
Medication
Hepatitis B can be either acute or chronic: Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least six months. People with this type of hepatitis may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of their lives. Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms.
Procedures
Current treatments for hepatitis B fall into two general categories: Immune modulator Drugs – These are interferon-type drugs that boost the immune system to help get rid of the hepatitis B virus. They are given as a shot (similar to how insulin is given to people with diabetes) over 6 months to 1 year.
Self-care
Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms. But those with chronic hepatitis B often need treatment to help manage the condition. Chronic hepatitis B also increases your risk of developing cirrhosis and certain types of liver cancer.
Nutrition
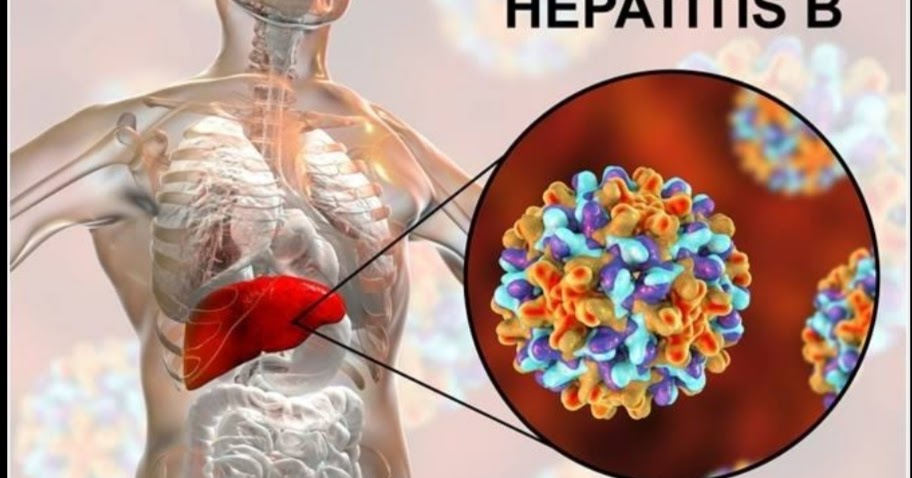
It affects people of all ages around the world. The hepatitis B virus attacks the liver. The virus can lead to serious illness, liver damage and, in some cases, death. What is hepatitis B? Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection that causes inflammation (swelling and reddening) that can lead to liver damage.
How long does hepatitis B last?
How is hepatitis B treated?
Can You recover from hepatitis B without treatment?
How does hepatitis B affect people around the world?
How long does treatment for hepatitis B last?
It's usually given by injection once a week for 48 weeks. Common side effects include flu-like symptoms, such as a fever and muscle and joint pain, after you start to take the medicine, although these should improve with time. Tests will be carried out during treatment to see how well it's working.
Is hepatitis B treatment for life?
Most people diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B infection need treatment for the rest of their lives. Treatment helps reduce the risk of liver disease and prevents you from passing the infection to others.
Why does hepatitis B have no cure?
Chronic hepatitis B hasn't been cured so far in part because current therapies have failed to destroy the viral reservoir, where the virus hides in the cell. This is in contrast to hepatitis C virus, which has no such viral reservoir and can now be cured with as little as 12 weeks of treatment.
What is the long term effect of hepatitis B?
Chronic hepatitis B can develop into a serious disease resulting in long-term health problems, including liver damage, liver failure, liver cancer, and even death.
Can hepatitis B be cured permanently?
A vaccine can prevent hepatitis B, but there's no cure if you have the condition. If you're infected, taking certain precautions can help prevent spreading the virus to others.
How long should I take tenofovir?
Treatment for HIV is usually lifelong. Continue to take tenofovir regularly for as long as your doctor tells you to, even if you feel well. This is to keep your immune system healthy.
When will hepatitis B cure come?
There's no cure for hepatitis B. The good news is it usually goes away by itself in 4 to 8 weeks. More than 9 out of 10 adults who get hepatitis B totally recover. However, about 1 in 20 people who get hepatitis B as adults become “carriers,” which means they have a chronic (long-lasting) hepatitis B infection.
Can hepatitis B positive change negative?
The hepatitis B e-antigen test result is often used to monitor the effectiveness of many hepatitis B drug therapies that aim to change a chronically infected person's e-antigen status from “positive” to “negative.” By achieving a “negative” e-antigen result, this means that the hepatitis B drug successfully stopped or ...
What is the latest news of hepatitis B cure?
