
Why does the government put fluoride in the water?
The idea, in a nutshell, is that governments put fluoride in our water supply in order to negatively affect huge populations, for their own financial gains. That fluoride is actually a strong tranquilliser in disguise. That the US want their citizens to be zombies.
What happens when you add fluoride to water?
Water authorities add fluoride to the municipal water supply, because studies have shown that adding it in areas where fluoride levels in the water are low can reduce the prevalence of tooth decay in the local population. Tooth decay is one of the most common health problems affecting children.
What are the negative side effects of fluoride?
This could be considered one of the most overlooked dangers of fluoride. Studies have shown that fluoride can adversely affect your blood glucose and insulin levels. Evidence shows that those with higher levels of fluoride in their body had higher glucose levels in the blood and also diminished levels of insulin.
Why do they put fluoride in drinking water?
The thought behind using fluoride in drinking water was that it helped prevent cavities was made into a theory and then it hit the mainstream. In the United States, large amounts of fluoride and other byproducts of the fertilizer industry were disposed of in the State of Florida.
Why is fluoride in our water supply?
Adding fluoride to the water supply reduces the incidence of tooth decay. Fluoride protects teeth from decay by demineralization and remineralization. Too much fluoride can lead to dental fluorosis or skeletal fluorosis, which can damage bones and joints.
What is fluoride used for?
Fluoride is used to prevent tooth decay. It is taken up by teeth and helps to strengthen teeth, resist acid, and block the cavity-forming action of bacteria. Fluoride usually is prescribed for children and adults whose homes have water that is not fluoridated (already has fluoride added).
What is fluoride in drinking water?
Water fluoridation is the process of adding fluoride to the water supply so the level reaches approximately 0.7 ppm, or 0.7 milligrams of fluoride per liter of water; this is the optimal level for preventing tooth decay (1).
How does fluoride prevent tooth decay?
Fluoride prevents tooth decay by making the enamel more resistant to the action of acids. They and accelerate the buildup of healthy minerals in the enamel, further slowing the occurrence of decay. Studies even show that in some cases, fluoride can stop already started teeth decay.
What is the mechanism of action of fluoride?
Fluoride Mechanisms of Action. Inhibition of Demineralization If fluoride is present in plaque fluid (FL) when bacteria produce acids, it will penetrate along with the acids at the subsurface, adsorb to the crystal surface (FA) and protect crystals from dissolution [26].
Do we need fluoride?
yes, fluoride helps prevent tooth decay – in fact, since 1950 the American Dental Association has backed fluoride as “safe, effective and necessary in preventing tooth decay”. By strengthening enamel and slowing its breakdown, fluoride limits the ability for plaque and bacteria to go to work on your teeth.
How does fluoride strengthen enamel?
When your saliva contains traces of fluoride, your tooth enamel is able to take it up. Once in the enamel the fluoride combines with phosphate and calcium to create fluoroapatite. This provides a powerful defence against acid and is extremely resistant to decay and cavities.
How does fluoride promote remineralization?
Fluoride enhances remineralization. Fluoride speeds up the growth of the new surface by bringing calcium and phosphate ions together and is also preferentially incorporated into the remineralized surface. This produces a surface which is now more acid resistant.
What does fluoride treatment do for your teeth?
Fluoride helps prevent tooth decay by making the tooth more resistant to acid attacks from plaque bacteria and sugars in the mouth. It also reverses early decay.
What is the process of testing water for fluoride?
This process of testing the water supply for fluoride and adjusting it to the right amount to prevent cavities is called community water fluoridation. Since 1945, hundreds of cities have started community water fluoridation and in 2016, nearly 73% of the United States served by community water systems had access to fluoridated water.
What are the benefits of fluoride?
Fluoride benefits children and adults throughout their lives. For children younger than age 8, fluoride helps strengthen the adult (permanent) teeth that are developing under the gums. For adults, drinking water with fluoride supports tooth enamel, keeping teeth strong and healthy. The health benefits of fluoride include having: 1 Fewer cavities. 2 Less severe cavities. 3 Less need for fillings and removing teeth. 4 Less pain and suffering because of tooth decay.
