
What should I know about sulfonamide before taking it?
Let your doctor know right away if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction ( anaphylaxis ), which may include rash, hives, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. Tell your doctor about all medical conditions you have — especially kidney, liver, or blood disorders — before taking a sulfonamide.
How do sulfonamide antimicrobials work?
Sulfonamide antimicrobials are bacteriostatic (stop bacteria from reproducing but don't necessarily kill them) and work by interfering with the synthesis of folic acid in bacteria, which is essential for nucleic acid formation and ultimately DNA and RNA. Humans obtain folic acid from their diet,...
How are sulfonamides metabolized?
Several pathways metabolize sulfonamides. Ingested Sulfasalazine reaches the colon unchanged where bacterial enzymes cleave the azo-bond of the drug into sulphapyridine and 5-aminosalicylic acid components. Sulphapyridine is absorbed and acetylated in the liver by N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT 2).
What is the history of sulfonamide?
Sulfanilamide was the first sulfonamide developed in 1906, although it was not used as an antimicrobial agent until the late 1930s.
Which is long acting sulfonamide?
A long acting sulfonamide used for the treatment or prevention of malaria....Long-Acting Antibacterial Sulfonamides.DrugTargetTypeSulfamerazineDihydropteroate synthasetargetSulfamerazineSerum albumincarrierSulfadimethoxineCytochrome P450 2C9enzymeSulfameterDihydropteroate synthasetarget8 more rows
Why are sulfa antibiotics so effective?
Sulfa drugs work by binding and inhibiting a specific enzyme called dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). This enzyme is critical for the synthesis of folate, an essential nutrient. Mammals get folate from their diet, but bacteria must synthesize this vitamin.
How fast do sulfa drugs work?
Bactrim (sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim) is absorbed by the body and begins to kill bacteria within 1 to 4 hours after taking your dose. For more common problems like urinary tract infections and ear infections, most people will start to feel relief after a few days.
Why sulfonamides are ineffective after pus formation?
Urinary alkalinization increases both the fraction of the dose eliminated unchanged in urine and the solubility of sulfonamides in urine. Topical wound powders containing sulfonamides are not useful because blood, pus and tissue breakdown products impede antibacterial effectiveness and wound healing can be delayed.
How do sulfonamides antibiotics work?
Sulfonamide antibiotics work by interfering with folic acid synthesis in susceptible organisms, due to their structural similarity to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) in bacterial cells. Folic acid is essential for nucleic acid synthesis.
How do sulfonamides work against bacteria?
Sulphonamides do not kill bacteria, but it interferes with the ability of bacteria to grow and multiply (bacteriostatic). Folic acid is a key component of bacteria that it uses for growth and multiplication. Sulfa drugs block the ability of the bacteria to use folic acid, thereby inhibiting the growth process.
What is the mechanism of action of sulfonamide?
Mechanism of action As a sulfonamide antibiotic, sulfanilamide functions by competitively inhibiting (that is, by acting as a substrate analogue) enzymatic reactions involving para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). Specifically, it competitively inhibits the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase.
How do the sulfonamides interfere with bacterial metabolism?
Both trimethoprim and the sulfonamides interfere with folate metabolism in the bacterial cell by competitively blocking the biosynthesis of tetrahydrofolate, which acts as a carrier of one-carbon fragments and is necessary for the ultimate synthesis of DNA, RNA and bacterial cell wall proteins (Fig.
How do glycopeptides work?
Glycopeptide antibiotics work by inhibiting the cell wall synthesis of the bacteria. By attaching to its target (D-alanyl-D-alanine terminus) which is part of the cell wall, the invading bacteria are unable to divide and multiply.
What is the major nursing responsibility when administering sulfonamide preparation?
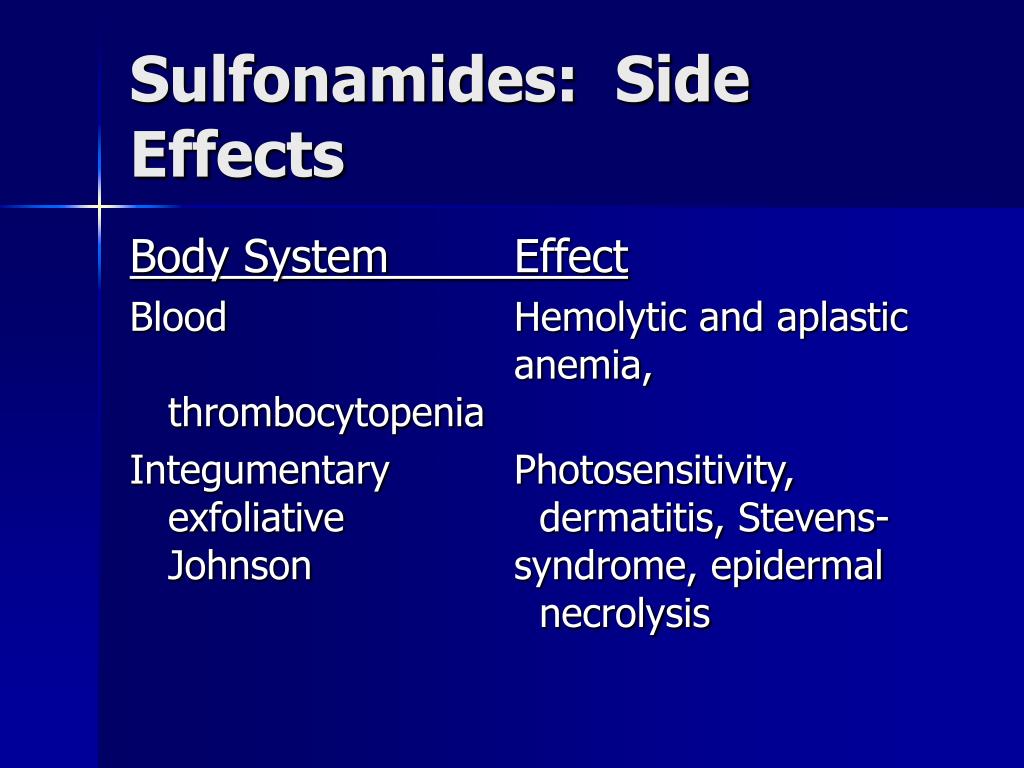
The medication can cause increased photosensitivity, and patients should be educated to use sunscreen and protective clothing with sun exposure. The patient should also report any rash, sore throat, fever, or mouth sores that might occur. Unusual bleeding or bruising should also be reported to the provider.
How does sulfanilamide prevent bacteria producing folic acid?
Sulfonamides, which are derivatives of sulfanilamide, interfere with microbial folic acid synthesis by competitively inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase. This enzyme is involved in the step in folic acid synthesis that precedes the step blocked by pyrimethamine and TMP.
Are sulfonamides broad or narrow spectrum?
Sulfonamides are synthetic, broad-spectrum bacteriostatic antibiotics. Because of associated toxicity and high rates of resistance, their use is now very limited.
How to protect lips from sun?
Apply a sun block lipstick that has an SPF of at least 15 to protect your lips. Do not use a sunlamp or tanning bed or booth. If you have a severe reaction from the sun, check with your doctor. This medicine may also cause some people to become dizzy.
What to wear when you have a sunburn?
Wear protective clothing, including a hat. Also, wear sunglasses. Apply a sun block product that has a skin protection factor (SPF) of at least 15. Some patients may require a product with a higher SPF number, especially if they have a fair complexion.
Can sulfonamides cause skin to be sensitive to sunlight?
Check with your medical doctor or dentist if you have any questions about proper oral hygiene (mouth care) during treatment. Sulfonamides may cause your skin to be more sensitive to sunlight than it is normally.
Can sulfonamide cause skin rash?
Sulfonamides may cause your skin to be more sensitive to sunlight than it is normally. Exposure to sunlight, even for brief periods of time, may cause a skin rash, itching, redness or other discoloration of the skin, or a severe sunburn. When you begin taking this medicine:
Can sulfonamide cause blood problems?
If your symptoms do not improve within a few days, or if they become worse, check with your doctor. Sulfonamides may cause blood problems .
What is sulfonamide used for?
Most sulfonamides are antibiotics, but some are prescribed for treating ulcerative colitis. Sulfonamide antibiotics work by disrupting the production of dihydrofolic acid, a form of folic acid that bacteria and human cells use for producing proteins.
What are some examples of sulfonamides?
Sulfonamides are a class of drugs from a sulfur-containing chemical (sulfanilamide). Examples of sulfonamides include sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim ( Bactrim, Bactrim DS, Co-trimoxazole, Septra, Septra DS, Cotrim, SMZ-TMP, SMZ-TMP DS, Sulfatrim); sulfasalazine (Azulfidine, Sulfazine); and sulfisoxazole (Truxazole, Gantrisin). Some of these drugs are available only in generic forms. Side effects of sulfonamides may include dizziness, lethargy, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, headache, serious skin rashes and anorexia. Sulfonamides are not recommended for women who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Side effects and drug interactions should be reviewed prior to taking this medication.
Can you take trimethoprim while pregnant?
For this reason, sulfamethoxazole/ trimethoprim should not be used near term (late in pregnancy) among women. Sulfonamides (for example, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim) should not be used by nursing mothers because sulfamethoxazole is excreted in breast milk and can cause kernicterus.
Can sulfonamides be used in urine?
All sulfonamides can crystallize in the urine when the urine is acidic. Since methenamine ( Hiprex, Urex, Mandelamine) causes acidic urine, it should not be used with sulfonamides. Blood levels of digoxin may increase blood levels of digoxin ( Lanoxin) and possibly lead to serious toxic effects.
How to report a drug problem to the FDA?
You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit the FDA MedWatch website or call 1-800-FDA-1088. References. FDA Prescribing Information.
Does sulfonamide cause bleeding?
Sulfonamides can increase the blood-thinning effects of warfarin ( Coumadin ), possibly leading to abnormal bleeding. The increased metabolism (break-down and elimination) of cyclosporine by the liver caused by sulfonamides (reduces the effectiveness of cyclosporine and can add to the kidney damage caused by cyclosporine.
Can sulfonamide be stopped?
Sulfonamides should be stopped at the first appearance of a skin rash before the rash becomes severe. Serious rashes include: Stevens-Johnson syndrome, which includes symptoms like: aching joints, aching muscles, redness, blistering, and. peeling of the skin. Toxic epidermal necrolysis, which includes symptoms like:
What is sulfasalazine used for?
Sulfonamides with 5-aminosalicyclic acid are the structural components of sulfasalazine, which is widely used for long term management of inflammatory bowel disease. The combination of sulfadoxine and pyrimethamine is used as prophylaxis against chloroquine-resistant malaria.
What is the name of the sulfonamide?
Formulations of sulfonamides currently in general use in the United States include sulfadiazine, sulfadoxine, and sulfisoxazole as well as the combination formulations including sulfasalazine and trimethoprim-sulfamethazole (TMP-SMZ, also referred to as co-trimoxazole).
What is sulfonamide made of?
The term sulfonamide applies to derivatives of para-aminobenzene sulfonamide (sulfanilamide), which is composed of a benzene ring with a sulfate and amide group at one end and an amide group at the other (para-position).
When were sulfonamides first used?
The sulfonamides were the first effective antibiotics to be introduced into clinical medicine and have been in use continuously since the 1930’s. They are considered bacteriostatic and appear to act by inhibition of bacterial biosynthesis of folic acid, which is needed for cell growth, at least in those bacteria that are sensitive to sulfonamides.
How long does it take for a syringe to appear?
Most typically, the injury appears precipitously within one to three weeks of starting therapy, often preceded or accompanied by signs of hypersensitivity such as fever, rash, facial edema, lymphadenopathy, arthralgias, and eosinophilia or atypical lymphocytosis (or both).
Is sulfonamide bacteriostatic?