A consortium of leading virologists, immunologists and physicians specialized in treating viral hepatitis, will use a newly designed therapeutic vaccine, TherVacB, as an immunotherapy to cure HBV. TherVacB will be evaluated in a three-year clinical trial starting in 2022 conducted in Europe and in Africa.
How long can hepatitis B patient live without treatment?
The hepatitis B virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During this time, the virus can still cause infection if it enters the body of a person who is not protected by the vaccine.
Can the liver repair itself from hepatitis B?
Fortunately, the liver can function even when up to 75% of it is diseased or removed. This is because it has the amazing ability to create new liver tissue from healthy liver cells.
Can acute hepatitis B be cured?
There are effective drug therapies that can control and even stop the hepatitis B virus from further damaging a liver. There are also promising new drugs in the research pipeline that could provide a cure in the very near future.
What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a liver disease that can cause serious damage to your health. One reason that is dangerous is that it can easily go undetected for years while damaging your liver. Talk with your healthcare provider about being tested for hepatitis B if you have any reason to believe that you were not vaccinated or if you have engaged in risky behavior. If you do test positive, follow the directions from your healthcare provider so that you can live a longer, healthier and happier life.
How many drugs are there for hepatitis B?
Usually, drug therapy is used only if you have active liver disease. There are seven drugs that are approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat hepatitis B. Two are injectable forms of interferon, while the five other antivirals are tablets. You will need to take these medications every day.
Why is the liver important?
Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods. You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis.
What to do if you test positive for hepatitis B?
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy.
What is a liver biopsy?
Liver biopsy: A small sample of your liver tissue is removed though a tiny incision and sent to a lab for analysis. The blood test that is used to diagnose hepatitis B is not a test that you get routinely during a medical visit.
What to do if you have a short lived infection?
Instead, your doctor will likely suggest that you get plenty of rest, drink lots of fluids and maintain a healthy diet to support your body as it fights off the infection.
How many people are carriers of HBV?
Between 6% and 10% of those people who’ve been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers.
What is the best treatment for hepatitis B?
Treatment for chronic hepatitis B may include: Antiviral medications. Several antiviral medications — including entecavir (Baraclude), tenofovir (Viread), lamivudine (Epivir), adefovir (Hepsera) and telbivudine (Tyzeka) — can help fight the virus and slow its ability to damage your liver. These drugs are taken by mouth.
What to do if you have hepatitis B?
Receive kidney dialysis. Take medications that suppress the immune system, such as those used to prevent rejection after an organ transplant. Use illegal injected drugs. Are in prison. Were born in a country where hepatitis B is common, including Asia, the Pacific Islands, Africa and Eastern Europe.
What happens to the liver when you get a liver transplant?
During a liver transplant, the surgeon removes your damaged liver and replaces it with a healthy liver. Most transplanted livers come from deceased donors, though a small number come from living donors who donate a portion of their livers. Other drugs to treat hepatitis B are being developed.
What is the best way to test for liver damage?
Liver ultrasound. A special ultrasound called transient elastography can show the amount of liver damage. Liver biopsy. Your doctor might remove a small sample of your liver for testing (liver biopsy) to check for liver damage.
How to get rid of hepatitis A?
Eat a healthy diet full of fruits and vegetables, exercise regularly, and get enough sleep. Take care of your liver. Don't drink alcohol or take prescription or over-the-counter drugs without consulting your doctor. Get tested for hepatitis A and C. Get vaccinated for hepatitis A if you haven't been exposed.
Does hepatitis B go away on its own?
Treatment for acute hepatitis B infection. If your doctor determines your hepatitis B infection is acute — meaning it is short-lived and will go away on its own — you may not need treatment. Instead, your doctor might recommend rest, proper nutrition and plenty of fluids while your body fights the infection.
How long does hepatitis B last?
Acute hepatitis B lasts for a short period of time. Chronic hepatitis B lasts for at least six months. People with this type of hepatitis may carry the hepatitis B virus for the rest of their lives. Most people with acute hepatitis B make a full recovery. Some may never even show any symptoms.
How to treat hepatitis B?
working in a medical setting. using intravenous drugs. If you’ve been exposed to the hepatitis B virus and haven’t been vaccinated, try to see a doctor right away. They can administer the first dose of the vaccine, though you’ll need to follow up to receive the remaining doses over the next few months.
What is the best treatment for hepatitis B?
antiviral tablets, such as tenofovir or entecavir. Antiviral medications can help to reduce symptoms and prevent liver damage. But they rarely completely get rid of the hepatitis B virus. Instead, the goal of treatment is to have the lowest viral load possible.
