
Medication
Sep 02, 2016 · The ingestion of excessive amounts of vitamin D 3 (or vitamin D 2) results in hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria due to the formation of supraphysiological amounts of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] that bind to the vitamin D receptor, albeit with lower affinity than the active form of the vitamin, 1,25(OH) 2 D, and the formation of 5,6-trans 25(OH)D, which binds …
Procedures
Jan 03, 2016 · Hyperphosphatemia-induced hypocalcemia inhibits vitamin D bioactivation in the kidney and the resulting low 1,25(OH)2 vitamin D levels may result in increased PTH secretion. Secondary hyperparathyroidism from long-term hyperphosphatemia has been well described and is usually associated with renal insufficiency.
Nutrition
Jan 01, 2021 · Hypercalcemia is frequently encountered in malignancies and carries a poor prognosis. Aggressive hydration and bisphosphonates are the basis of treatment. Hypocalcemia is managed with the replacement of Ca +2, vitamin D, and Mg (if indicated). However, excessive replacement of Ca +2 and vitamin D should be avoided.
Do high doses of vitamin D supplements lead to hypercalcemia?
Bone resorption also can be reduced by getting patients out of bed to stand or walk. Glucocorticoids may be effective in patients with hypercalcemia associated with high levels of vitamin D, such as sarcoidosis, some lymphomas, or vitamin D intoxication. Patients with mild to moderate hypercalcemia may be asymptomatic.
Why does vitamin D need calcium and phosphorus?
Nov 02, 2011 · Due to vitamin D's integral role in the absorption of calcium, more severe vitamin D deficiency may result in hypocalcemia that may vary in clinical manifestations. In general, hypocalcemia has a spectrum of clinical manifestations. In mild or chronic hypocalcemia, symptoms may be few, such as numbness or muscle cramps, or they may be absent.
Is vitamin D really a vitamin or hormone?
Dec 12, 2012 · It is also recommended that sufficient vitamin D supplementation be given before and after zoledronic acid infusion in order to ensure and maintain adequate vitamin D levels. 3 In spite of the above recommendations, and in spite of the several cases reported in the literature of symptomatic hypocalcemia due to post-intravenous bisphosphonate therapy where vitamin D …
What are the complications of vitamin D deficiency?
PTH is needed for vitamin D activation. The ionized calcium in the extracellular fluid is the principal regulator of PTH secretion. Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption of calcium from small intestine. Hypercalcemia can affect the kidney (nephrolithiasis), bones (osteoporosis) and overall wellbeing (leading to malaise, fatigue, confusion).
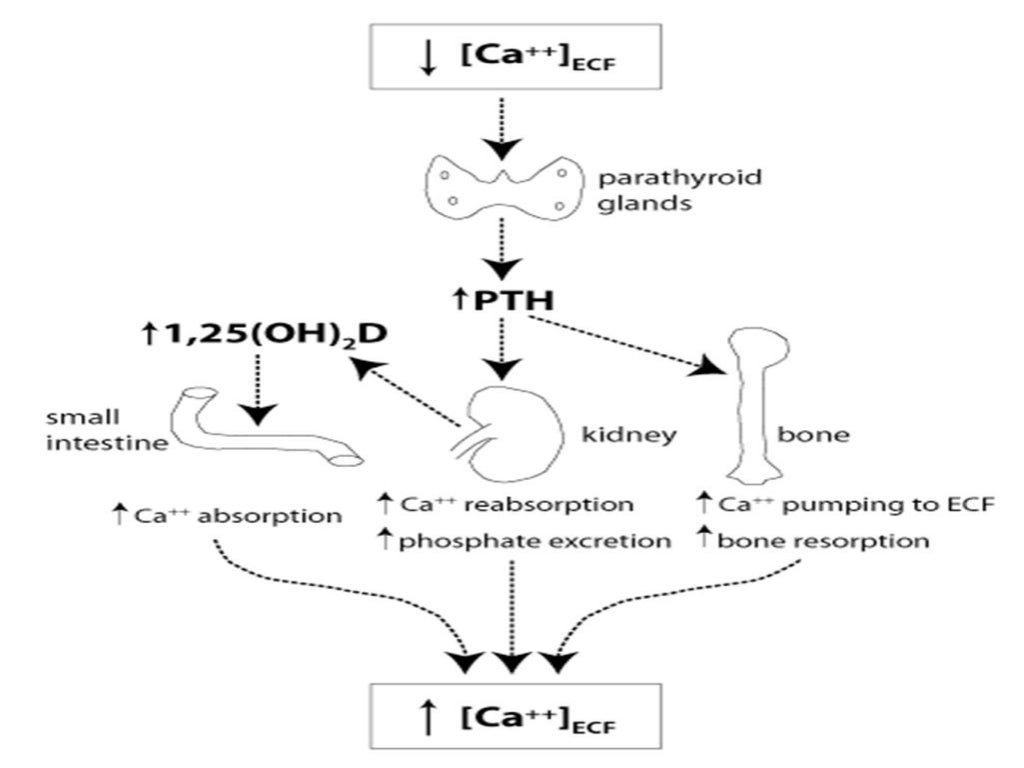
How does vitamin D help hypocalcemia?
