Tuberculosis is an airborne infectious disease treated with combination therapeutic regimens. Adherence to long-term antituberculosis therapy is crucial for maintaining adequate blood drug level. The emergence and spread of drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains are mainly favored by the inadequate medical management of the patients.
Full Answer
Why is it important to finish treatment for tuberculosis (TB)?
It is very important that people who have TB disease are treated, finish the medicine, and take the drugs exactly as prescribed. If they stop taking the drugs too soon, they can become sick again; if they do not take the drugs correctly, the TB bacteria that are still alive may become resistant to those drugs.
What are the treatment regimens for tuberculosis (TB)?
Of the approved drugs, the first-line anti-TB agents that form the core of treatment regimens are: Regimens for treating TB disease have an intensive phase of 2 months, followed by a continuation phase of either 4 or 7 months (total of 6 to 9 months for treatment).
Who should be treated for latent TB infection?
Treatment of latent TB infection should start after excluding the possibility of TB disease. Groups Who Should be Given High Priority for Latent TB Infection Treatment include: People with a positive TB blood test (interferon-gamma release assay or IGRA). HIV-infected persons.
What is a TB infection?
“TB” is short for a disease called tuberculosis. TB is spread through the air from one person to another. People who become infected with TB germs, but do not feel sick have what is called latent TB infection The reason a person does not feel sick is because the TB germs are latent, or inactive (sleeping), in their body.

How can you tell the difference between Crohn's and TB?
Introduction. Crohn's Disease (CD) is classically characterized by inflammation and ulceration at the ileocecal junction. Symptoms of CD include moderate to severe abdominal pain, bloody stool, and weight loss. Intestinal tuberculosis (ITB) can similarly present as inflammation and ulceration at the ileocecal junction.
How do you treat abdominal TB?
Abdominal TB needs to be treated with at least 3-4 anti TB drugs for the initial 2 months and subsequently 2 anti TB drugs for at least 7-10 months. The commonly used drugs during the initial 2 months therapy (intensification phase) are Isoniazid (INH), Rifampicin, Ethambutol and Pyrazinamide.
How is ileocecal TB diagnosed?
The most common site of GI TB is the ileocecal region, if the area can be reached with a flexible endoscope. A rapid diagnosis can be achieved if smear or culture results are positive or if caseating granulomas are seen in biopsy samples.
What is ileocecal tuberculosis?
Ileocecal tuberculosis is the most common site of gastrointestinal tuberculosis, which in turn is the third most common site of extrapulmonary tuberculosis.
How effective is TB treatment?
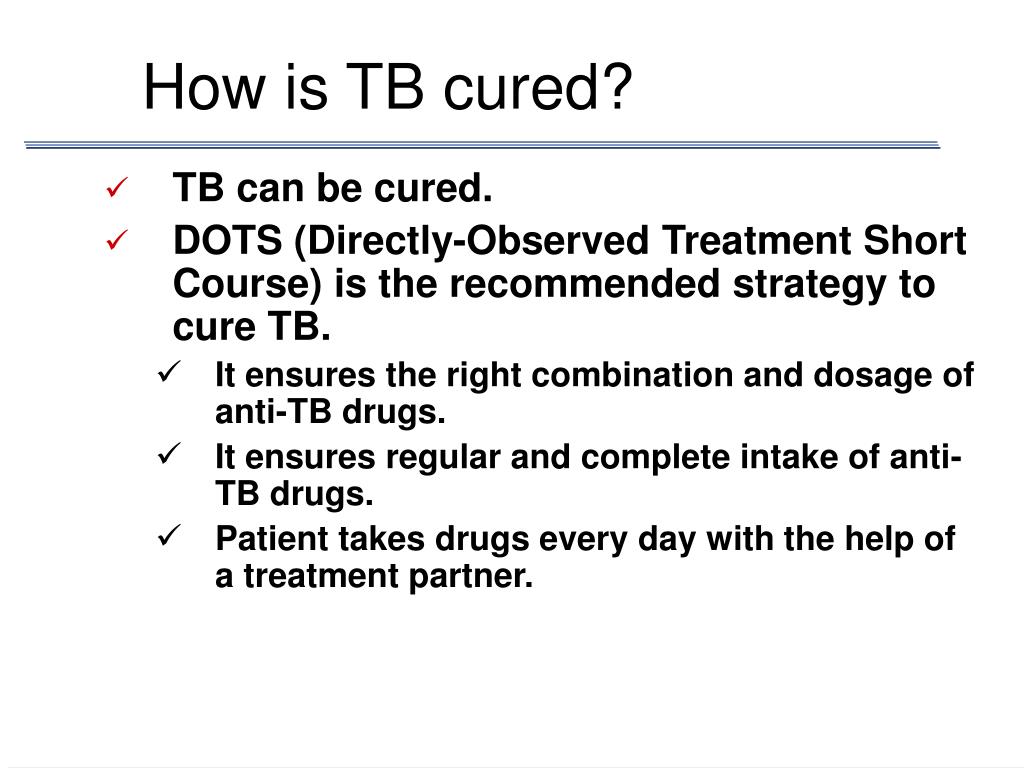
TB treatment is effective. Worldwide, nearly 90% of cases of TB and 48% of cases of drug-resistant TB are cured. However, treatment is not quick or easy. The length of treatment and side effects from the drugs used pose huge problems for TB patients and for global efforts to tackle the disease.