They are considered bacteriostatic and appear to act by inhibiti …. The sulfonamides represent a large class of antibiotics that have multiple clinical uses. The sulfonamides were the first effective antibiotics to be introduced into clinical medicine and have been in use continuously since the 1930’s. They are considered bacteriostatic and appear ...
Can sulfonamide be used for urinary tract infections?
However, sulfonamides are still widely used especially for urinary tract infections in combination with trimethoprim and for treatment or prevention of parasitic (toxoplasmosis, pneumocystosis jiroveci) and malarial infections usually combined with trimethoprim or pyrimethamine.
How does sulfonamide work?
Sulfonamides work by preventing the growth of bacteria in the body. They come in different formulations and may be taken as an oral, topical, vaginal, or ophthalmic (eye) medicine. The discovery of sulfonamides paved the way for the widespread use of antibiotics. The first sulfonamide, Prontosil, was tested in the 1930s.
What is sulfa medicine?
Sulfonamides, or "sulfa drugs," are a group of medicines used to treat bacterial infections.
Can sulfonamide cause allergies?
Allergies to Sulfonamides. Allergies to sulfonamides are common. Tell your doctor if you have allergies to food dyes, preservatives, or animals. Let your doctor know right away if you experience signs of a severe allergic reaction ( anaphylaxis ), which may include rash, hives, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, or swelling of the face, lips, ...
Can sulfonamides make you dizzy?
These drugs may make your skin more sensitive to the sun. Avoid unnecessary exposure to sunlight, and wear sunscreen and protective clothing while outdoors. Sulfonamides may make you dizzy. Don't drive or perform activities that require alertness until you know how your medicine affects you.
Can you give sulfonamide to an infant?
Keep all appointments with your doctor's office and laboratory. These medicines shouldn't be given to infants under 2 months old. Elderly people may be more sensitive to the side effects of sulfonamides.
Can you take sulfonamides before 65?
Talk to your doctor if you're over 65. Tell your doctor about all prescription, non-prescription, illegal, recreational, herbal, nutritional, or dietary drugs you're taking before using sulfonamides.
What is sulfonamide?
What are Sulfonamides? Sulfonamides (sulphonamides) are a group of man-made (synthetic) medicines that contain the sulfonamide chemical group. They may also be called sulfa drugs. Many people use the term sulfonamide imprecisely to refer only to antibiotics that have a sulfonamide functional group in their chemical structure.
How many people have sulfonamide allergic reactions?
Sulfonamide allergic reactions affect 1.5-3% of the population but are 10 times more likely in people with HIV. Management depends on the type and severity of the reaction. Mild reactions can be treated with drug discontinuation and antihistamine administration.
What is the N4 amine group in sulfonamide?
Sulfonamide antibiotics have an N4 amine group in their structure which is thought to contribute to their higher incidence of allergic-type reactions. Non-antibiotic sulfonamides lack this structure.
What are the symptoms of erythema nodosum?
Erythema nodosum: Symptoms include red, hot and painful lumps on the shins or about the knees and ankles, often associated with joint pains or fever. Erythema multiforme: Symptoms include the appearance of skin lesions that look like targets (show three concentric zones of color).
What are some examples of sulfonamides?
Examples of some conditions that may be treated with sulfonamides include: Bacterial infections: eg, sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim, sulfisoxazole. Crohn’s disease: eg, sulfasalazine. Diabetes: eg, glyburide, tolbutamide.
How long does it take for a rash to form after taking a med?
Fixed drug eruptions: Symptoms develop within 30 minutes to 8 hours of taking the drugs and include well-defined, round or oval patches of redness and skin swelling, sometimes surmounted by a blister. Type I immediate, IgE-mediated, true allergic response: Hives occur within 30 minutes of drug administration.
Is sulfonamide safe?
Are sulfonamides safe? Sulfonamide-containing drugs are frequently implicated in allergic and non- allergic reactions. The term “sulfa allergy” (or “sulfur allergy”) most commonly refers to an immunological response to sulfonamides, and it is a term that is often misused and misinterpreted.