Vitamin D is required for the intestinal absorption of calcium. Sunlight is the prime source of vitamin D. However, in our current lifestyle, exposure to sunlight is less and food alone might not be sufficient, thereby leading to hypocalcemia.
Does vitamin D Help with hypercalcemia?
2 Vitamin D supplementation has been proposed as a viable treatment option for PHPT despite concerns of further aggravating hypercalcemia. 3 Preliminary studies indicate that vitamin D replacement in mild PHPT reduces parathyroid levels significantly without exacerbating hypercalcemia.
Does vitamin D deficiency cause hypercalcemia or hypocalcemia?
Vitamin D deficiency can cause mild hypercalcemia but can also mask underlying primary hyperparathyroidism—as it did in this case. A Tc-99 sestamibi parathyroid scan will often localize a parathyroid adenoma.
Should you take vitamin D if you have hypercalcemia?
Monitored vitamin d therapy safe for patients with high blood calcium levels. Summary: Patients with a gland disorder that causes excessive calcium in their blood who also have vitamin D deficiency can safely receive vitamin D treatment without it raising their calcium levels, a new study has determined.Jun 26, 2012
How does Vit D cause hypercalcemia?
The ingestion of excessive amounts of vitamin D3 (or vitamin D2) results in hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria due to the formation of supraphysiological amounts of 25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] that bind to the vitamin D receptor, albeit with lower affinity than the active form of the vitamin, 1,25(OH)2D, and the ...
How does vitamin D affect calcium?
When vitamin D level is low, the absorption of calcium in the intestines becomes less, which then causes the level of calcium in the blood to go down. As a consequence the parathyroid glands become more active and produce more PTH that causes calcium to come out of the bones, therefore weakening the bones.
Can hypocalcemia cause vitamin D deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency or resistance interferes with these processes, sometimes causing hypocalcemia and hypophosphatemia. Since hypocalcemia stimulates the release of parathyroid hormone (PTH), however, the development of hypocalcemia is often masked.Jul 6, 2021
What is the best treatment for hypercalcemia?
Aggressive intravenous rehydration is the mainstay of management in severe hypercalcemia, and antiresorptive agents, such as calcitonin and bisphosphonates, frequently can alleviate the clinical manifestations of hypercalcemic disorders.May 1, 2003
What is the prevalence of hypercalcemia?
Incidence and prevalence of calcium metabolism disorders. Hypercalcemia is fairly common with a prevalence of approximately 1-4% in the general population and 0.17-3% in hospitalized populations [4]. Hypocalcemia is significantly more prevalent in hospitalized patients (10-18%).
What are the three forms of calcium?
The three different forms of serum calcium. Complexed calcium is bound to anions such as citrate, oxalate, carbonate, and phosphate. Intracellular Ca+2 is bound to calmodulin and other Ca+2-binding proteins. Hypoalbuminemia will lead to hypocalcemia due to a decrease in protein-bound Ca+2.
How much Ca+2 is in the human body?
The human body contains about 1,000-1,300 g of Ca+2, making Ca+2 the fifth most abundant element in the body [1]. About 99.3% of total body Ca+2 is in the bone (skeleton) and teeth, 0.6% is in soft tissues, and 0.1% resides in the extracellular fluid (ECF), including 0.03% in plasma [4]. Intracellular Ca+2 concentration is very low (about 100 nM), ...
What is milk alkali syndrome?
Milk-alkali syndrome (calcium-alkali syndrome) is caused by increased intestinal absorption of Ca+2 due to high intake of Ca+2 and vitamin D , especially when taken with antacids (alkali) [32,33]. It is associated with the kidneys' inability to excrete excess Ca+2. Patients can also have nephrocalcinosis [8].
What is the function of the CaSR?
The CaSR is a G protein-coupled receptor that regulates PTH secretion from the parathyroid glands. The CaSR senses extracellular ionized Ca+2. When serum Ca+2 is high, the CaSR is activated with a subsequent increase in renal Ca+2 excretion (calciuria) and inhibition of PTH secretion [7].
What causes hypercalcemia?
Severe hypercalcemia is a potentially life-threatening complication of several diseases. Most commonly it is caused by cancers that enhance bone resorption. Impaired renal calcium excretion resulting from a combination of volume contraction and calcium-induced renal injury (nephrocalcinosis) plays a critical role in the genesis and aggravation ...
How long does it take for calcium to be reduced?
One of these agents in combination with volume expansion can reduce serum calcium concentrations to near normal in most patients within 3 to 6 days.
Can glucocorticoids cause hypercalcemia?
Glucocorticoids may be effective in patients with hypercalcemia associated with high levels of vitamin D, such as sarcoidosis, some lymphomas, or vitamin D intoxication. Patients with mild to moderate hypercalcemia may be asymptomatic.
Does calcitonin help with bone resorption?
