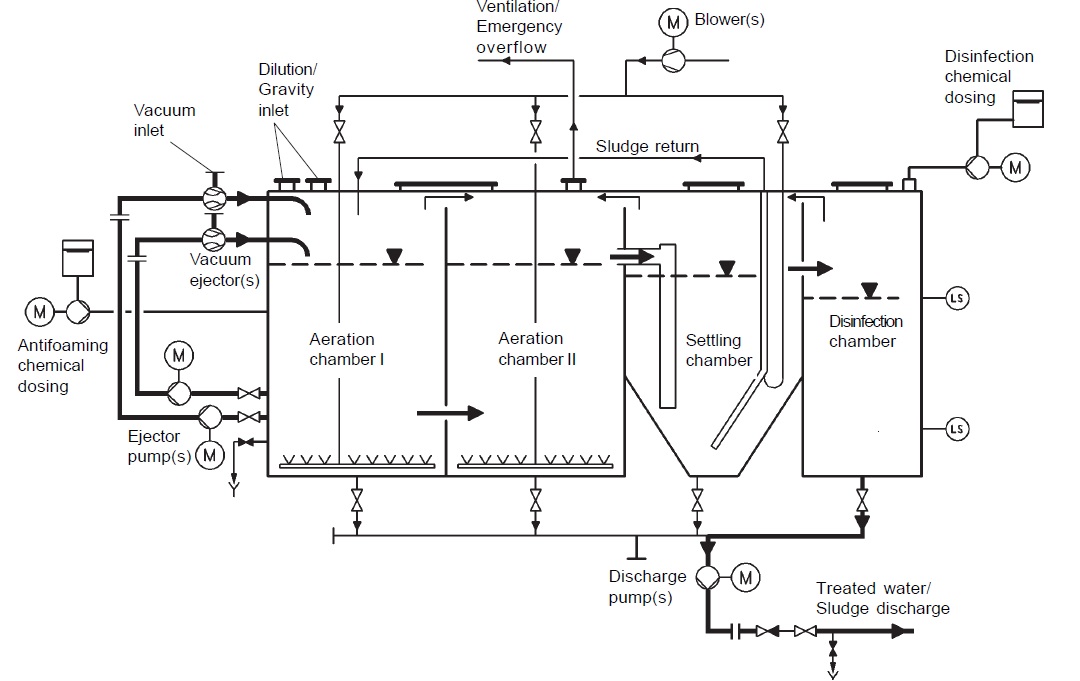
How does an effluent treatment plant work?
- Makeup water intake. As water circulates through a cooling tower system, a portion is lost to evaporation, bleed to drain, and leaks. ...
- Filtration. Upon intake, the stream is typically filtered through one or more filtration units for removal of sediment, turbidity, and organic material. ...
- Softening. ...
- Chemical addition. ...
- Side-stream filtration. ...
- Post-treatment. ...
What is primary treatment of wastewater treatment plant?
Tube Settler/Lamella Clarifier
- It is a compact inclined plate type clarifier. ...
- To provide a large projected area like clarifier lamella clarifier is used which is based on the principle of settling heavier particles under gravity, providing a number of inclined plates.
- Settling capacity is increased by the use of the tube settler. ...
What are types of sewage treatment plants?
What are the types of sewage treatment plant?
- Suspended Media Filters (SMF)
- Activated sludge plant (ASP)
- Rotating disc system.
- Submerged aerated filter (SAF)
- Sequencing batch reactor (SBR)
- Non-electric filter.
- Trickling filter.
What causes high nitrate in effluent?
- Nitrification is a bio-chemical reaction that occurs inside bacteria.
- Two species of bacteria are involved in the process – Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter.
- These bacteria are collectively known as nitrifiers and are autotrophic, i.e. they get their carbon source from inorganic carbon (carbonates, bicarbonates) or carbon dioxide.
What is meant by effluent treatment plant?
TREATMENT. EFFLUENT. SLUDGE. • ETP (Effluent Treatment Plant) is a process design for treating the. industrial waste water for its reuse or safe disposal to the environment.
What is ETP and why it is important?
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETP's) are used by all leading industries to treat their wastewater. All the leading pharmaceutical, chemical, textile, and other industry that generate the wastewater used ETP's to purify water and remove any non toxic or toxic materials or chemical from it.
What is effluent short answer?
Definition of effluent (Entry 2 of 2) : something that flows out: such as. a : an outflowing branch of a main stream or lake. b : waste material (such as smoke, liquid industrial refuse, or sewage) discharged into the environment especially when serving as a pollutant.
What is effluent summary?
Effluent is an outflowing of water or gas to a natural body of water, from a structure such as a sewage treatment plant, sewer pipe, industrial wastewater treatment plant or industrial outfall. Effluent, in engineering, is the stream exiting a chemical reactor.
What are the parameters of ETP?
Under this study the various parameters such as temperature, pH, chemical oxygen demand(COD), suspended solids(SS), total dissolved solids(TDS), phosphorus and heavy metals are determined by taking samples at inlet and outlet of effluent treatment plant and compared with the Indian standards for effluent discharge into ...
How many levels of treatment are there in ETP?
How many levels of treatment are there in ETP? There are three levels of the wastewater treatment procedure, known as primary (Separate sludge from liquid), secondary (Reduce biological population) and tertiary water treatment (to reduce harmful Chemicals).
How many types of effluents are there?
There are three types of wastewater, or sewage: domestic sewage, industrial sewage, and storm sewage.
What is difference between sewage and effluent?
Sewage is a type of wastewater produced by a community of people due to activities like bathing, washing, cleaning. It also contains faecal matter. Effluent is the liquid waste that flows out of a factory and farm into water bodies such as rivers, ponds, and lakes.
What is the type of effluent system?
Conventional effluent treatment systems are typically based on a series of water treatment facilities in which all the wastewater collected from water-using operations are combined and treated as a single effluent stream. This centralised approach treats wastewater collectively in sequence.
What are effluent standards?
Effluent standards are concentrations of pollutants expressed in terms of parts per million for waste water discharged through outfall pipes from publicly owned sewage treatment plants or industrial plants.
What is effluent level?
Abnormally high sewage effluent levels in the septic tank are any effluent levels above the outlet pipe - indicating a blockage, clog, or flooded drainfield. Remember we're talking about the effluent, not the floating scum that we discussed just above.
What is the cause of effluent?
Effluents that are released by industries are toxic and hazardous in nature. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, pigments, petrochemicals, dye, paints, pesticides, chemical, lubricants, and tanneries create a lot of toxic effluents, which are released to nearby water bodies after minimal treatment.
Why are water treatment plants so inefficient?
However, inadequate operations and managerial skills are one of the main reasons for the inefficient operation of these treatment plants. Therefore, many water treatment plants are operated inefficiently and their positive effect towards the prevention of pollution is unnecessarily limited.
What is industrial wastewater treatment?
Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by- product. The treated industrial wastewater (or effluent) may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to surface water in the environment. The main objectives of an ETP are:
What is ETP in industrial estate?
In addition, the ETP also facilitates in reduction of number of discharge points in an industrial estate for better enforcement by environmental regulatory agencies in terms of pollution reduction and environmental improvements.
How does industrialization affect the environment?
The process of industrialization is adversely impacting the environment globally . Pollution generated by incorrect management of industrial wastewater is one of the major environmental problems in India as well, especially with burgeoning small scale industrial sector in the country.
What is process inefficiency?
Process Inefficiencies: Industries usually operate ETPs without any actual lab or pilot tests being performed for particular effluent quality treatment, resulting in process inefficiency and non-compliance of discharges effluent.
What is Effluent Treatment?
Effluent Treatment is the process of removing solid, chemical, and organic substances from the wastewater produced by industries as an outcome of the production process and recycle the water for industrial use or discharge it into the environment safely.
Why is Effluent Treatment important for industries?
Industries use water in their production processes. For example, Pulp & Paper mills, water, cooling system, food & beverages, etc. Every industry needs to adhere to the government guidelines when they discharge the treated wastewater into the environment.
How does Effluent Treatment Plant work?
Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP) has many stages in treating the wastewater produced by the factories. The influent water has acid, oil, grease, and other solid substances like plastic, paper. The Effluent water is recycled back for industry use or discharged to the environment.
ETP Process Stages
Screening is the first stage where influent water enters. Oil skimmer, Bar Screens, and Grit chambers are used in this stage. An oil skimmer is a type of machine that removes the oil and grease floating on the water. Bar Screen is another piece of equipment that is used as a filter to remove large solid substances like plastic, paper, etc.