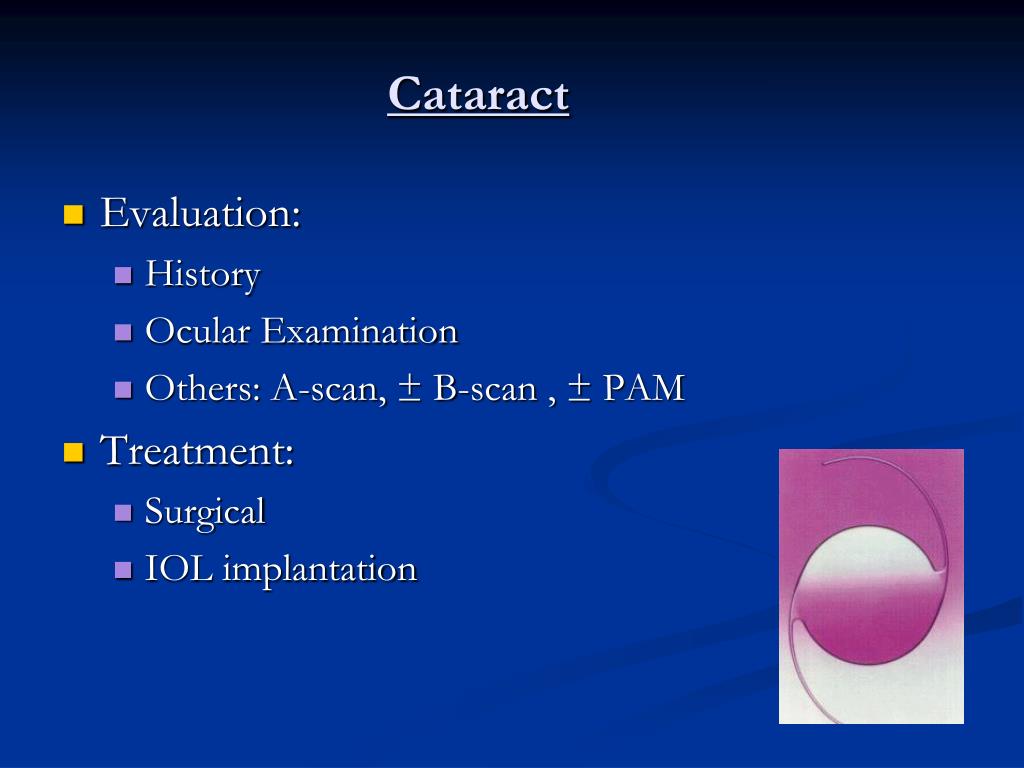
Surgery or laser treatment may, however, be initially considered in cases where there is severe glaucomatous damage, very high IOP or concern regarding patient compliance Systemic medications are only used as a temporary measure If the IOP reduction is still insufficient to reach the target IOP with 1 medication at maximum dose:
What is the first-line treatment for elevated intraocular pressure associated with glaucoma?
Typically, treatment for open-angle glaucoma begins with prescription eye drops designed to either reduce the production of aqueous in the eye or increase its drainage from the eye. These eye drops need to be used daily or several times a day. Since POAG is a chronic condition, you likely will need to use the drops for the rest of your life.
What is primary open angle glaucoma (POAG)?
The goal of treatment for open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension is to improve quality of life through reduction of intraocular pressure (IOP) to preserve visual function. Prostaglandins, as a newer class of ocular hypotensive agents, have been shown to be effective in IOP reduction by the primary mechanism of action of increase the uveoscleral outflow.
What is the treatment for open angle glaucoma?
May 14, 2014 · A recent JAMA Rational Clinical Examination systematic review of primary open-angle glaucoma diagnosis found that the risk of glaucoma was highest when examination revealed an increased cup-disk ratio (CDR), CDR asymmetry, disc hemorrhage, or elevated intraocular pressure. 11 Primary open-angle glaucoma was also more likely when there was a ...
What causes primary open-angle glaucoma?
Primary open-angle glaucoma was defined by the presence of a glaucomatous visual field defect. Additionally, the distinction was made between high-tension glaucoma, defined as POAG with an IOP of more than 21 mmHg, and normal-tension glaucoma, defined as …
What is the treatment of high IOP?
Glaucoma is treated by lowering your eye pressure (intraocular pressure). Depending on your situation, your options may include prescription eyedrops, oral medications, laser treatment, surgery or a combination of any of these.Oct 23, 2020
What happens if glaucoma pressure gets too high?
Vision loss from glaucoma occurs when the eye pressure is too high for the specific individual and damages the optic nerve. Any resultant damage cannot be reversed. The peripheral (side) vision is usually affected first.Aug 20, 2021
How can I lower my glaucoma IOP?
The medications available for reducing IOP in glaucoma patients include topical β-adrenergic antagonists (eg, timolol, betaxolol), carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (eg, dorzolamide, brinzolamide), cholinergics (eg, pilocarpine), α-adrenergic agonists (eg, brimonidine), prostaglandins (eg, latanoprost, travoprost), and ...
What is considered dangerously high eye pressure?
An IOP reading higher than 22 mm Hg is considered ocular hypertension. High eye pressure significantly increases your risk of damage to the optic nerve, causing glaucoma and permanent vision loss.
Is eye pressure of 50 high?
Eye pressure levels between 21-30 mmHg associated with glaucoma usually cause damage over a number of years. However, an IOP in the 40-50 mmHg range can lead to retinal vascular occlusion, a potentially serious condition in which blood vessels that serve the retina are blocked.
What is the success rate of laser iridotomy?
Success rates of laser iridotomy have been reported to be from 65-76%,7,8 and are relatively low in patients of east Asian descent. Identifying factors associated with successful laser iridotomy for patients with AACG would be quite helpful in designing a proper treatment plan for each patient after laser iridotomy.Dec 4, 2009
When do you treat IOP?
If your intraocular pressure is 28 mm Hg or higher, you are treated with medicines. After 1 month of taking the drug, you have a follow-up visit with your eye doctor to see if the medicine is lowering the pressure and there are no side effects.Jul 21, 2020
How do beta blockers reduce IOP?
Topical beta-blockers reduce the intraocular pressure (IOP) by blockade of sympathetic nerve endings in the ciliary epithelium causing a fall in aqueous humour production.
What is the drug of choice for glaucoma?
Brimonidine. Brimonidine is the a-2 agonist of choice in glaucoma treatment, which acts by decreasing the aqueous humor secretion and increasing the uveoscleral outflow. It does not cross the blood-brain barrier and is 30 times more selective for the a-2-adrenergic receptor than apraclonidine.
What medications increase eye pressure?
Steroids. Corticosteroids, or steroids, can raise eye pressure, especially in those persons who have open-angle glaucoma, first-degree relatives of those with open-angle glaucoma, elderly and young (<6 years) persons, those with type 1 diabetes and those with high myopia (short-sightedness).
How is IOP measured?
In most ophthalmologist's offices, eye pressure is measured using “Goldmann applanation tonometry,” and this is considered a “gold standard” eye pressure measurement. In this test, the eyes are anesthetized with numbing drops. In addition, a small amount of non-toxic dye is placed in the eye.Jul 7, 2021
What are the symptoms of high eye pressure?
Acute angle-closure glaucomaSevere headache.Eye pain.Nausea and vomiting.Blurred vision.Halos around lights.Eye redness.Oct 23, 2020
What are the risk factors for open angle glaucoma?
Some of the risk factors for primary open-angle glaucoma have been extensively described and studied, including elevated intraocular pressure, advancing age, family history, African ancestry, myopia, and perhaps presence of certain systemic diseases, such as diabetes and hypertension.
How old do you have to be to get a baseline exam for glaucoma?
It is recommended that people over 40 years of age should receive a baseline examination.
What is the anterior chamber angle of POAG?