Combining calcitonin with plicamycin or a bisphosphonate can enhance the rate of decline of the serum calcium level. Bone resorption also can be reduced by getting patients out of bed to stand or walk.
What is vitamin D hypercalcemia?
Vitamin D Hypercalcemia: Here’s What You Need to Know. Hypercalcemia is a medical condition that causes calcium in the blood to surpass a normal level. Too much calcium can result in bone weakness, kidney stones, and heart and brain disruptions. Hyperparathyroidism (HPT) is one of the leading causes of hypercalcemia.
How much vitamin D is safe?
It also points out that 1,000 to 2,000 IU of vitamin D is safe and helps ensure the blood maintains an adequate amount of vitamin D to support various body functions. Conversely, too much vitamin D may actually cause hypercalcemia and therefore symptoms include: ● Depression. ● Fatigue.
Who is the doctor for parathyroid surgery?
Dr. Larian is available to discuss parathyroid gland surgery and its benefits and help patients determine if they qualify for this procedure. To learn more or to schedule a consultation with Dr. Larian, please contact us online or call us today at 310.461.0300.
What is the role of the parathyroid gland?
The parathyroid glands are responsible for calcium regulation in the body. They produce parathyroid hormone (PTH) to help manage calcium in the body. But, if one or more of the parathyroid glands malfunctions, they may produce an excess amount of calcium. In this instance, HPT and hypercalcemia can occur.
Can vitamin D be taken in the body?
Ultimately, vitamin D supplementation can do harm in the body, if not monitored or done properly. . If people are considering vitamin D supplements, they should first consult with a doctor. This allows people to determine if vitamin D supplements can safely and effectively be incorporated into an everyday diet.
Is vitamin D good for your skin?
The vitamin is also delivered to the skin via natural sunlight. The body uses vitamin D to promote calcium absorption in the gut. Additionally, vitamin D supports bone growth and remodeling and the neuromuscular and immune functions. Clearly, vitamin D is beneficial, regardless of how it is obtained. On the other hand, there may be instances in ...
Abstract
Options for chronic treatment of hypoparathyroidism include calcitriol, recombinant human parathyroid hormone, and high-dose vitamin D (D 2 ). D 2 is used in a minority of patients because of fear of prolonged hypercalcemia and renal toxicity. There is a paucity of recent data about D 2 use in hypoparathyroidism.
Materials and Methods
Patients with hypoparathyroidism who were treated at the University of Maryland Medical Center between 1 January 2003 and 1 January 2013 were identified from billing records (inpatient and outpatient), using the ICD-9 code for hypoparathyroidism, after obtaining Institutional Review Board approval.
Results
The initial list of potential participants received from our billing department contained 155 patient names. Of these, no records were available in our EMR for 52, so these patients were excluded.
Discussion
Currently only a minority of patients with hypoparathyroidism are treated with ergocalciferol due at least partially to a concern for potential toxicity given its long biological half-life ( 9 ). As a result, calcitriol is the most commonly used treatment, in the United States, with use of recombinant human parathyroid hormone increasing.
Conclusions
We found no evidence of higher serum creatinine in patients with hypoparathyroidism who were chronically treated with D 2 compared with calcitriol. Additionally, we observed significantly less morbidity from hypocalcemia in patients who were treated with D 2 compared with calcitriol.
Author notes
Address all correspondence and requests for reprints to: Elizabeth A. Streeten, MD, Department of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Nutrition, University of Maryland Medical Center, Howard Hall 567, 660 West Redwood, Baltimore, Maryland 21201. E-mail: [email protected].
How to prevent calcium deficiency?
Be aware that foods high in calcium, such as dairy products, can also be high in saturated fat and trans fat. Choose low-fat or fat-free options to reduce your risk of developing high cholesterol and heart disease.
How long does it take for hypocalcemia to occur?
Neonatal hypocalcemia occurs in infants soon after birth. Most cases of neonatal hypocalcemia occur within the first two days after birth. But late onset hypocalcemia can occur three days after birth, or later.
Why is calcium important?
Calcium is a vital mineral. Your body uses it to build strong bones and teeth. Calcium is also needed for your heart and other muscles to function properly. When you don’t get enough calcium, you increase your risk of developing disorders like: osteoporosis. osteopenia.
What is the normal level of albumin?
Normal calcium levels for adults can range from 8.8 to 10.4 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), according to the Merck Manual.
Why is calcium important during menopause?
During menopause, women should also increase their calcium intake to reduce the risk of osteoporosis and calcium deficiency disease.
What foods are high in saturated fat?
portobello mushrooms. eggs. As with calcium-rich dairy products, some vitamin D-rich dairy products can also be high in saturated fat. Sunlight triggers your body to make vitamin D, so getting regular exposure to the sun can also help boost your vitamin D levels.
Can calcium cause seizures?
So, calcium deficiencies can bring on seizures in otherwise healthy people. If you start experiencing neurological symptoms like memory loss, numbness and tingling, hallucinations, or seizures, make an appointment to see your doctor as soon as possible.