Case Report
A 31-year-old female with Crohn’s disease and no known drug allergies underwent colonoscopy on 3/20/00 that revealed proctitis. She was treated with Ciprofloxacin and Sulfasalazine. On April 16, 2000, she developed arthralgias, and on April 20, she developed back pain, fatigue, headache, and fever to 104° F.
Discussion
Several pathways metabolize sulfonamides. Ingested Sulfasalazine reaches the colon unchanged where bacterial enzymes cleave the azo-bond of the drug into sulphapyridine and 5-aminosalicylic acid components [ 9 ]. Sulphapyridine is absorbed and acetylated in the liver by N-acetyltransferase 2 (NAT 2).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Richard Wang, DO, and David Marcozzi, MD for assistance in procuring and testing for slow acetylation in our patient.
What enzyme is used to synthesize folic acid?
Bacteria resistant to sulfa drugs often have mutations in the DHPS enzyme. These mutations occur on 2 floppy loops that sit near the enzyme's active site.
How do sulfa antibiotics work?
Sulfa antibiotics work because they fit into the DHPS active site and take PABA's place. By embedding sulfa antibiotics into the enzyme crystals, the scientists found that the sulfa drugs are held in place by the floppy loop structures. However, a small portion of the drug sticks out of the binding pocket. The researchers discovered that DHPS ...
How does sulfa work?
Sulfa drugs work by binding and inhibiting a specific enzyme called dihydropteroate synthase (DHPS). This enzyme is critical for the synthesis of folate, an essential nutrient. Mammals get folate from their diet, but bacteria must synthesize this vitamin.
What is the DHPS enzyme?
The scientists isolated the DHPS enzyme from 2 bacterial species: Bacillus anthracis, which causes anthrax, and Yersinia pestis, which causes plague.
What is the first class of antibiotics ever discovered?
Bacillus anthracis. CDC/ Dr. William A. Clark. Researchers have finally found out how sulfa drugs —the first class of antibiotics ever discovered—work at the molecular level. The finding offers insights into designing more robust antibiotic therapies.
What is sulfa used for?
While antibiotic resistance remains a problem for this class of antibiotics, sulfa drugs are still commonly used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Sulfa drugs work by binding ...
What is a sulfa allergy?
A sulfa allergy is a rash or more serious reaction to sulfa drugs. These drugs can treat a range of health problems from eye infections to rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Sulfa drugs, also called sulfonamides, include antibiotics as well as other types of drugs. Allergies happen most often with antibiotics. About 3 percent of people have some type of ...
How to prevent sulfa allergy?
Sulfa Allergy Prevention. If you have a drug allergy, it’s best to avoid medications that will cause a bad reaction or side effect. Here are some other tips: Notify your health care providers. Tell them about any drug allergies so they can make a note in your medical records. Wear a medical bracelet.
What are the symptoms of sulfa allergy?
If you’re allergic to sulfa drugs or any other medication, you may have one or more of these symptoms: Skin rash or hives. Itchy eyes or skin. Breathing problems. Face swelling. The reaction can also cause these serious skin reactions: Sulfonamide drug hypersensitivity syndrome.
What are some examples of sulfa drugs?
Here are a few examples of common sulfa drugs that could cause problems: Sulfamethoxazole / trimethoprim ( Bactrim, Sulfatrim ), a sulfa combination drug that can be taken in liquid or pill form for many types of infections. Sulfacetamide ( BLEPH -10), drops for eye infections.
How many people have a reaction to sulfa?
About 3 percent of people have some type of reaction to them. Tell your doctor right away if you think you’re having a reaction to a sulfa drug. They’ll decide whether to take you off the drug and how to treat your symptoms.
When was sulfa first used?
Sulfa antibiotics have been widely used for more than 70 years. The first antibiotic was a sulfa drug introduced in 1936. Today, these drugs include burn creams, vaginal suppositories, and eye drops as well as medications for many types of infections.
Is sulfa related to sulfites?
Sulfa drugs and sulfites are not related. Neither are their allergies. There’s no need to give up dried fruit, wine, or other items that have sulfites if you’re sensitive to sulfa drugs. Share on Facebook Share on Twitter Share on Pinterest Email Print. Pagination.
