveling a direct route, without unreasonable delay, between Alaska and another state, and the closest hospital that can treat you is in Canada.
Does Medicare cover U.S. citizens living abroad?
Medicare does not usually cover care that you receive outside the United States. However, it may be beneficial to enroll in Parts A and B if you live abroad on a temporary basis, or travel back to the U.S. frequently. Most people qualify for premium-free Part A, meaning you will pay nothing for coverage.
Do any countries accept U.S. Medicare?
Here's what you need to know:Medicare doesn't normally cover healthcare costs outside the U.S. (The official definition of the U.S. includes the 50 states and the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico, Guam, the U.S. Virgin Islands, American Samoa, and the Northern Mariana Islands—you can use your Medicare benefits in ...
What is not covered by Medicare in Canada?
The Canadian public healthcare system, known as Medicare, is funded by taxes. It covers all care deemed “medically necessary,” including hospital and doctor visits, but generally does not provide prescription, dental, or vision coverage.
Is Medicare in Canada free?
Medicare includes coverage for hospital services such as surgery, hospital fees and most importantly, doctors' visits, and is available for Canadians all across the provinces and territories.
Who is eligible for Medicare in Canada?
all Canadian citizensMedicare is available to all Canadian citizens and permanent residents. If you are on a Temporary Resident Visa (visitor, student, or work) you do not have medicare and you are responsible for making sure you have some kind of medical coverage, most likely from your home country.
Does any Medicare plans cover international travel?
Medicare itself doesn't cover healthcare during international travel. However, some Medicare Advantage (Part C) plans may cover certain emergencies if they occur outside the United States. In most cases though, you'll need supplemental travel insurance.
Do I need travel insurance if I have Medicare?
Do I need travel insurance if I have Medicare? The short answer: Yes. According to Medicare.gov, health care you get while traveling outside the U.S. isn't covered.
Is Medicare accepted everywhere?
If you have original Medicare (Medicare Part A and Medicare Part B) you are covered anywhere in the United States. You must, however, use hospitals and doctors that accept Medicare. Anywhere in the United States includes: all 50 states.
What is Medicare in Canada?
Medicare is a term that refers to Canada's publicly funded health care system. Instead of having a single national plan, we have 13 provincial and territorial health care insurance plans. Under this system, all Canadian residents have reasonable access to medically necessary hospital and physician services without paying out-of-pocket.
How long can you use your health insurance card if you move to another province?
When a resident moves to another province, they can continue to use their original health care insurance card for 3 months. This gives them enough time to register for the new plan and receive their new health insurance card.
What is the role of the provincial and territorial governments in Canada?
The provincial and territorial governments are responsible for the management, organization and delivery of health care services for their residents. The federal government is responsible for: setting and administering national standards for the health care system through the Canada Health Act. providing funding support for provincial ...
Who must insure all medically necessary services?
The provincial and territorial plans must insure all medically necessary services provided by: hospitals. physicians. dentists, when the service must be performed in a hospital. Medically necessary services are not defined in the Canada Health Act.
Do provincial health insurance plans have to meet the health care standards?
Provincial and territorial health care insurance plans must meet the standards described in the Canada Health Act. This is necessary to get their full payment under the Canada Health Transfer.
How long does it take to get health insurance after moving to another province?
Residents moving from one province/territory to another continue to be covered by their "home" province/territory during any minimum waiting period, not to exceed three months , imposed by the new province/territory of residence. After the waiting period, the new province/territory of residence assumes your health care coverage.
What is a resident in Canada?
The Act further defines a resident as: "a person lawfully entitled to be or to remain in Canada who makes his home and is ordinarily present in the province, but does not include a tourist, a transient or a visitor to the province.". Therefore, residence in a province or territory is the basic requirement for provincial/territorial health insurance ...
What services are charged for uninsured physicians?
Uninsured physician services for which patients may be charged include prescription renewals by telephone; the provision of medical certificates required for work, school, insurance purposes and fitness clubs; testimony in court; and cosmetic services.
How long does it take to get health insurance back?
A three-month waiting period is usually applied before coverage is reinstated. For information on requirements and conditions for reinstating health insurance coverage, contact the Ministry of Health of the province or territory to which you intend to return.
Does Canada have a national health insurance plan?
Canada does not have a single national health care plan, but rather a national health insurance program, which is achieved by a series of thirteen interlocking provincial and territorial health insurance plans, all of which share certain common features and basic standards of coverage. Under the Canada Health Act, ...
How to get free health care in Canada?
How to access free health care in Canada. To access free health care, you need to apply for a provincial health card. Once you are approved, you will receive your provincial health card . The health card proves that you are covered by a provincial health care program. You will have to show your health card each time you visit a doctor ...
How is health care paid in Canada?
In Canada, public health care is paid for through tax money. Basic health care services, like hospital visits and medical treatment, are free. All Canadian citizens and permanent residents may apply for public health insurance. This insurance can save you money and provide you and your family peace of mind when it comes to health care.
What are some examples of medical services not covered by provincial health care programs?
Necessary surgery. Laboratory and other diagnostic procedures. Some examples of the hospital and medical services not covered by provincial health care programs include: Most prescription drugs. Dental services. Eye exams and eyewear, like glasses or contacts.
