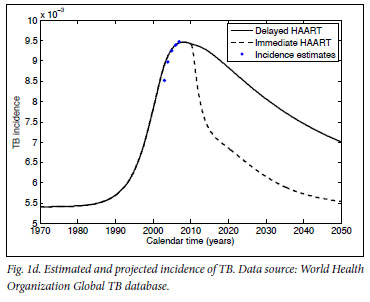
What are the treatment guidelines for HIV?
HIV Treatment Overview 1 To protect your health, it is important to get on... 2 Treatment guidelines from the U.S. 3 Like most medicines, antiretroviral therapy (ART)... 4 Drug Resistance. Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV.
How effective is HIV treatment for HIV infection?
A person with HIV who takes HIV medicine as prescribed and gets and stays virally suppressed or undetectable can stay healthy and has effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to HIV-negative partners. Substantially reduces, but does not eliminate risk.
What are the targets of the HIV treatment strategy?
Further, the Strategy’s targets include reducing the percentage of persons in HIV medical care who are homeless to no more than 5 percent, and reducing the death rate among persons with diagnosed HIV infection by at least 33 percent.
What is HIV viral eradication?
HIV Viral Eradication Viral eradication for HIV would involve the complete elimination of HIV from the body, including the destruction of cells infected with latent HIV.
What is the treatment success rate for AIDS?
Results: Of registered patients, 17.7% were diagnosed at AIDS stage. By June 2016, 27.2% of study population progressed to AIDS, and 8081 (25.1%) of patients died. The survival rate was 88%, 85%, 77%, and 67% for 1, 2, 5, and 10 years, respectively.
Is there any treatment to cure AIDS?
Currently, there's no cure for HIV / AIDS . Once you have the infection, your body can't get rid of it. However, there are many medications that can control HIV and prevent complications. These medications are called antiretroviral therapy (ART).
What is the most effective treatment against AIDS?
How are HIV and AIDS treated? The most effective treatment for HIV is antiretroviral therapy (ART). This is a combination of several medicines that aims to control the amount of virus in your body. Antiretroviral medicines slow the rate at which the virus grows.
Why is it difficult to eradicate AIDS?
So far, HIV has proved almost impossible to eradicate from the human body because the virus integrates into long-lived immune system cells and remains dormant in those cells for many years. In most viral infections the immune system recognises infected cells and kills those cells.
What is HIV treatment?
HIV treatment (antiretroviral therapy or ART) involves taking medicine as prescribed by a health care provider. HIV treatment reduces the amount of...
When should I start HIV treatment?
Start HIV treatment as soon as possible after diagnosis. All people with HIV should take HIV treatment, no matter how long they’ve had HIV or how h...
What if I delay HIV treatment?
If you delay treatment, HIV will continue to harm your immune system. Delaying treatment will put you at higher risk for transmitting HIV to your p...
Are there different types of HIV treatment?
There are two types of HIV treatment: pills and shots. Pills are recommended for people who are just starting HIV treatment. There are many FDA-app...
What are HIV treatment shots?
HIV treatment shots are long-acting injections used to treat people with HIV. The shots are given by your health care provider and require routine...
Can I switch my HIV treatment from pills to shots?
Talk to your health care provider about changing your HIV treatment plan. Shots may be right for you if you are an adult with HIV who has an undete...
What are the benefits of taking my HIV treatment as prescribed?
HIV treatment reduces the amount of HIV in the blood (viral load). Taking your HIV medicine as prescribed will help keep your viral load low. HIV t...
Does HIV treatment cause side effects?
HIV treatment can cause side effects in some people. However, not everyone experiences side effects. The most common side effects are Nausea and vo...
What should I do if I’m thinking about having a baby?
Let your health care provider know if you or your partner is pregnant or thinking about getting pregnant. They will determine the right type of HIV...
Can I take birth control while on HIV treatment?
You can use any method of birth control to prevent pregnancy. However, some HIV treatment may make hormone-based birth control less effective. Talk...
Timely and Accessible HIV Treatment: A Critical Need
While the health and prevention benefits of ART are clear, only 54.7 percent of people living in the United States with diagnosed HIV infection are...
Disparities in HIV Treatment and Care
There are numerous disparities in HIV treatment and care among certain subpopulations in the U.S. For example, CDC’s report on monitoring indicates...
National Priorities: Improving Access to HIV Care and Increasing Viral Suppression
The scientific data showing the benefits of early HIV treatment for health of people living with HIV and prevention informed the National HIV/AIDS...
Measuring Progress: Improving The Health of People With HIV
By 2020, the Strategy aims to increase the percentage of newly diagnosed persons linked to HIV medical care within one month of their HIV diagnosis...
What is the treatment for HIV?
HIV treatment involves taking medicines that slow the progression of the virus in your body. HIV is a type of virus called a retrovirus, and the combination of drugs used to treat it is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of how long they’ve had the virus or how healthy they are.
Why do you prescribe HIV?
Your health care provider may prescribe medicines to prevent certain infections. HIV treatment is most likely to be successful when you know what to expect and are committed to taking your medicines exactly as prescribed.
What is drug resistance in HIV?
What Is HIV Drug Resistance? Drug resistance can be a cause of treatment failure for people living with HIV. As HIV multiplies in the body, it sometimes mutates (changes form) and produces variations of itself. Variations of HIV that develop while a person is taking ART can lead to drug-resistant strains of HIV.
How long do HIV side effects last?
Some side effects can occur once you start a medicine and may only last a few days or weeks.
How soon can you start ART for HIV?
Treatment guidelines from the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services recommend that a person living with HIV begin ART as soon as possible after diagnosis. Starting ART slows the progression of HIV and can keep you healthy for many years.
Is HIV treatment a prevention?
There is also a major prevention benefit. People living with HIV who take HIV medication daily as prescribed and get and keep an undetectable viral load have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to their HIV-negative partners. This is called treatment as prevention.
Can HIV be drug resistant?
A person can initially be infected with drug-resistant HIV or develop drug-resistant HIV after starting HIV medicines. Drug-resistant HIV also can spread from person to person. Drug-resistance testing identifies which, if any, HIV medicines won’t be effective against your specific strain of HIV.
How to treat HIV?
The most effective treatment for HIV is antiretroviral therapy (ART). This is a combination of several medicines that aims to control the amount of virus in your body. Antiretroviral medicines slow the rate at which the virus grows. Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy.
Why is HIV treatment important?
Treatment is especially important for pregnant women, people who have other infections (such as tuberculosis or hepatitis), and people who have symptoms of AIDS. Research suggests that treatment of early HIV with antiretroviral medicines has long-term benefits, such as a stronger immune system.
What happens if you get HIV late?
If HIV progresses to a late stage, treatment will be started or continued to keep your immune system as healthy as possible. If you get any diseases that point to AIDS, such as Pneumocystis pneumonia or Kaposi's sarcoma, your doctor will treat them.
Why is it important to take a medicine after HIV treatment?
Taking these medicines can reduce the amount of virus in your body and help you stay healthy. After you start treatment, it's important to take your medicines exactly as your doctor tells you. When treatment doesn't work, it is often because HIV has become resistant to the medicine.
Why do people get medicine for HIV?
Health care workers who are at risk for HIV because of an accidental stick with a needle or other exposure to body fluids should get medicine to prevent infection. Also, medicine may prevent HIV infection in a person who has been raped or was accidentally exposed to the body fluids of a person who may have HIV.
Can you get HIV treatment if you don't have sex?
But you may decide not to get treated at first. If you put off treatment, you will still need regular checkups to measure the amount of HIV in your blood and check how well your immune system is working. You may want to start HIV treatment if your sex partner doesn't have HIV.
Can HIV be used as a complementary medicine?
Some people with HIV may use complementary medicine to help with fatigue and weight loss caused by HIV infection and to reduce the side effects caused by antiretroviral therapy (ART). Talk to your doctor before using them. Some complementary therapies for other problems may actually be harmful.
How much of HIV can be prevented?
CDC has found that more than 90 percent of new HIV infections could be averted by diagnosing people living with HIV and ensuring they receive prompt, ongoing care and treatment.
What are the disparities in HIV treatment?
There are numerous disparities in HIV treatment and care among certain subpopulations in the U.S. For example, CDC’s report on monitoring indicates that African Americans living with diagnosed HIV infection have percentages of linkage to care and viral suppression that are lower than whites and far below national goals.
What is the HIV rate in 2020?
By 2020, the Strategy aims to increase the percentage of newly diagnosed persons linked to HIV medical care within one month of their HIV diagnosis to at least 85 percent ; increase the percentage of persons with diagnosed HIV infection who are retained in HIV medical care by at least 90 percent ; and increase the percentage of persons with diagnosed HIV infection who are virally suppressed to at least 80 percent. Further, the Strategy’s targets include reducing the percentage of persons in HIV medical care who are homeless to no more than 5 percent, and reducing the death rate among persons with diagnosed HIV infection by at least 33 percent.