How many people in the US have fluoride in their water?
Fluoride in the Water Today. In 2018, community water systems that contain enough fluoride to protect teeth served more than 200 million people or 73% of the US population. Because it is so beneficial, the United States has a national goal for 77% of Americans to have water with enough fluoride to prevent tooth decay by 2030.
How does fluoride help teeth?
Fluoride helps to rebuild and strengthen the tooth’s surface, or enamel. Water fluoridation prevents tooth decay by providing frequent and consistent contact with low levels of fluoride. By keeping the tooth strong and solid, fluoride stops cavities from forming and can even rebuild the tooth’s surface. Community water fluoridation is the process ...
Why was it important to study the relationship between tooth decay and fluoride in drinking water?
The study found that children who drank water with naturally high levels of fluoride had less tooth decay. 2 This discovery was important because during that time most children and adults in the United States were affected by tooth decay. Many suffered from toothaches and painful extractions—often losing permanent teeth, including molars, even as teenagers.
What is community water fluoridation?
Community water fluoridation is the process of adjusting the amount of fluoride in drinking water to a level recommended for preventing tooth decay. Although other fluoride-containing products, such as toothpaste, mouth rinses, and dietary supplements are available and contribute to the prevention and control of tooth decay, ...
Where does fluoride come from?
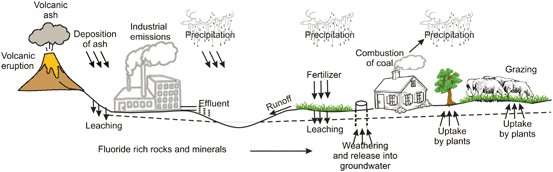
The mineral fluoride occurs naturally on earth and is released from rocks into the so il, water, and air. All water contains some fluoride. Usually, the fluoride level in water is not enough to prevent tooth decay; however, some groundwater and natural springs can have naturally high levels of fluoride.
What is the main additive used in water fluoridation?
Since the early 1950s, FSA has been the main additive used for water fluoridation in the United States. The favorable cost and high purity of FSA make it a popular additive. Sodium fluorosilicate and sodium fluoride come from processing FSA , or from processing hydrogen fluoride.
What are the EPA requirements for fluoride?
All additives used by water treatment plants, including fluoride additives, must meet strict quality standards that assure the public’s safety. These additives are subject to a stringent system of standards, testing, and certificates by AWWA and NSF International.
What is the gas used to make fluorosilicic acid?
The fluoride gas is captured and used to create fluorosilicic acid. According to the American Water Works Association Standards Committee on Fluorides, the sources of fluoride products used for water fluoridation in the United States are as follows: Approximately 90% are produced during the process of extracting phosphate from phosphoric ore.
What is the difference between fluorosilicic acid and sodium fluorosilicate?
Sodium fluorosilicate: a dry salt additive, dissolved into a solution before being added to water. Sodium fluoride: a dry salt additive, typically used in small water systems, dissolved into a solution before being added to water.
What is the solution to neutralize FSA?
FSA can be partially neutralized by either table salt (sodium chloride) or caustic soda to get sodium fluorosilicate. If enough caustic soda is added to completely neutralize the fluorosilicate, the result is sodium fluoride. About 90% of the sodium fluoride used in the United States comes from FSA.
What is phosphorite mixed with?
Phosphorite contains calcium phosphate mixed with limestone (calcium carbonates) minerals and apatite— a mineral with high phosphate and fluoride content. It is refluxed (heated) with sulfuric acid to produce a phosphoric acid-gypsum (calcium sulfate-CaSO4) slurry.
Can fluoride be used in water fluoridation?
Some have suggested that pharmaceutical grade fluoride additives should be used for water fluoridation. Pharmaceutical grading standards used in formulating prescription drugs are not appropriate for water fluoridation additives. If applied, those standards could actually exceed the amount of impurities allowed by AWWA and NSF/ANSI in drinking water.
How does fluoridation save money?