What is a benefits package?
A benefits package will cover some, or all of the costs for dental, medications, and other services not covered by a government healthcare program. Canadians in every province can purchase additional private health insurance to cover services not covered by a government health care program, or an employer’s health care benefits program.
What is covered by the provincial health care system?
In general, government health care programs cover things such as: Appointments with your family doctor. Visits to walk-in clinics and some other health care providers.
Where to go if you have a medical emergency?
If you have a medical emergency, go to the emergency room at the nearest hospital. For non-emergencies, you can schedule an appointment with your family doctor to get treatment or a referral to a health care specialist.
Do you have to pay for a replacement health card?
You may have to pay a small replacement fee. It’s a good idea to carry your health card in your wallet at all times in case of a medical emergency. In an emergency, hospitals will treat you without seeing your card first but, you will have to show your card later if you want the province to cover your hospital bills.
What is the Canadian Medicare system?
The Canadian Medicare takes into consideration the needs of children, disabled citizens and the elderly. For senior citizens or veterans and disabled children, there is a need for special care and attention, and the health care system was designed with this in mind.
What are the benefits of Canada's health care system?
Available to everyone. The health care system which is also called Medicare in Canada is offered to all citizens and is not determined by the finances of individuals. 2. Health Education Programs. The Canadian government through the provincial and territorial governments runs health educational programs regularly.
How is Medicare paid?
Medicare is paid for through taxes, and there is no cost when you use medical care . This basic medical insurance provided by the government is governed by the provincial governments; the provinces have different regulations. The system is governed and developed by Medicare in each Province of Canada and each province has control over ...
What percentage of Canadians have extended health insurance?
Canadians tend to focus on the publicly funded side of the health system, although 60 percent of them have extended coverage, usually through employers or unions. But with baby boomers retiring — and the rise of contracting out — more will be paying out of pocket for those extras in the future.
Is health insurance free in Canada?
Health Insurance. The Canadian health care system has been a resounding success since its introduction in the country in 1967. The publicly funded health care system provides health services that are mostly free to Canadian citizens and managed and administered on a provincial and territorial level guided under the Canadian Health Act.
Does Canada pay for prescriptions?
However, the public funded healthcare system does not cover prescription drugs, home care or long-term care, prescription glasses or dental care, therefore Canadian citizens pay for these services either out of their pockets or through private medical insurance and employer-sponsored plans.
What are the two main classes of medications in Canada?
In Canada, there are two main classes of medications: Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs: These drugs can be legally purchased by any consumer without written permission from a doctor. Prescription drugs: These are drugs that are only meant for use by the individual to whom they are prescribed.
How long does it take to get on a waitlist for a family doctor?
Pro-tip: Most provinces allow you to sign up for a waitlist for a family doctor, but this can take months or even years. It is often faster to contact clinics directly and ask if they are accepting new patients or to ask friends if their doctors are taking on new patients.
What is a walk in clinic?
Walk-in clinic (usually faster, short-term): A walk-in clinic allows patients to simply walk in and wait to see a doctor. If you need your prescription and you need it soon, you may want to go to a walk-in clinic. You can use Medimap to locate the walk-in clinic closest to you. However, walk-in clinics can have very long wait times.
Does Canada have universal health care?
While Canada is known for its free universal health care system, unfortunately this does not always extend to prescription drugs. If you are a temporary resident in Canada (visitor, worker, student) it is recommended that you have some kind of insurance.
Is prescription medication covered by the health care system?
Any prescription drugs that are administered while you’re in the hospital will be covered by the health care system, but any drugs that you get outside of the hospital setting — for example, prescription drugs you purchase at a pharmacy — will not be covered.
Looking for Medicine from Canada
Q. I have been searching online for legitimate Canadian pharmacies. They all require a prescription. My doctor says it is illegal for her to write a prescription for a Canadian pharmacy. What can I do?
Finding the Right Online Pharmacy
You are wise to be cautious about which online pharmacy you use. Some unscrupulous websites trade on the good reputation Canadian drugstores have earned. Make sure it is really a legitimate Canadian pharmacy before you send or fax your U.S. prescription. We tell you how in our Guide to Saving Money on Medicines.
How long after a blood transfusion can you return to Canada?
If you had injections or blood transfusions abroad, discuss testing for blood-borne infections with your health care professional. For at least 12 months after returning, tell any health care professional you may consult that you have received medical treatment outside of Canada.
How to make a decision about medical procedures abroad?
Consider their advice before making any decisions about having a medical procedure abroad. Make sure: you are healthy enough to travel. your routine immunizations are up-to-date. any ongoing medical conditions are well controlled. you have enough of any medication needed for the length of the trip.
What are the risks of medical care abroad?
serious illness or complications arising from medical care received abroad have been reported, including infections with multidrug resistant bacteria that are difficult to treat. standards for regulating drugs may be different than those in Canada and, as a result medication may be: unsafe. of poor quality.
Is hospital accreditation strict?
hospital accreditation standards may differ or not be as strict as in Canada. licensing standards may also differ for: nurses. doctors. pharmacists. infection prevention and control in medical facilities may not be regulated enough to ensure patient safety. bacterial infections resistant to antibiotic treatment are a global problem, ...