How many people die from HIV each year?
When people with HIV do not receive the treatment and care they need, the disease worsens and eventually progresses to AIDS. Today, nearly 13,000 people with AIDS in the United States die each year. People with HIV who have not achieved viral suppression also remain at risk of transmitting the virus to others.
What are the roles of federal agencies in HIV care?
Federal agencies play a variety of roles in supporting HIV care and treatment for people living with HIV in the United States. Some deliver HIV clinical services, others help pay for HIV care and treatment, while others provide housing, training, employment, or income supports that assist people living with HIV to remain in care ...
How does early HIV treatment help?
The Strategy calls for a concerted national effort to improve health outcomes for people living with HIV by establishing seamless systems to link people to treatment and care immediately after diagnosis. The Strategy also calls for efforts to support maintenance in care; increase the capacity of health and social support systems; and increase the number and diversity of professionals who provide clinical care and related services to those with HIV. Further, the Strategy supports comprehensive, patient-centered care for people living with HIV, including addressing co-occurring health conditions and challenges in meeting basic needs, such as housing, which can cause individuals to leave care and treatment.
How does ART help HIV?
When used consistently, antiretroviral therapy (ART) can reduce the amount of virus in the blood and body fluids to very low or undetectable levels (known as viral suppression). As a result, people living with HIV who start ART early, remain on treatment, and achieve and maintain viral suppression can stay healthy and live a near-normal lifespan.
What is HIV medicine?
HIV medicine is called antiretroviral therapy, or ART. If taken as prescribed, HIV medicine reduces the amount of HIV in the body ( viral load) to a very low level, which keeps the immune system working and prevents illness.
What is the number to call for HIV testing?
Provides clinicians with around-the-clock advice on indications and interpretations of HIV testing in pregnancy, and consultation on antiretroviral use during pregnancy, labor and delivery, and the postpartum period. 1-888-448-8765 | 24 hours, seven days a week.
How does HIV help you stay healthy?
Getting and keeping an undetectable viral load * is the best thing people with HIV can do to stay healthy. Another benefit of reducing the amount of virus in the body is that it helps prevent transmission to others through sex or syringe sharing, and from mother to child during pregnancy, birth, and breastfeeding.
How does HIV medicine affect the immune system?
If taken as prescribed, HIV medicine reduces the amount of HIV in the body ( viral load) to a very low level, which keeps the immune system working and prevents illness. This is called viral suppression —defined as having less than 200 copies of HIV per milliliter of blood.
Can HIV be transmitted to HIV-negative partners?
A person with HIV who takes HIV medicine as prescribed and gets and stays virally suppressed or undetectable can stay healthy and has effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to HIV-negative partners.
How does HIV eradication work?
HIV Viral Eradication. Viral eradication for HIV would involve the complete elimination of HIV from the body, including the destruction of cells infected with latent HIV. One strategy under study would deplete the HIV reservoir by prodding the virus out of its latent state so that an enhanced immune system or administered therapies can target ...
What is the role of latency reversing agents in HIV?
Currently, several latency-reversing agents are under investigation in the laboratory and in human clinical trials. Once the latent HIV begins to replicate after the “kick” stage, components of the immune system or therapeutic agents kill the HIV-infected cells to ensure a complete eradication of the latent HIV reservoir.
Can bone marrow cure HIV?
Moreover, attempts to cure HIV with bone marrow transplants in other individuals have not been successful, primarily because the procedure has only been performed in patients with both HIV and blood cancers, which have a high mortality rate even after bone marrow transplants.
Can you get AIDS without ART?
Employing Stem Cell Transplantation and Gene Therapy. In the absence of ART, the vast majority of people living with HIV will eventually develop complications, including AIDS. However, some people living with HIV maintain low levels of virus in the blood—or viral load—even without therapy, indicating that their immune cells are protected from HIV.
What is the cure for HIV?
There are two different visions of a potential HIV cure: treatment-free remission and viral eradication. Treatment-free remission means the virus is controlled without the need for ART drugs, which a person has to take every day for life. Millions of people who have HIV can’t afford ART, so other treatments are needed.
What drugs can kill HIV?
Other types of drugs that may be able to seek out and kill HIV include histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, protein kinase activators, latency securing agents, and immunotoxins. These drugs may be used in combination.
What would be the first part of HIV?
The first part would involve drugs that make the cells in the HIV reservoir multiply and express proteins that are a like a signal to your immune system. The second part would include drugs that detect those protein signals, then seek out and kill the virus.
Can HIV be treated with ART?
Millions of people who have HIV can’t afford ART, so other treatments are needed. This idea of an HIV cure is also called a functional cure. Treatment-free remission means that you’d: Live a healthy life that’s of normal length. Not have to take ART or any other HIV-related drugs to keep the virus under control.
Can HIV be wiped out?
They don’t prevent infection, but stimulate your own immune system to fight it. Viral eradication is another way of looking at a potential cure. It’s also known as a sterilizing cure. Scientists believe it would take a two-part treatment to wipe out HIV in a person’s body.
Can you get HIV if you stop taking ART?
They’re at almost no risk of passing the virus to others. But if you have HIV and take ART drugs, the virus still lives inside a group of cells called the HIV reservoir. If you stop taking ART, the virus in the reservoir can spike again. Right now, there’s still no complete cure for HIV infection.
Where do HIV patients get their services?
Some patients receive services directly at the health center itself, while others are referred to an HIV specialist in the community. Major investments in the network of community health centers over the past several years have created more opportunities for HIV care delivery.
Why is it important to treat viral infections?
These things are important because with the proper care and treatment, you can reduce your viral load, protect your health, enjoy a long and healthy life, and reduce the potential of transmitting the virus to others. But you might have concerns about how to pay for this. There are resources that can help you pay for the care you need.
What is a PAP program?
Patient Assistance Programs (PAPs) are programs administered by pharmaceutical companies to offer free or reduced-cost antiretroviral (ARV) medicines to low-income people living with HIV who are uninsured or underinsured, and who do not qualify for assistance programs such as Medicaid, Medicare, or AIDS Drug Assistance Programs. Each pharmaceutical company has different eligibility criteria for qualifying for their PAP.
Is Medicaid a critical source of coverage for many people living with HIV/AIDS?
It is a critical source of coverage for many people living with HIV/AIDS. States establish and administer their own Medicaid programs and determine they type, amount, duration, and scope of services within broad federal guidelines.
Is there a limit on Medicaid enrollment?
There is no limited enrollment period. If you qualify, your coverage can begin immediately. Even if your state hasn’t expanded Medicaid, you should still apply for coverage to see if you qualify under your state’s existing rules. See if you qualify to save in your state..
Can you apply for medicaid if you have HIV?
As a result, in states that opt for Medicaid expansion, people living with HIV who meet the income threshold no longer have to wait for an AIDS diagnosis in order to become eligible for Medicaid. You can apply for and enroll in Medicaid at any time. There is no limited enrollment period.
How many HIV cases will be averted by 2030?
The initiative seeks to reduce the number of new HIV infections in the United States by 75 percent by 2025, and then by at least 90 percent by 2030, for an estimated 250,000 total HIV infections averted.
What is the end of the HIV epidemic?
What Is Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S.? English (PDF 228 KB) Ending the HIV Epidemic in the U.S. (EHE) is a bold plan announced in 2019 that aims to end the HIV epidemic in the United States by 2030. Agencies across the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) developed an operational plan to pursue that goal accompanied by ...
Can HIV be transmitted to a partner?
Thanks to advances in antiretroviral therapy, the medicine used to treat HIV, individuals with HIV who take their medicine as prescribed and, as a result, maintain an undetectable viral load can live long, healthy lives and have effectively no risk of sexually transmitting HIV to a partner.
How can clinicians ensure routine HIV screening?
One way clinicians can ensure routine HIV screening is by helping individuals access the HIV prevention drug PrEP. Since its approval by the FDA in 2012, pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) has been gaining popularity among those at higher risk for HIV-infection.
What is the window period for HIV?
A “window period” – a few days after immediate infection – when the virus is not detected by a screening, may result in a negative test result even if the individual does in fact have the virus – meaning he or she may begin PrEP despite already having acquired HIV.
How many days after HIV infection did Hiroyu Hatano start ART?
This was the case with one of two individuals in a groundbreaking story spearheaded by former UCSF physician Hiroyu Hatano and a team currently led by Drs. Steve Deeks and Tim Henrich. The doctors studied two individuals who began ART at an estimated 10 (Participant A) and 12 (Participant B) days after HIV infection.
Can HIV be treated early?
Of course, early treatment requires regular testing.