What is the cause of hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. The virus is passed from person to person through bodily fluids, including blood or semen. Hepatitis B can cause a range of symptoms, such as: abdominal pain. dark-colored urine.
How to reduce the risk of hepatitis B?
You can reduce your risk of developing hepatitis B or spreading the virus to others by: using protection, such as condoms, during sexual activity. getting regularly tested for hepatitis B. not sharing personal items that might contain blood, such as razors or toothbrushes. not sharing needles or syringes.
Is hepatitis B curable?
yellowing of the skin or eyes. Hepatitis B isn’t curable, but ongoing research is looking into the use of DNA technology to prevent the virus from reproducing in the body. Experts are also looking into ways to use the body’s own immune system kill off the virus.
Does hepatitis B need to be treated?
Acute hepatitis B doesn’t always require treatment. In most cases, a doctor will recommend monitoring your symptoms and getting regular blood tests to determine whether the virus is still in your body. While you recover, allow your body to rest and drink plenty of fluids to help your body fight off the infection.
What is the life cycle of HBV?
HBV is a hepatotropic DNA virus that replicates by means of reverse transcription of a pregenomic RNA. The life cycle of HBV is depicted in Fig. Fig.11.3The circulating virion comprises an envelope and a nucleocapsid that contains a partially double‐stranded, relaxed, circular DNA.
What are the treatments for HBV?
These treatments are effective in suppressing HBV replication and in decreasing the risk of developing cirrhosis, liver failure, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), and death. However, these treatments do not eliminate the virus, ...
Can antiviral therapy prevent HCC?
It is also unclear whether antiviral therapy initiated in the absence of standard indications will prevent HCC in patients who are genetically predisposed, are infected with an unusually virulent strain of HBV, or had been exposed to environmental carcinogens.
What drugs target B lymphocytes?
Rituximab and other drugs that target B lymphocytes (black box warning), high-dose steroids, and. anti-TNF agent; with HIV infection who have discontinued therapy with antiretroviral drugs that also have activity against HBV; undergoing solid organ or bone marrow transplantation; and.
How old do you have to be to have symptoms of HBV?
Not all people with acute HBV infection have symptoms. The presence of signs and symptoms varies by age. Most children <5 years of age and newly infected immunosuppressed adults are generally asymptomatic, whereas 30%–50% of people age ≥5 years have signs and symptoms ( 6 ).
What to do if you have positive HBsAg?
People with positive HBsAg should be referred to a specialist in the management of hepatitis B infection and receive further serologic evaluation, prevention counseling, and evaluation for antiviral treatment (see Management of HBsAg-Positive Persons ).
What does HBsAG stand for?
Sex partners of people testing positive for hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) Sexually active people who are not in a long-term, mutually monogamous relationship (e.g., people with more than one sex partner during the previous 6 months) People seeking evaluation or treatment for a sexually transmitted infection.
When should I test for HBs?
Testing should not be performed before age 9 months in order to avoid detection of anti-HBs from hepatitis B immune globulin (HBIG) administered during infancy and to avoid detection of HBsAg from vaccine (HBsAg can be transiently positive for 1–18 days after vaccination).
How many people die from cirrhosis in childhood?
Approximately 25% of people who become chronically infected during childhood and 15% of those who become chronically infected after childhood die prematurely from cirrhosis or liver cancer, and most remain asymptomatic until onset of cirrhosis or end-stage liver disease ( 9, 10 ).
Can yeast get hepatitis B?
Anyone who has had a serious allergic reaction to a prior dose of hepatitis B vaccine, a component of the hepatitis B vaccine, or yeast should not receive hepatitis B vaccine. When hepatitis B vaccine is administered as part of a combination vaccine, contraindications to other vaccines should be checked.
How long does hepatitis B stay in your system?
Once you are diagnosed with chronic hepatitis B, the virus will most likely stay in your blood and liver for a lifetime. It is important to know that you can pass the virus along to others, even if you don’t feel sick.
How long does it take to test positive for hepatitis B?
If you test positive for the hepatitis B virus for longer than 6 months, this indicates that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection. All patients with chronic hepatitis B infections, including children and adults, should be monitored regularly since they are at increased risk for developing cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
Can hepatitis B be managed?
The most important thing to remember is that hepatitis B is a chronic medical condition (such as diabetes and high blood pressure) that can be successfully managed if you take good care of your health and your liver. You should expect to live a long, full life.

Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Coping and Support
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment