Explore
Mar 25, 2021 · Keeping your blood sugar levels on target as much as possible can help prevent or delay long-term, serious health problems. While this is important, closely managing your blood sugar levels also increases your chance for low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Blood sugar below 70 mg/dL is considered low.
Should I check my blood sugar levels before and after HBO?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO therapy) is a medical treatment that helps ... It is very important to maintain good hygiene and health during the treatments. ... we will check your blood sugar before and after the treatment. If you are not diabetic, we will check your blood sugar prior to …
Why is it important to keep blood sugar levels on target?
Blood sugar levels and insulin levels in five diabetic and five non-diabetic subjects were measured both while breathing normobaric air and hyperbaric oxygen. Mean blood sugar levels decreased ...
How does hyperbaric oxygen affect blood glucose levels?
Jun 01, 2017 · Significance: Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is an important advanced therapy in the treatment of problem wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers and late effect radiation injury. HBOT remains among the safest therapies used today. Nonetheless, there are side effects associated with HBOT. It is important for providers to be able to identify, understand, and …
What is hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBO)?
treatment with HBO therapy? Please arrive at least 15-20 minutes before your appointment. 1. Before going into the chamber for treatment, we will ask you to change into scrubs. 2. Make sure you use the restroom before the treatment. 3. We will take your temperature, blood pressure and pulse. 4. If you have diabetes, we will check your blood sugar

Does hyperbaric oxygen therapy affect blood sugar?
Studies show all patients undergoing hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) experience a reduction in blood glucose levels compared to prehyperbaric oxygen treatment levels.Apr 4, 2014
Which complication of diabetes can be treated by hyperbaric oxygen?
Among patients with T2DM, HBOT is mostly used for the treatment of chronic diabetic ulcers, which involves intermittent administration of 100% oxygen, usually in daily sessions of 90 minutes each, at pressures of 1.5–3.0 ata in an airtight cabin.Jun 1, 2020
Which complication of diabetes can be diagnosed by the ankle brachial index?
Abstract. Introduction: The ankle brachial index (ABI), i.e. the ratio of systolic blood pressure (SBP) on the ankle and on the arm, is diagnostic for peripheral occlusive artery disease and a marker of cardiovascular (CV) risk.
What is the most common complication of hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Barotrauma of the ear Barotrauma is a term that refers to injury due to increased pressure. Barotrauma of the ear is the most frequent complication of HBO. The middle-ear is an air-filled cavity behind the ear drum that connects to the throat through a slit-like passage called the eustachian tube.
Which organ does type 1 diabetes affect?
Over time, type 1 diabetes complications can affect major organs in your body, including heart, blood vessels, nerves, eyes and kidneys. Maintaining a normal blood sugar level can dramatically reduce the risk of many complications. Eventually, diabetes complications may be disabling or even life-threatening.
What hormone is released when blood glucose levels rise?
Glucagon works along with the hormone insulin to control blood sugar levels and keep them within set levels. Glucagon is released to stop blood sugar levels dropping too low (hypoglycaemia), while insulin is released to stop blood sugar levels rising too high (hyperglycaemia).
Which medication is categorized as a starch blocker?
Amylase inhibitors, also called starch blockers, prevent starches from being absorbed by the body.May 16, 2014
Which medications may induce diabetes?
Which drugs can induce diabetes?Corticosteroids.Thiazide diuretics.Beta-blockers.Antipsychotics.Statins.
Which treatment is useful in decreasing the serum ketone level in patients with diabetic ketoacidosis?
Serum ketone level should be used in the diagnosis and management of DKA. Subcutaneous insulin can be used for treatment of uncomplicated DKA.Mar 1, 2013
Who is not a candidate for hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Relative contraindications to evaluate before treatment include, but are not limited to, the following: Uncontrolled hypertension (blood pressure can increase during treatment) Diabetes mellitus with glucose levels greater than 300 or less than 100.Feb 7, 2022
Does using oxygen make your lungs weaker?
Home oxygen therapy is not addictive and it will not weaken your lungs. You will get maximum benefit by using oxygen for the amount of time prescribed by your doctor.Feb 19, 2018
Can hyperbaric oxygen help dementia?
It accounts for 60 to 80 percent of all dementia cases. There is no cure and no currently approved treatment that slows disease progression. However, recent studies show that hyperbaric oxygen therapy, or HBOT, offers an important treatment option for those suffering from Alzheimer's disease.
What is hyperbaric oxygen treatment?
Hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) has been shown to reduce a patient’s blood glucose level during an individual treatment. Anecdotal evidence suggests patients with diabetes are concerned about suffering a hypoglycaemic episode during HBOT. It is suspected that patients who have diabetes undertake protective health behaviours by intentionally increasing their blood glucose levels prior to HBOT. Aim: To explore the emotional and physical experiences of patient self-management behaviours of their blood glucose levels during a course of hyperbaric oxygen treatment. Method: The use of semi-structured in-depth interviews, each interview was audio recorded and transcribed verbatim. Participants (n = 15), were prior patients living with diabetes who had undergone HBOT at a tertiary hospital in an Australian state during 2014–2017. Interpretive description along with thematic analysis of all interviews was undertaken. Findings: Four themes emerged from the interviews, each deriving from the participants’ experiences 1.Varying recognition of self-management requirement of diabetes; 2. Hypoglycaemia fear; 3. Treatment-based adaptation; and 4. Ownership / monitoring. Participants reported that they altered their diabetic regime/blood glucose management to undertake a course of HBOT. Discussion: Patient engagement throughout HBOT, leads them to elevate their blood glucose, although not advocated, to above normal levels, adopting these behavioural changes as a self-protective mechanism. Conclusion: Improving the patient experience of hyperbaric oxygen treatment is multifactorial and often dependant on the relationship between the clinician and the patient. Consistent monitoring of blood glucose during HBOT, may ameliorate negative feelings that are often associated with this treatment option.
How is blood glucose measured?
Blood glucose is commonly measured in diabetic patients undergoing hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) from a 'finger-prick' capillary sample. Although this method is an accurate reflection of venous glucose under normal conditions it has not been validated under hyperbaric, hyperoxic conditions. Four patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing HBOT had venous blood samples drawn simultaneously with routine capillary samples before, during and immediately after three of four HBOT sessions. The Bland-Altman method of assessing agreement between these two measures was used separately for the three time periods. The relationship between venous and finger-prick glucose at room air was altered significantly by HBOT. The bias (finger-prick minus venous measurements) was significantly less than zero during the HBOT session but not immediately after completion of the session. Owing to the small sample size, the limits of agreement straddled zero at all time points, although the lower limit was close to zero during treatment (finger measurement appeared to be higher than venous measurement on room air and lower than venous undergoing HBOT). Finger-prick capillary sampling may not be an accurate reflection of venous glucose during HBOT.
What is hyperbaric oxygen?
Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO2) is commonly used to treat non-healing wounds in diabetic patients. Although anecdotal evidence from hyperbaric centres suggests that diabetics are vulnerable to hypoglycaemia when they are treated with hyperbaric oxygen, there has been little definitive human or animal research showing the effects of hyperbaric oxygen on blood sugar and insulin levels. Blood sugar levels and insulin levels in five diabetic and five non-diabetic subjects were measured both while breathing normobaric air and hyperbaric oxygen. Mean blood sugar levels decreased significantly by 3.5 ± 0.7 mmol/l during hyperbaric oxygen breathing in the five diabetics. Insulin dosage was not changed in either condition.
Does hyperbaric oxygen decrease blood glucose?
A decrease in blood glucose levels (BGL) during hyperbaric oxygen treatment (HBOT) is a well-recognised phenomenon, but studies of this are limited and inconclusive. This study evaluated the effect of HBOT on BGL in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM), traumatic brain injury (TBI) or stroke and healthy volunteers in a prospective, open, controlled trial. Thirty-nine participants were enrolled and evaluated twice: once during HBOT (90 minutes at 203 kPa), and once during a control session on normobaric air. Sessions were held up to two weeks apart and participants were instructed to eat the same diet. BGL was measured before, during and at the completion of each session. For the whole study group, there was a small but statistically significant decrease in BGL in both the HBOT (7.27 ± 3.66 mmol⁻¹ before to 6.71 ± 3.88 mmol ⁻¹ after, P = 0.037) and control (air) sessions (7.43 ± 3.49 mmol L⁻¹ before to 6.71 ± 3.77 mmol L⁻¹ after, P = 0.004). This fall did not differ between the two conditions (P = 0.59). Examining the three groups separately, BGL fell in all three subgroups, but this fall was only statistically significant for the air session in the diabetic group. There were no statistically significant differences in the BGL reduction when HBOT was compared to normobaric air in any of the three subgroups. BGL may decrease during HBOT and accordingly it should be monitored before entering the chamber. However, this decrease in BGL should probably not be attributed to the hyperbaric environment per se.
What is HBOT treatment?
HBOT is the treatment of patients with 100% oxygen at higher than atmospheric pressure.1This is provided in either a monoplace (single person) chamber typically compressed with oxygen or a multiplace chamber (multiple persons) compressed with air where oxygen is delivered by either a hood or mask.
What are the side effects of HBOT?
Middle ear barotrauma . MEB is one of the most common side effects of HBOT. Patients may report difficulty with ear equalization, a feeling of pressure, ear pain, and discomfort during compression, which is the initial phase of HBOT.9.
Is HBOT a side effect?
As with all medical treatments, HBOT has known potential side effects as a result of treatment.
Does HBOT increase blood pressure?
Blood pressure effects . HBOT causes an increase in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure (DBP). This holds true for both hypertensive and nonhypertensive patients.81 ,82Overall, the effect on blood pressure is mild.
Is PBT considered an HBOT?
The lung is an open air space system. As such, PBT is not expected with HBOT in the absence of pulmonary disease. As such, all potential candidates for HBOT must be thoroughly screened for pulmonary disease, which may increase the risk of PBT. Screening begins with a thorough history and physical examination.
Is hbot safe for diabetics?
Significance:Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is an important advanced therapy in the treatment of problem wounds, including diabetic foot ulcers and late effect radiation injury. HBOT remains among the safest therapies used today. Nonetheless, there are side effects associated with HBOT. It is important for providers to be able to identify, ...
Does HBOT help with ulcers?
HBOT has been shown to significantly improve healing rates in certain problem wounds, including advanced diabetic foot ulcers and late effect radiation injury. It is provided in a variety of clinical settings by providers with varying levels of expertise.
Why is it important to have an hbo technician watch patients at all times?
It is important to have the HBO technician watch patients at all times, check in with the patients about their comfort level and any ear pain, and remind the patients on clearing their ears. It is important to monitor the "grading" of the ear and the signs and symptoms of barotraumas.
Why is it important to monitor insulin intake?
Monitoring of the insulin used and food intake is essential in making sure the patient does have a critical drop in blood sugar while in the chamber. If needed, having the patient's endocrinologist involved can minimize the risk of having the patient be too low due to insulin dosage.
Can hyperbaric oxygen therapy affect vision?
Eyes Complications from Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy. There are only a few side effects from HBO which effect the patient's vision. If the patient has cataracts, it can actually worsen the cataract. If a patient has near vision, during the course of treatment the vision can temporarily improve. However, far vision can worsen.
Is hyperbaric oxygen therapy tolerated?
In general, HBO is very well tolerated and requires little other than a commitment to the treatment series.
Does hyperbaric oxygen therapy affect glucose levels?
The Effects of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy on Blood Glucose Levels. Glucose metabolism is somehow effected by hyperbaric hyperoxia and tends to be seen more severely in those who are insulin dependent. The research on the mechanism that causes this drop is still not completely understood.
Why Is It Important To Have Balanced Blood Sugar Levels?
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels is a very important part of avoiding long-term health issues, managing your weight and just feeling good. Health problems related to blood sugar imbalances are a rapidly growing burden that is reaching epidemic proportions.
Balancing Blood Sugar: Why Is It Important?
Blood sugar refers to the amount of sugar or glucose in the blood at any given time. Glucose is the body’s preferred source of fuel.
Common Questions About Blood Sugar
How often should I test my blood sugar? This is a very common question, and the answer isn't the same for everyone. In general, you should test as often as you need to get helpful information. There's no point in testing if the information you get doesn't help you manage your diabetes.
Why Did Pain Evolve, When Most Life Forms Can Survive Without It?
Consider this as an example: (GRAPHIC PICTURE AHEAD) This is gangrene — tissue death due to infection. Gangrene is common in uncontrolled/untreated diabetics who suffer loss of sensations including pain due to high blood sugar levels (a condition named peripheral neuropathy).
What Is Insulin?
Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas that allows your body to use sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates in the food that you eat for energy or to store glucose for future use. Insulin helps keeps your blood sugar level from getting too high (hyperglycemia) or too low (hypoglycemia). The cells in your body need sugar for energy.
Blood Sugar Regulation
Most cells in the human body use the sugar called glucose as their major source of energy. Glucose molecules are broken down within cells in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules, energy-rich molecules that power numerous cellular processes.
Blood Glucose Control (blood Sugar Levels)
Introduction to blood sugar levels Our blood glucose level, or blood sugar level, is the amount of glucose (sugar) in the blood. The amount of glucose in the blood is measured in millimoles per litre (mmol/l). Glucose levels are measured most commonly to diagnose or to monitor diabetes.
What is HBOT intervention?
They define HBOT as: “An intervention in which an individual breathes near 100% oxygen intermittently while inside a hyperbaric chamber that is pressurized to greater than sea level pressure.”. The body’s tissues need oxygen to function, and additional oxygen can help damaged tissue heal.
What is HBOT session?
An HBOT session typically involves: putting on a cotton medical gown. sitting or lying in a sealed chamber, either alone or with other people, in which case the chamber will be room-sized. receiving pressurized oxygen, which may arrive through a mask or a hood.
What is HBOT in diving?
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves breathing almost pure oxygen in a special room or small chamber. Its main use is to treat diving-related illness, but it may enhance healing in people with various other conditions. In 1662, a physician built the first hyperbaric chamber — a sealed room with a series of bellows and valves.
How many sessions of HBOT?
HBOT is usually an outpatient procedure, and a doctor will recommend a certain number of sessions, depending on a person’s condition. For some people with carbon monoxide poisoning, one session is enough. In some studies involving soft tissue necrosis, participants each received an average of eight treatments.
Is HBOT a good alternative therapy for ADHD?
There are calls for HBOT to receive approval as an alternative therapy for autism, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, better known as ADHD , cerebral palsy, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and others. There is strong support in some circles for using HBOT to help improve the quality of life of veterans.
Does HBOT help veterans?
There is strong support in some circles for using HBOT to help improve the quality of life of veterans. Advocates say that the treatment may benefit those who have experienced traumatic brain injury (TBI) and those who have PTSD. Researchers have been investigating the effects of HBOT on TBI.
Is HBOT a miracle cure?
A growing number of providers have started offering HBOT as an alternative therapy. Some call it a “miracle cure” and claim that it can help with a wide range of conditions. HBOT chambers are appearing in various facilities, from hospital outpatient departments to spas. There are even chambers for home use.
How to control high blood sugar?
If your blood sugar is often high, your doctor may change how much medicine you take or when you take it. Follow your diabetes meal plan. Ask your doctor or dietitian for help if you’re having trouble sticking to it. Check your blood sugar as directed by your doctor.
What is the target blood sugar?
A blood sugar target is the range you try to reach as much as possible. These are typical targets: Before a meal: 80 to 130 mg/dL. Two hours after the start of a meal: Less than 180 mg/dL. Your blood sugar targets may be different depending on your age, any additional health problems you have, and other factors.
How do you know if you have low blood sugar?
Signs of low blood sugar are different for everyone. Common symptoms include: Shaking. Sweating. Nervousness or anxiety. Irritability or confusion. Dizziness. Hunger. Know what your individual symptoms are so you can catch low blood sugar early and treat it.
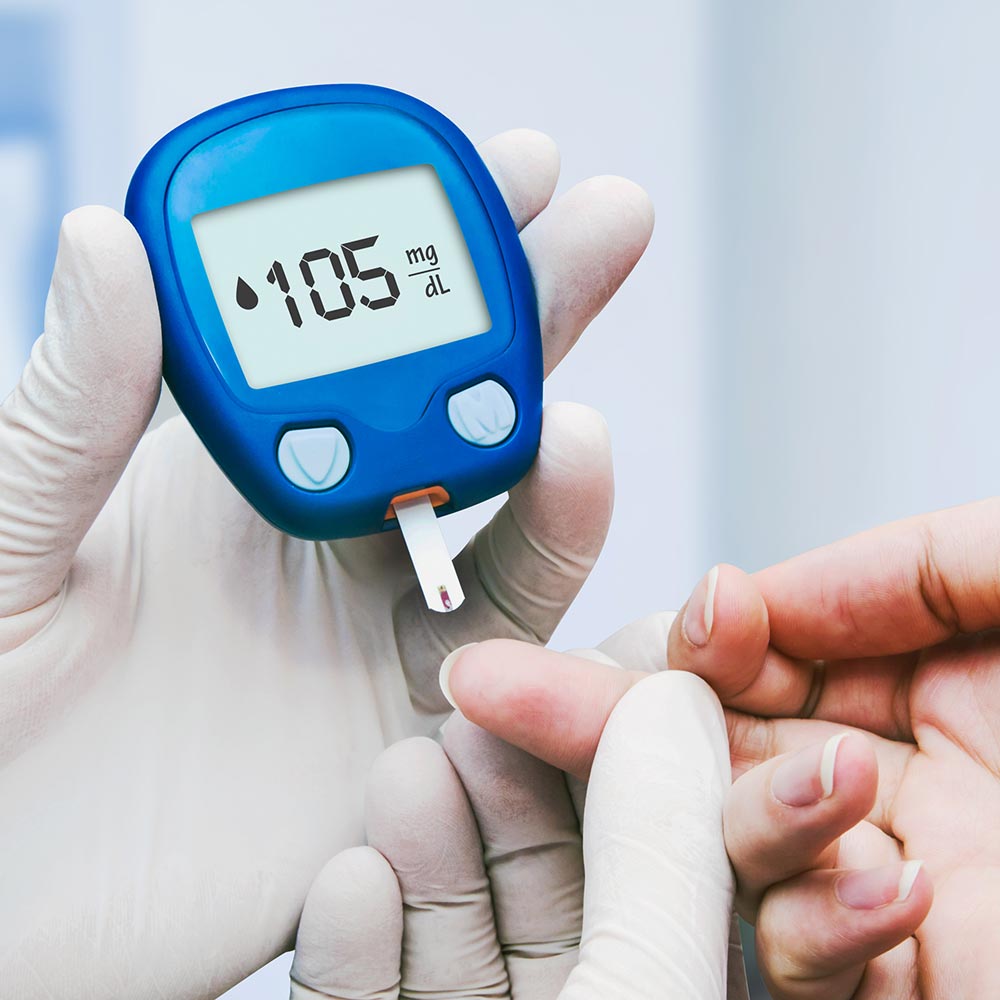
How to check blood sugar?
How can I check my blood sugar? Use a blood sugar meter (also called a glucometer) or a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to check your blood sugar. A blood sugar meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip.
How to get blood sugar to 70?
Drink four ounces of fruit juice. Drink four ounces of regular soda, not diet soda. Eat four pieces of hard candy. Wait for 15 minutes and then check your blood sugar again. Do one of the above treatments again until your blood sugar is 70 mg/dL or above and eat a snack if your next meal is an hour or more away.
Why is it important to monitor your A1C?
It’s important to keep your blood sugar levels in your target range as much as possible to help prevent or delay long-term, serious health problems , such as heart disease, vision loss, and kidney disease. Staying in your target range can also help improve your energy and mood.
Can you eat carbs if you have diabetes?
You can still eat carbs if you have diabetes. The amount you can have and stay in your target blood sugar range depends on your age, weight, activity level, and other factors. Counting carbs in foods and drinks is an important tool for managing blood sugar levels.
Why is blood sugar testing important?
Blood sugar testing is an important part of diabetes care. Find out when to test your blood sugar, how to use a blood sugar meter and more. By Mayo Clinic Staff. If you have diabetes, self-testing your blood sugar (blood glucose) can be an important tool in managing your diabetes and preventing complications.
What is blood sugar testing?
Blood sugar testing provides useful information for diabetes management. It can help you: Monitor the effect of diabetes medications on blood sugar levels. Identify blood sugar levels that are high or low. Track your progress in reaching your overall treatment goals. Learn how diet and exercise affect blood sugar levels.
How often do you need a glucose monitor?
A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) is a device that measures your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin. People with diabetes, particularly those with type 1 diabetes, may also choose to use CGMs. These devices measure your blood sugar every few minutes using a sensor inserted under the skin.
What is the recommended blood sugar level for diabetics?
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) generally recommends the following target blood sugar levels: Between 80 and 130 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or 4.4 to 7.2 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) before meals.
How to check blood sugar with a meter?
Insert a test strip into your meter. Prick the side of your fingertip with the needle (lancet) provided with your test kit. Touch and hold the edge of the test strip to the drop of blood. The meter will display your blood sugar level on a screen after a few seconds.
What to do if you get results that don't fall within the range of your target goals?
If you manually log your results, record the date, time, test results, medication and dose, and diet and exercise information. Bring your record of results with you to your doctor's appointments. Talk to your doctor about what steps to take if you get results that don't fall within the range of your target goals.
Do you need a blood sugar meter for CGM?
The meter measures the amount of sugar in a small sample of blood, usually from your fingertip, that you place on a disposable test strip. Even if you use a CGM, you'll still need a blood sugar meter to calibrate your CGM device daily. Your doctor or diabetes educator can recommend an appropriate device for you.
