Full Answer
How does photopheresis treatment work?
The IV is attached to the Photopheresis treatment machine. Blood is withdrawn from the patient (pumped out of the patient through the IV) and fed into a bag until a sufficient quantity is gathered (about two cups). The blood is then spun down to separate the red cells and white cells.
What is photopheresis treatment for GvHD?
In medicine, Photopheresis is a medical treatment process used to treat a variety of diseases, one of which is GvHD. It is touted as one of the least toxic and least invasive treatment strategies available for GvHD. It is also known by the name 'Extra-corporeal Photopheresis', or abbreviated as 'ECP' or just called 'photo' or 'light therapy'.
What should I do after photopheresis?
After photopheresis, follow these guidelines. Leave the bandage on the needle site for 3 hours after your procedure. Avoid heavy lifting for the rest of the day. If you have bruising, place a cold compress to the needle site for the first 24 hours. If you have discomfort, place a warm compress on the site.
What is photopheresis (ECP)?
Photopheresis (also known as extracorporeal photochemotherapy, ECP) is a blood-filtering treatment that works with your body’s own immune system to treat disease.

What is a photopheresis procedure?
Photopheresis is a form of apheresis in which a small amount of white blood cells are treated with a photoactive drug which is then activated with ultravioulet (UV) light. Apheresis procedures involve removing blood from the patient and passing the blood through an apparatus that separates it into components.
What is photopheresis used to treat?
Photopheresis is used to modulate the body's immune response system to make the immune system more tolerant. The treatment is used to treat: Lung transplant rejection. Heart transplant rejection.
Is photopheresis painful?
Photopheresis is considered a safe procedure that brings little, if any, discomfort.
How long does it take photopheresis to work?
If there is no response in 3 or 4 months, then the procedure should be stopped. In sclerodermatous skin changes, the improvement occurs very gradually, and 6–12 months of treatment may be required before tapering is used.
Why is photopheresis done?
Photopheresis is a procedure that might be recommended to prevent or to treat graft versus host disease (GvHD). This procedure offers another way to try to suppress the donor lymphocytes (type of white blood cells) that stimulate immune reactions and aid in the development of GvHD.
Is photopheresis successful?
For the 91 patients who achieved 6-month freedom from treatment failure, 1-year, 2-year and 3-year survival rates were 78.9%, 70.8% and 69.5%, respectively. Six-month freedom from treatment failure is a reasonable early surrogate for outcome and should be considered as a clinical trial endpoint.
How much does photopheresis cost?
It is estimated that on an average, the ECP therapy requires nearly two to three hours at a stretch for the treatment to complete for various disease. Also, the patient is required to undergo the treatment once every two weeks for a year. The cost of per treatment is around US$8000 per treatment.
How do you feel after photopheresis?
What are the side effects of photopheresis?You may experience a fever of 100.4° F (38° C) or higher within 6 to 8 hours after your procedure. ... You may have some tenderness or bruising at the needle site. ... Some people experience a drop in blood pressure that can cause lightheadedness or dizziness after the procedure.More items...•
Does GVHD ever go away?
GVHD usually goes away a year or so after the transplant, when your body starts to make its own white blood cells from the donor cells. But some people have to manage it for many years.
How is extracorporeal photopheresis done?
In this procedure, your child's blood is drawn and the white blood cells are separated from the rest of the blood. The white blood cells are then combined with a photoactive drug, exposed to ultraviolet light to “activate” the medicine, and finally reinfused back into your child.
What is leukapheresis procedure?
Leukapheresis is a procedure used to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or patients with very high white blood cell counts. During leukapheresis, your blood passes through a machine that takes out the white blood cells and returns all the other blood cells and plasma back into the bloodstream.
What does ECP mean medical?
External counterpulsation (ECP) is a non-invasive, outpatient treatment for coronary artery disease with angina refractory to medical and/or surgical therapy.
How long does it take for apheresis to work?
The procedure typically takes 2 hours.
Is photopheresis safe?
Photopheresis is a safe procedure with a few possible side effects. If intravenous catheters are placed, the arms will be propped on pillows and you will be asked to intermittently pump a fist to help promote blood flow. One may experience bruising or discomfort at the insertion sites.
How to contact photopheresis center?
Referrals may be faxed to (410) 955-5322. To contact the photopheresis center if you are undergoing treatment or have non-scheduling questions, please call (410) 502-0020.
What is the treatment for white blood cells?
Photopheresis. Photopheresis is a form of apheresis in which a small amount of white blood cells are treated with a photoactive drug which is then activated with ultravioulet (UV) light.
What is photopheresis therapy?
What is photopheresis? Photopheresis or extracorporeal photoimmune therapy is a procedure that might be recommended by your doctor to prevent or to treat graft versus host disease (GvHD).
How is blood taken during photopheresis?
During photopheresis, blood is taken from one lumen of your central venous catheter and processed through a cell separation machine. This machine removes and treats your lymphocytes and then returns them and the rest of your blood to your body.
What happens to lymphocytes during photopheresis?
When the treated lymphocytes are re-infused, they will stimulate an immune response in your body to fight the development or progression of Gv HD. Your doctor might use photopheresis alone or in combination with other treatments.
What is the procedure to treat graft versus host disease?
Photopheresis is a procedure that might be recommended to prevent or to treat graft versus host disease (GvHD). This procedure offers another way to try to suppress the donor lymphocytes (type of white blood cells) that stimulate immune reactions and aid in the development of GvHD.
How does a nurse do a photopheresis?
Your nurse will place a needle into your arm or will connect your CVC to the photopheresis machine. The photopheresis machine will draw your blood and separate the white blood cells from the rest of the parts of your blood. The remaining cells in your blood will be placed back into your vein through your arm or CVC.
Where is the CVC placed for photopheresis?
If they can’t, you’ll have a central venous catheter (CVC) placed in a large vein below your collarbone. Your blood will be taken from the CVC for the photopheresis procedure. If you need to have a CVC placed, your healthcare provider will give you more information about it.
What is the treatment for GVHD?
The treated white blood cells will then be re-infused into your body through your arm or CVC. The treated cells will help your immune system fight GVHD or CTCL. Another medication called heparin is used during the procedure to prevent your blood from clotting in the photopheresis machine. Back to top.
What is the procedure called for graft versus host disease?
Photopheresis (FOH-to h-feh-REE-sis), or extracorporeal photoimmune therapy , is a procedure that treats graft versus host disease (GVHD, a disease caused when donated stem cell graft attacks normal tissue) or cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). During photopheresis, some of your blood is taken from your vein.
What is the phone number for the Koch Apheresis Unit?
If you have any questions or concerns, call the Blood Donor Room at 212-639-6178 or the Koch Apheresis Unit at 646-608-3142. They can be reached Monday through Friday from 8:00 am to 6:00 pm. After 6:00 pm and on the weekends, call 212-639-2000.
What is the treatment for white blood cells?
Your white blood cells are treated with a medication called methoxsalen, exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light, and then put back in your vein, along with your other blood cells.
Can you drink too much before photopheresis?
Eat low-fat meals and don’t skip any meals. You won’t be able to use the bathroom during photopheresis, so don’t drink too much for a few hours before your procedure. If you need to use the bathroom during the procedure, you may use a bedpan or urinal.
What is photopheresis used for?
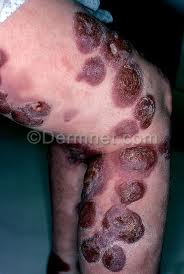
Photopheresis is most commonly used to treat cutaneous T-cell lymphomas (CTCL), such as mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome. The Stanford Multispecialty Cutaneous Lymphoma Clinic (CLC) is a leading center of excellence for managing patients with CTCL.
What is the treatment for apheresis?
Photopheresis. Photopheresis is one method of apheresis therapy offered at the Stanford Cancer Center. The treatment is also called extracorporeal ("out of the body") photochemotherapy (ECP) because it involves a light-activated drug, such as psoralen, that enters the patient's bloodstream.
What is photopheresis used for?