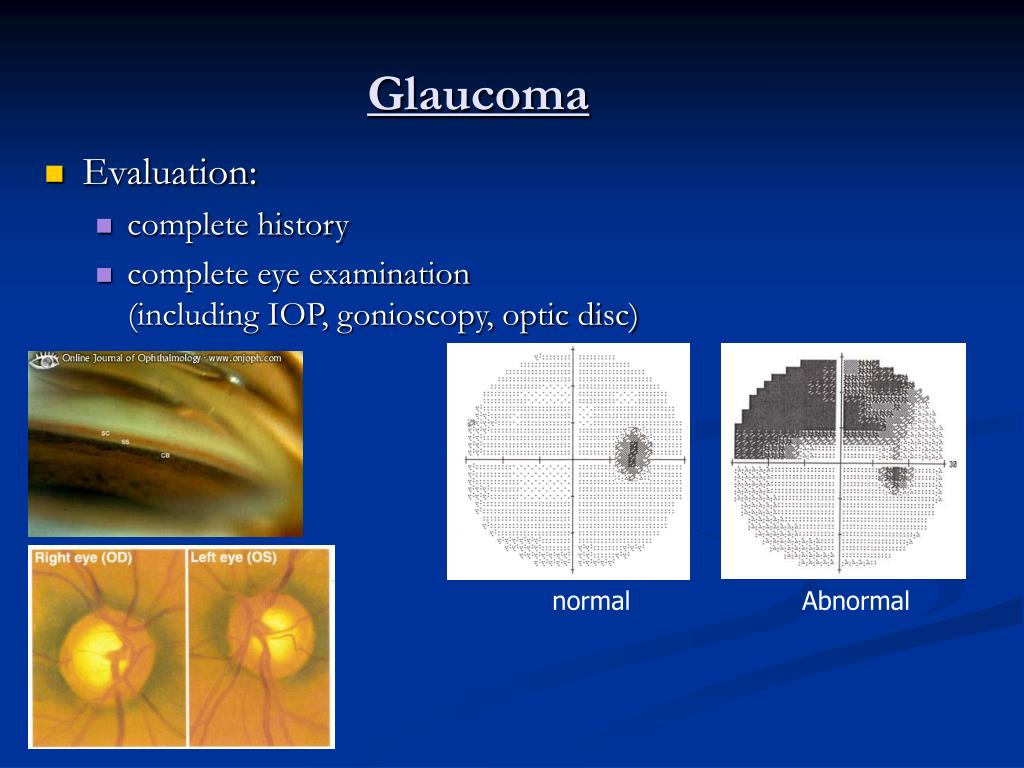
By definition, the anterior chamber angle of POAG patients is open. The Van Herick test provides an estimate of anterior chamber depth peripherally and reveals an irido-corneal distance of greater than 25% of corneal thickness. Gonioscopy is essential to make the diagnosis of POAG and should be performed on the initial visit. Various classifications systems have been described to assess the extent of an open angle. Gonioscopy helps to differentiate POAG from secondary open angle glaucomas (such as pigment dispersion in pigmentary glaucoma or neovascularization of the angle in neovascular glaucoma).
What is POAG in ophthalmology?
This definition does not include IOP - i.e. POAG is diagnosed based on signs of glaucomatous optic neuropathy regardless of the level of IOP. Patients can be classified as normal tension glaucoma (NTG) or high tension glaucoma (HTG) based on the IOP. Sometimes an IOP spike may be missed in a clinical setting. In these cases, if HTG is suspected, measurement of IOP at hourly intervals throughout the day, beginning in the early morning, may be indicated. This is termed phasing. If a patient has all the features of POAG but consistently normal IOPs (less than or equal to 21 mmHg), this is considered NTG (discussed further in another section).
What is a POAG?
Primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) is a subset of the glaucomas defined by an open, normal appearing anterior chamber angle and raised intraocular pressure (IOP), with no other underlying disease . If there is an identifiable underlying cause for raised IOP, this is termed secondary glaucoma.
What is the most common cause of blindness worldwide?
It is a progressive condition and is the most common cause of irreversible blindness worldwide. Primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) is a subset ...
What are the characteristics of optic disc damage?
Characteristics signs of optic disc damage. Visual function loss on perimetry. Frequently, the diagnosis is not clear-cut and the patient may present with some risk factors and signs, but not others. In such cases, the patient may be labeled as a glaucoma suspect.
What percentage of glaucoma cases are caused by optic nerve degeneration?
Learn about the most common type of glaucoma that accounts for 70 - 90 percent of all cases. Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases in which the optic nerve degenerates. The optic nerve transmits all of the visual information from the retina, the light-sensing tissue of the eye, to the brain. The damage to the optic nerve is generally thought ...
What is POAG in the eye?
The angle is the location where the aqueous humor (the fluid that is produced inside the eye) drains out of the eye into the body’s circulatory system. POAG is chronic, progressive, and occurs in both eyes, although one eye may have severe disease, and the other eye has very little or early disease.
What is the purpose of an eye doctor?
An eye doctor will perform a comprehensive eye exam, including an eye pressure measurement and a dilated exam of your optic nerve and retina. He or she will examine your drainage angle using a special mirrored lens. As part of the evaluation, you will be asked to perform a test of your side (peripheral) vision.
Can glaucoma evolve over time?
It is important to note that sometimes the diagnosis of glaucoma evolves over time when there are demonstrated changes from one exam to the next. In cases when the diagnosis is less clear, you may be diagnosed as a “glaucoma suspect.”.
Is glaucoma a risk factor?
Family history of glaucoma is an important risk factor. Several studies of large populations of patients have demonstrated that having a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) with glaucoma increases the risk of having glaucoma. This is an important fact to remember because if you have glaucoma, it would be prudent to encourage your first-degree relatives (if children, when they are adults over 40), to have a comprehensive eye exam with an eye doctor.
Does glaucoma affect your vision?
The goal of treatment is to slow the disease so that glaucoma will not impact your vision-related quality of life and to do so without intolerable side effects. Therefore, it is important for you to review your specific situation with your eye doctor, and discuss treatment options and their risks and benefits.
Is POAG a progressive disease?
POAG is chronic, progressive, and occurs in both eyes, although one eye may have severe disease, and the other eye has very little or early disease. This is one of the reasons patients report no symptoms since the “good” eye can often compensate for the “bad” eye until the disease reaches very advanced stages.
What is the treatment for glaucoma?
Eye pressure control also plays a major role in the treatment of glaucoma. Lowering eye pressure is the only treatment we currently have, whether through medications, laser, or surgery.
What is the relationship between glaucoma and eye pressure?
When people hear the word “glaucoma,” many of them connect the eye disease with elevated eye pressures ( also known as intraocular pressure or IOP). However, the relationship between glaucoma and eye pressure is complicated and has changed over time. Historically, glaucoma was identified as a disease in which the eye was firm or hard due ...
What is the normal pressure of a person with glaucoma?
If someone has normal-tension or normal-pressure glaucoma, their eye pressure has never been recorded above 21 mmHg, yet they still have optic nerve damage. Does this mean that their eye pressure has never been greater than 21 mmHg? That is difficult to say since a single eye pressure measurement at any given time on any given day in the ophthalmologist’s office is a tiny “snapshot” of what the eye pressure truly is.
How many people have glaucoma?
3 million Americans have glaucoma— and only half know they have it. We are the top private nonprofit funder of glaucoma research. BrightFocus makes innovative science possible around the world— 1,625 research projects involving more than 5,363 scientists in 25 countries. You can make a difference.
Does glaucoma progress slowly?
However, your glaucoma continues to progress slowly. In that case, despite the initial eye pressure lowering, your ophthalmologist may determine that this new lower eye pressure is still “too high” and your eyes need to have even lower eye pressures. Finally, it is important to realize that most patients with the most common form of glaucoma, ...
Is eye pressure too high for optic nerve?
Third, the eye pressure that is “too high” for your optic nerve is sometimes determined over time. Let’s say you begin treatment with an eye drop to lower eye pressure, and it is successful in lowering your eye pressure by 20 percent. However, your glaucoma continues to progress slowly. In that case, despite the initial eye pressure lowering, ...
Is 21 mmHg a good eye pressure?
First, we know that statistically speaking, having eye pressures over 21 mmHg (millimeters of mercury) is not very common in a generally healthy population. We also know that eye pressure tends to increase as we get older since the drainage system does not function as well. Second, we know that an optic nerve that is healthy can withstand ...
How many people have open angle glaucoma?
Open-angle glaucoma is the most common type in the United States, where 9 in 10 people with glaucoma have the open-angle type. Many people don’t have any symptoms until they start to lose their vision, and people may not notice vision loss right away.
What is the treatment for glaucoma?
Treatments: Medicines, laser treatment. Angle-closure glaucoma, also called narrow-angle or acute glaucoma, is a medical emergency . Go to the doctor or emergency room immediately if you suddenly have: Intense pain in your eye. Nausea. Red eyes. Blurred vision.
What happens when the pigment in your eye flakes off?
Pigment dispersion syndrome happens when the pigment (color) from your iris (the colored part of your eye) flakes off. The loose pigment may block fluid from draining out of your eye, which can increase your eye pressure and cause pigmentary glaucoma.
What is the name of the condition in which a baby's eye keeps fluid from draining?
Congenital glaucoma. Treatments: Medicines, surgery. Some babies are born with glaucoma — this is called congenital glaucoma. About 1 out of 10,000 babies born in the United States have a defect (problem) in the eye that keeps fluid from draining normally.
What is the name of the eye disease that causes loss of peripheral vision?
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that are usually characterized by damage to the optic nerve and gradual vision loss that starts with losing peripheral (side) vision. People who have high eye pressure are at higher risk for glaucoma.
What causes a neovascular glaucoma?
It’s usually caused by another medical condition, like diabetes or high blood pressure.
What causes a sharp pain in the eye?
Red eyes. Blurred vision. In this type of glaucoma, the outer edge of the iris (the colored part of your eye) blocks fluid from draining out of the front of the eye. The fluid builds up quickly, causing a sudden increase in eye pressure.
Is there a secondary glaucoma?
There was no evidence of a secondary glaucoma. This might look like garden-variety primary open-angle glaucoma, but this combination of characteristics is pretty atypical, and that’s why I would argue that it’s a subset of primary open-angle glaucoma that deserves it’s own category.
Does African heritage cause glaucoma?
At this point, we don’t know the reason.
Is POAG a low pressure?
Clearly, POAG can occur across a broad spectrum of intraocular pressures. Using terms such as low-pressure or normal-tension glaucoma is also misleading; it suggests that these individuals and high-tension glaucoma patients have different diseases, when in fact they may have overlapping pathologic features. Here, I’d.

Summary
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis of POAG requires assessment of : 1. Intraocular pressure 2. Open- normal appearing anterior chamber angle 3. Characteristics signs of optic disc damage 4. Visual function loss on perimetry Frequently, the diagnosis is not clear-cut and the patient may present with some risk factors and signs, but not others. In such cases, the patient may...
Management
- Vision loss from POAG is irreversible. Management is, therefore, aimed at slowing the progression of the disease, thereby maintaining optimum visual function.
Additional Resources
- International Glaucoma Association
- NICE (National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence) guidelines
- European Glaucoma Society
- Boyd K, McKinney JK. Glaucoma. American Academy of Ophthalmology. EyeSmart® Eye health. https://www.aao.org/eye-health/diseases/glaucoma-list. Accessed March 13, 2019.
References
- Denniston A, Murray P. Oxford Handbook of Ophthalmology. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press; 2006:276-277.
- Rhee D. Glaucoma: Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Ophthalmology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2002:204-229.
- Schacknow P, Samples J. The Glaucoma Book: A Practical, Evidence-Based Approach to Pati…
- Denniston A, Murray P. Oxford Handbook of Ophthalmology. Oxford, United Kingdom: Oxford University Press; 2006:276-277.
- Rhee D. Glaucoma: Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Ophthalmology. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2002:204-229.
- Schacknow P, Samples J. The Glaucoma Book: A Practical, Evidence-Based Approach to Patient Care. New York, NY: Springer; 2010:399-420.
- Stamper R, Lieberman M, Drake M. Becker-Shaffer’s Diagnosis and Therapy of the Glaucomas. 8th Edition. New York, NY: Mosby; 2009:239-265.