By preventing cavities and tooth decay, community water fluoridation saves money for families and the United States healthcare system. The median lifetime cost per individual to fluoridate an entire water supply is less than the cost of a single dental filling. According to the CDC, an economic review of multiple research studies found that savings for cities ranged from $1.10 to $135 for every $1 invested in community water fluoridation. The ADA reports that most cities save $38 in dental treatment costs for every $1 invested in water fluoridation.
Why do children get fluorosis?
Many people have heard that children can develop dental fluorosis if they consume too much fluoride while teeth are developing. While this is true, the issue does not typically occur due to community water fluoridation. Most often dental fluorosis develops because people receive too much fluoride from a total of all sources, such as children swallowing too much fluoridated toothpaste. This is why it’s important for parents to supervise their kids when they are brushing their teeth. Children should also use no more than a pea-sized portion of toothpaste while brushing.
Is fluoride safe for tooth decay?
Community water fluoridation is widely recognized as one of the most equitable, safe and cost-effective steps cities can take to prevent tooth decay. Unfortunately, widespread misinformation has caused some people to doubt the safety and efficacy of fluoride in the water supply. Here’s what you should know about the benefits of water fluoridation.
Is it safe to use fluoridation in the water?
For over 70 years, the best scientific evidence has shown that community water fluoridation is both effective and safe. Despite misinformation available on the internet, water fluoridation has not been shown to increase the risk of health problems in children or adults. Endorsed by several U.S. Surgeons General, community water fluoridation offers an impressive safety track record which has earned support from more than 100 health organizations, including the American Medical Association and the CDC.
What is the goal of water fluoridation?
The goal of water fluoridation is to prevent tooth decay by adjusting the concentration of fluoride in public water supplies. Tooth decay ( dental caries) is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide.
What is fluoride in water?
Water fluoridation is the controlled adjustment of fluoride to a public water supply solely to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water contains fluoride at a level that is effective for preventing cavities; this can occur naturally or by adding fluoride.
How many countries have fluoridated water?
As of 2012, 25 countries have artificial water fluoridation to varying degrees, 11 of them have more than 50% of their population drinking fluoridated water. A further 28 countries have water that is naturally fluoridated, though in many of them the fluoride is above the optimal level. As of 2012, about 435 million people worldwide received water ...
Why is water fluoridation controversial?
The water fluoridation controversy arises from political, moral, ethical, economic, and safety concerns regarding the water fluoridation of public water supplies. For deprived groups in both maturing and matured countries, international and national agencies and dental associations across the world support the safety and effectiveness of water fluoridation. Authorities' views on the most effective fluoride therapy for community prevention of tooth decay are mixed; some state water fluoridation is most effective, while others see no special advantage and prefer topical application strategies.
How effective is fluoride in preventing tooth decay?
Other fluoride therapies are also effective in preventing tooth decay; they include fluoride toothpaste, mouthwash, gel, and varnish, and fluoridation of salt and milk. Dental sealants are effective as well, with estimates of prevented cavities ranging from 33% to 86%, depending on age of sealant and type of study.
What is the best level of fluoride in water?
Higher concentrations of fluorine are found in alkaline volcanic, hydrothermal, sedimentary, and other rocks derived from highly evolved magmas and hydrothermal solutions, and this fluorine dissolves into nearby water as fluoride. In most drinking waters, over 95% of total fluoride is the F − ion, with the magnesium –fluoride complex (MgF +) being the next most common. Because fluoride levels in water are usually controlled by the solubility of fluorite (CaF 2 ), high natural fluoride levels are associated with calcium -deficient, alkaline, and soft waters. Defluoridation is needed when the naturally occurring fluoride level exceeds recommended limits. It can be accomplished by percolating water through granular beds of activated alumina, bone meal, bone char, or tricalcium phosphate; by coagulation with alum; or by precipitation with lime.
What are the requirements for water fluoridation?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention developed recommendations for water fluoridation that specify requirements for personnel, reporting, training, inspection, monitoring, surveillance, and actions in case of overfeed, along with technical requirements for each major compound used.