What is Photopheresis? In medicine, Photopheresis is a medical treatment process used to treat a variety of diseases, one of which is GvHD. It is touted as one of the least toxic and least invasive treatment strategies available for GvHD. It is also known by the name 'Extra-corporeal Photopheresis', or abbreviated as 'ECP' or just called 'photo' ...
How long does photopheresis last?
Initially, Photopheresis was prescribed for four weeks, and only for skin GvHD. The initial use of 'photo', as it is often called by the patients, showed remarkable (very good) results. Nearly all of the patients who were prescribed photo were positively affected by it.
Why do you have to have two appointments for photopheresis?
Originally, when Photopheresis came into fruition and use back in 1988, two appointments were set on consecutive days to check the efficacy of the treatment and for safety purposes. The fact that more blood is processed by two appointments is a collateral benefit. There is no chemical reason for the two appointments.
How is a photopheresis IV started?
In a Photopheresis treatment, an IV is started, if a central line or PICC is absent. The IV is attached to the Photopheresis treatment machine. Blood is withdrawn from the patient (pumped out of the patient through the IV) and fed into a bag until a sufficient quantity is gathered (about two cups).
How many treatments per week for photo?
Expect to have two treatments per week, although some people have three appointments. Photo is usually quite uneventful, even mundane, so you might fall asleep. If you move in your sleep, it may affect the machine, sounding the annoying alarms that the tech must turn off when adjusting the machine.
Is photopheresis a standardized treatment plan?
While there is a common standard for GvHD patients, treatment plans are individualized. Doctors prescribing Photopheresis fall on the standardized treatment plan developed for their oncology department (and likely adopted from all other oncology departments).
Does photopheresis help with GvHD?
Originally, Photopheresis was begun to treat skin GvHD, and it was found that other types of GvHD also improved for some people, while the Photopheresis (aka photo) didn't help a relatively few number of people (see statistics above). Photopheresis is also used in a variety of other treatments, such as the few listed below.
What is the photopheresis system?
The THERAKOS CELLEX Photopheresis System is indicated for use in the ultraviolet-A (UVA) irradiation, in the presence of the photoactive drug 8-methoxypsoralen (8-MOP®), of extracorporeally circulating leukocyte-enriched blood, in the palliative treatment of the skin manifestations of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), in persons who have not been responsive to other forms of treatment.
How long after photopheresis can you get sun exposure?
Advise patients to wear UVA absorbing, wrap-around sunglasses and cover exposed skin or use a sunblock (SPF 15 or higher), and avoid all exposure to sunlight for twenty-four (24) hours following photopheresis treatment.
What is the purpose of the THERAKOS system?
The THERAKOS Photopheresis System is an immunomodulatory therapy that uses extracorporeal photopheresis (ECP) to help enhance immunologic response.*. THERAKOS Photopheresis was first approved by the FDA in 1987 for the palliative treatment of CTCL skin symptoms in patients who were not responsive to other types of treatment. 1.
How many treatment centers are there for THERAKOS?
THERAKOS Photopheresis is now available in more than 170 treatment centers across the United States. 3 Treatment centers are independent, third-party facilities not owned, operated, or controlled by Mallinckrodt Pharmaceuticals. *The exact mechanism of UVADEX is not known.
What are the other systemic therapies?
Chemotherapy. Other systemic therapies (eg, retinoids, interferons) Treatment decisions can incorporate the disease stage, overall prognosis, patient quality of life, and most bothersome symptoms, as well as treatment history and patient preference. 6. SEE THE CLINICAL EFFICACY OF ECP.
Is the THERAKOS system FDA approved?
A Systemic Treatment Option. THERAKOS Photopheresis is the only FDA-approved photopheresis system. It is a systemic treatment indicated for the palliative treatment of CTCL skin manifestations in patients unresponsive to other forms of treatment. 1.
Is photopheresis a retinoid?
Photopheresis is not a retinoid, an inter feron, or chemotherapy. 5,6 THERAKOS Photopheresis inhibits DNA synthesis and cell division, inducing apoptosis in treated white blood cells, including CTCL cells. 2,7,8 The exact mechanism of UVADEX is not known.