How do you know if TB treatment is working?
After taking TB medicine for several weeks, a doctor will be able to tell TB patients when they are no longer able to spread TB germs to others. Most people with TB disease will need to take TB medicine for at least 6 months to be cured.
How is ileocecal tuberculosis treated?
The treatment of choice for intestinal perforation TB is resection of the affected bowel segment followed by an end-to-end anastomosis (12). Anti-tuberculous therapy should be started as soon as possible with a four-drug regimen for 6 to 9 months (13).
What is intestine TB?
Gastrointestinal tuberculosis (TB) is a relatively uncommon form of TB which is defined as infection of the peritoneum, abdominal organs or abdominal lymphatic system [1].
What causes abdominal TB?
Risk factors for development of abdominal TB include cirrhosis, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, diabetes mellitus, underlying malignancy, malnutrition, treatment with antitumor necrosis factor agents [6], corticosteroids, and use of continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis [7-11].
Why is TB common at ileocecal junction?
The most common site of gastrointestinal involvement is the ileocecal region which is involved in 64% of cases of gastrointestinal TB and is thought to be due to the abundant lymphoid tissue and the stasis of the stools around that segment.
What are the 3 types of tuberculosis?
Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that usually infects the lungs. It may also affect the kidneys, spine, and brain. Being infected with the TB bacterium is not the same as having active tuberculosis disease. There are 3 stages of TB—exposure, latent, and active disease.
How can TB cause intestinal obstruction?
The most common complication of abdominal tuberculosis is obstruction due to narrowing of the lumen by hyperplastic caecal tuberculosis, by strictures of the small intestine, which are commonly multiple, or by adhesions and emergency surgery has to be resorted for confirmation of the diagnosis or for relief of ...
Can abdominal TB be cured?
Most current guidelines recommend treating people that have abdominal TB with antituberculous treatment (ATT) for six months, but some clinicians treat for longer periods due to concerns that six months is not adequate to achieve cure and prevent relapse of the disease after the end of treatment.
Is abdominal TB fatal?
Abdominal TB leads to severe illness in adults and children, and can cause complications, such as bowel rupture, which can lead to death.
What are the symptoms of TB in stomach?
Symptoms of gastrointestinal TB are referable to the infected site and may include the following:Nonhealing ulcers of the mouth or anus.Difficulty swallowing (with esophageal disease)Abdominal pain mimicking peptic ulcer disease (with gastric or duodenal infection)Malabsorption (with infection of the small intestine)More items...
Is abdominal TB contagious?
Answers (1) No. Abdominal TB is not communicable.
Why is latent TB important?
Treatment of latent TB infection is essential to controlling TB in the United States because it substantially reduces the risk that latent TB infection will progress to TB disease.
Where is TB common?
From countries where TB is common, including Mexico, the Philippines, Vietnam, India, China, Haiti, and Guatemala, or other countries with high rates of TB. (Of note, people born in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, or Western and Northern European countries are not considered at high risk for TB infection, unless they spent time in a country ...
How many people have latent TB?
In the United States, up to 13 million people may have latent TB infection. Without treatment, on average 1 in 10 people with latent TB infection will get sick with TB disease in the future. The risk is higher for people with HIV, diabetes, or other conditions that affect the immune system.
What is a TST reaction?
People with a tuberculin skin test (TST) reaction of 5 or more millimeters who are: HIV-infected persons. Recent contacts to a patient with active TB disease. Persons with fibrotic changes on chest radiograph consistent with old TB. Organ transplant recipients.
Can TB be treated with LTBI?
Persons with no known risk factors for TB may be considered for treatment of LTBI if they have either a positive IGRA result or if their reaction to the TST is 15 mm or larger. However, targeted TB testing programs should only be conducted among high-risk groups.
Can TB spread to others?
People with latent TB infection do not have symptoms, and they cannot spread TB bacteria to others. However, if latent TB bacteria become active in the body and multiply, the person will go from having latent TB infection to being sick with TB disease.