Authors' conclusions: The available evidence does not support the use of beta blockers as first-line drugs in the treatment of hypertension. This conclusion is based on the relatively weak effect of beta blockers to reduce stroke and the absence of an effect on coronary heart disease when compared with placebo or no treatment.
Full Answer
Should beta‐blockers be used as initial therapy for hypertension?
Abstract. In the past 4 decades, beta blockers (BBs) have been widely used in the treatment of uncomplicated hypertension and are still recommended as first-line agents in national and international guidelines. Their putative cardioprotective properties, however, derive from the extrapolation into primary prevention of data relative to the reduction of mortality observed in …
Are first‐line beta‐blockers better than thiazides for hypertension?
Jun 28, 2006 · Beta-blockers Should Not Be First Line Treatment For Hypertension. Beta-blockers should not be routinely used for the treatment of high blood pressure, says the National Institute for Health and ...
Are first‐line beta‐blockers as effective as first-line ACE inhibitors?
9 rows · Jan 20, 2017 · Beta‐blockers were thought to have similar beneficial effects when used as first‐line therapy ...
Does beta‐blocker therapy for hypertension (atenolol) reduce stroke risk?
Nov 01, 2007 · Authors' conclusions: The available evidence does not support the use of beta blockers as first-line drugs in the treatment of hypertension. This conclusion is based on the relatively weak effect...

Are beta blockers effective first line treatments for hypertension?
Authors' conclusions: The available evidence does not support the use of beta blockers as first-line drugs in the treatment of hypertension.Nov 1, 2007
Should beta blockers remain first choice in the treatment of primary hypertension?
Practice: The authors stated that beta-blockers should not remain the first choice in the treatment of primary hypertension. Research: The authors stated that beta-blockers should not be used as reference drugs in future RCTs of primary hypertension.
Which antihypertensive medication is no longer considered as first line agent?
Although beta-blockers have fallen out of favor as first-line agents in those with uncomplicated hypertension, there will likely continue to be a role for beta-blockers in the treatment of patients with hypertension combined with chronic stable angina, HF or who are post-MI.Jun 1, 2009
Why are beta blockers not recommended?
There are some conditions in which beta blockers are not recommended. This includes uncontrolled heart failure, hypotension (low blood pressure), certain problems with the rhythm of your heart, or bradycardia (a very slow heart beat).
Why is propranolol not used frequently as an antihypertensive?
Propranolol is not recommended for the treatment of high blood pressure by the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8) because a higher rate of the primary composite outcome of cardiovascular death, myocardial infarction, or stroke compared to an angiotensin receptor blocker was noted in one study.
When are beta blockers first line?
Historically, β-blockers had been recommended as one of the first-line treatment options for primary hypertension by the Joint National Committee on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure from its first report in 1977 through its seventh report in 2003.Mar 29, 2021
Which are the drugs for 1st line treatment of hypertension?
Evidence-Based Answer Objectives: To quantify the benefits and harms of the major first-line antihypertensive drug classes: thiazides, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, alpha blockers, and angiotensin receptor blockers.Jun 1, 2010
Why are beta-blockers good for hypertension?
Beta blockers work by blocking the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. Beta blockers cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force, which lowers blood pressure.
Why are beta-blockers not recommended for people over 60?
It is argued that the use of beta blockers in older adults may not be justified because of physiologic changes in people over 60 years of age. These include a low cardiac output, bradycardia, high total peripheral resistance, reduced renal blood flow and glomerular filtration rate, and low plasma renin activity [18].Oct 16, 2017
Which beta-blocker is best for hypertension?
Propranolol and atenolol have been studied most intensely in hypertension. For secondary prevention of myocardial infarction, the evidence is best for timolol. Sotalol is probably the best antiarrhythmic among the beta-blockers. Whether any individual beta-blocker is best for heart failure remains to be seen.
What is a good substitute for metoprolol succinate?
A good alternative to metoprolol succinate is bisoprolol, which is also cardioselective and is once daily dosing, and has a simpler four step dosing range to the maximum dose of 10 mg.3. Wiysonge CS, et al. Beta-blockers for hypertension. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Click here.
Can beta blockers cause CVD?
Beta-blockers no longer first line for simple hypertension. Initiating treatment of hypertension with beta-blockers leads to modest CVD reductions and little or no effects on mortality (atenolol mainly studied).
Does beta blocker help with stroke?
Compared with placebo there was a reduction in stroke. The role of beta-blockers is now for heart rate slowing in tachyarrythmias, post myocardial infarct (and only for one year if no heart failure exists) and congestive heart failure and as a 4th or 5th line blood pressure lowering medication.
How many people are taking beta blockers in the UK?
At present there are about two million patients in the UK who are receiving Beta-blockers for hypertension. Patients need to know that Beta-blockers are also used for heart failure and angina. The drugs are still indicated for those conditions.
When was the beta blocker guidance published?
The watchdog stresses that patients must keep taking their beta-blockers until they see their doctors. The guidance, which was published in 2004, has been updated after NICE and the British Hypertension Society decided that the guidance’s section which deals with hypertension medications needed a further update.
What is the first line of therapy for hypertensive patients?
First line of choice of initial therapy should be either a calcium channel blocker or a thiazide-type diuretic. ( Black patients – does not include patients of mixed race or Asian patients).
Can beta blockers be used for hypertension?
Beta-blockers Should Not Be First Line Treatment For Hypertension. Beta-blockers should not be routinely used for the treatment of high blood pressure, says the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE), UK. NICE is the NHS watchdog for England and Wales.
What is the best blood pressure to treat stroke?
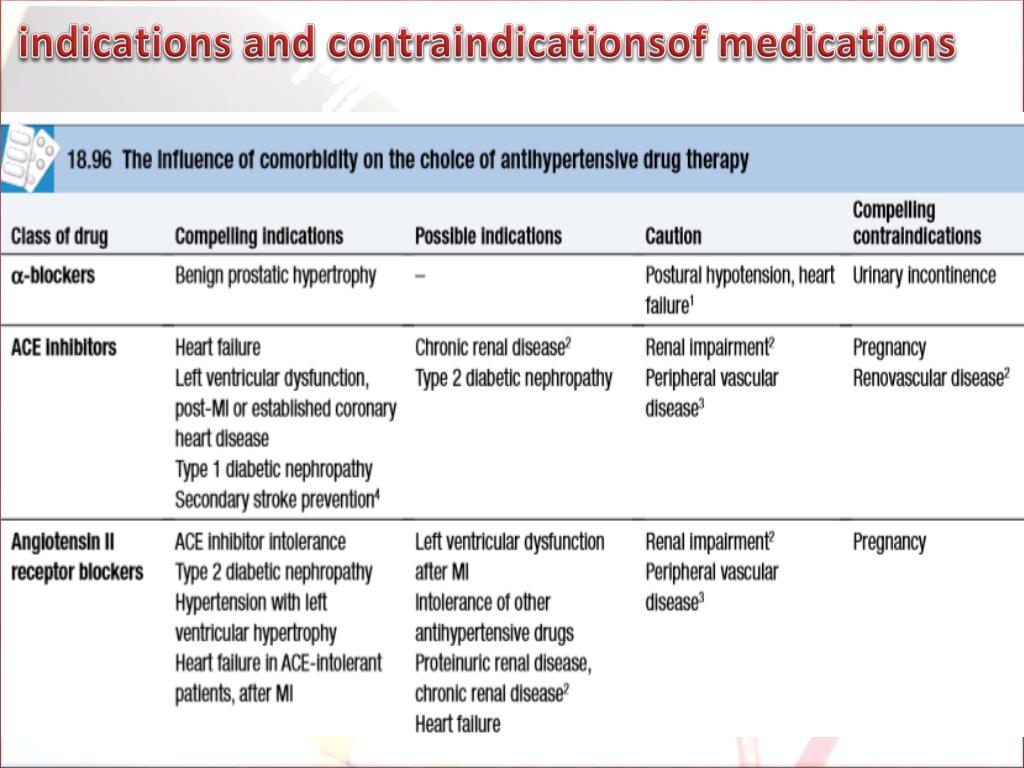
To reduce rates of stroke and coronary heart disease, the Seventh Report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure (JNC 7) recommends reducing blood pressures to 140/90 mm Hg in the general population and to 130/80 mm Hg in patients with diabetes or chronic kidney disease. 1 If patients do not meet blood pressure goals with lifestyle modifications, thiazide diuretics are recommended as first-line pharmacotherapies. Other antihypertensive medications are recommended if certain “compelling indications” are present: beta blockers for coronary heart disease with angina, beta blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) for heart failure, and ACE inhibitors or ARBs for diabetes. 1
Can beta blockers be used as an initial therapy for hypertension?
Evidence-Based Answer. Current evidence does not support the use of beta blockers as initial therapy for hypertension.
Is beta blocker better than diuretics?
Although beta blockers were no better or worse than diuretics, they were inferior to calcium channel blockers in reducing risk of mortality or total cardiovascular disease and were inferior to ACE inhibitors or ARBs and calcium channel blockers in reducing risk of stroke. The only findings favoring beta blockers showed that they were superior ...
Do beta blockers have differential effects?
However, it is not known whether beta blockers have differential effects on younger and older patients or whether there are differences among the subtypes of beta blockers. These summaries have been derived from Cochrane reviews published in the Cochrane Database of SystematicReviews in the Cochrane Library.
Can beta blockers be used as a first line drug?
Authors' conclusions: The available evidence does not support the use of beta blockers as first-line drugs in the treatment of hypertension. This conclusion is based on the relatively weak effect of beta blockers to reduce stroke and the absence of an effect on coronary heart disease when compared with placebo or no treatment.
Is allhat a calcium channel blocker?
ALLHAT (Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering treatment to prevent Heart Attack Trial) demonstrated that thiazide diuretics are as effective as calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors for reducing cardiovascular risk. 6. Read the full article. Get immediate access, anytime, anywhere.
Can you take multiple medications for hypertension?
It is unlikely there will ever be a single ideal first-line drug for hypertension and most patients will eventually need multiple drugs to control their blood pressure. Treatment needs to be individualised for all patients.
Do you need more than one beta blocker for hypertension?
Many patients will need more than one drug to treat their hypertension. Beta blockers remain important and effective drugs, but age and comorbidities need to be considered when selecting a first-line drug.
Can atenolol be used as a beta blocker?
Whether the atenolol findings can be generalised to all beta blockers is therefore uncertain, however given the variety of drugs in the class it would seem premature to dismiss them all for the treatment of hypertension. Beta blockers are effective at significantly reducing the risk of strokes compared to placebo or no drugs.
Does atenolol lower systolic pressure?
Specifically with atenolol, the central aortic systolic pressure is not reduced as much as the peripheral systolic pressure.
Do beta blockers have a weak antihypertensive effect?
This has been raised as evidence that beta blockers have a weak antihypertensive effect.
Do beta blockers have a lipophilic effect?
They vary in their lipophilicity, receptor specificity, mode of elimination, half-life, primary indications and cost. The exact mechanism by which beta blockers exert their antihypertensive effect is uncertain.
Do beta blockers reduce stroke risk?
A meta-analysis has found that, compared to placebo, beta blockers are effective drugs and are associated with a 19% lower relative risk of stroke. 1 Compared to other antihypertensive drugs, there were no differences for all cause mortality or for myocardial infarction, but beta blockers did not reduce stroke to the same extent.
Do BBs lower BP?
In the elderly, the hemodynamic profile is typically characterized by low cardiac output and high peripheral resistance. Focusing on their pure pharmacodynamic effects, most BBs lower BP by further decreasing cardiac output and increasing systemic vascular resistance. The difference pattern of hypertension, such as mainly systolic or diastolic, also might affect BBs efficacy. Because of their negative chronotropic effect, BBs should not be prescribed to patients with predominantly systolic hypertension. In fact, the decrease in heart rate tends to be compensated by a parallel increase in stroke volume, which will elevate systolic BP and decrease diastolic BP, resulting in an unfavorable increase in pulse pressure. Moreover, even taking into account the favorable independent prognostic impact conferred by lowering heart rate, 25 either by nonpharmacologic interventions or by heart rate–lowering drugs, a recent reanalysis from Bangalore et al 26 of nearly 65,000 patients with uncomplicated hypertension showed that, in patients treated with BBs, lower heart rates were associated with a significantly higher risk for all-cause mortality, CV mortality, myocardial infarction, stroke, and heart failure. The same concept can be also be applied to hypertensive patients with higher heart rates at rest, a group of patients in whom it is a widely accepted belief that BB therapy would be indicated as the first choice. In contrast, a recent reanalysis of a subgroup of ASCOT concluded that the superiority of amlodipine-based over atenolol-based therapy for patients with uncomplicated hypertension was independent from heart rate and, more interestingly, was maintained in those patients with higher baseline heart rates. 27
Can a BB cause vision problems?
BBs considered as a class have many undesirable adverse effects, including drowsiness, lethargy, sleep disturbance, visual hallucinations, depression, blurring of vision, dreams or nightmares, pulmonary side effects such as increased airway resistance in asthmatics, and peripheral vascular side effects such as cold extremities, Raynaud's phenomenon, and erectile and orgasmic dysfunction. It is common experience that BBs are often less tolerated in elderly patients than other drugs. For instance, in MRC trial, twice as many patients withdrew from the BB arm because of major adverse effects than from the diuretic arm. 9 Thus, BBs might expose elderly patients to adverse effects and costs while conferring little if any true benefit.
Does BB cause diabetes?
Metabolic side effects induced by long-term BB treatment could have a particular negative influence in younger patients. Traditional BBs, in fact, have been shown to increase insulin resistance and predispose patients to diabetes. In a meta-analysis including almost 150,000 patients without diabetes, the risk for new-onset diabetes was significantly increased with diuretics and BBs than with placebo or other classes of antihypertensive drugs. 32 Possible mechanisms by which BBs may contribute to the development of diabetes include weight gain, attenuation of the β-receptor-mediated release of insulin from pancreatic β cells and decreased blood flow through the microcirculation in skeletal-muscle tissue, leading to decreased glucose uptake and increased insulin-resistance. 33 Second, BBs can worsen the blood lipid profile. In fact, the long-term administration of BBs has been shown to increase triglyceride levels by 20% to 50% and decrease high-density lipoprotein cholesterol by 10% to 20%. 33 BB therapy also hampers exercise capacity. The mechanism of reduced exercise tolerance in patients taking BBs may be attributed to their hemodynamic effects, such as decrease in heart rate, cardiac output, and mean BP, together with some of their side effects, such as lethargy, sleep disturbance, or depression. As a consequence, BB use has been associated with small but systematic weight gain. In the few hypertension studies that reported weight status, in fact, BB use resulted in weight gains of as much as 1.2 kg. 34 The weight gain secondary to BBs can be attributed to their effect in decreasing metabolic activity by as much as 10% and also to other effects on energy metabolism. Given the negative influence of obesity on global CV risk and new-onset diabetes, the effects of BBs in obese patients or patients with risk factors for diabetes cannot be ignored.