
STDs Treatment
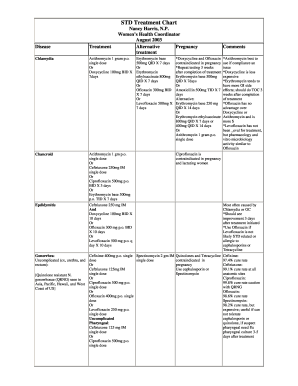
| Chancroid Treatment | Recommended Regimens: Azithromycin 1 g o ... |
| Chlamydia Treatment | Recommended Regimens: Azithromycin 1 g o ... |
| Crabs (Lice) Treatment | A lice-killing lotion containing 1% perm ... |
| Gonorrhea Treatment | Uncomplicated Gonococcal Infections of t ... |
| Hepatitis Treatment | Patients with acute hepatitis A usually ... |
Full Answer
What is the most common STD treatment?
Jul 15, 2021 · Worldwide, more than a million curable STIs are acquired every day. WHO estimated 374 million new cases of chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis and trichomoniasis in 15–49-year-olds in 2020. Since the publication of the WHO Guidelines for the management of sexually transmitted infections in 2003, changes in the epidemiology of STIs and progress in …
How to cure a STD?
European STI guidelines. Developed by WHO and the International Union against Sexually Transmitted Infections (IUSTI) Published European guidelines. Collected by IUSTI. WHO guidelines on care, treatment and support for women living with HIV/AIDS and their children in resource-constrained settings. For the control, prevention and management of STIs.
What STDs can you cure?
guidelines are focused on treatment and counseling and do not address other community services and interventions that are essential to STI and HIV prevention efforts. These STI treatment guidelines complement Recommendations for Providing Quality Sexually Transmitted Diseases Clinical Services, 2020 (2) regarding quality clinical services for STIs in primary care …
What STDs are treatable?
Jul 23, 2021 · These STI treatment guidelines complement Recommendations for Providing Quality Sexually Transmitted Diseases Clinical Services, 2020 (2) regarding quality clinical services for STIs in primary care and STD specialty care settings. This guidance specifies operational determinants of quality services in various clinical settings, describes on-site …
What are the best treatment for STD?
What are the 3 most common STDs that can be treated cured?
Three bacterial STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhoea and syphilis) and one parasitic STI (trichomoniasis) are generally curable with existing single-dose regimens of antibiotics.Nov 22, 2021
What antibiotics are used to treat sexually transmitted diseases?
- Azithromycin, Doxycycline, and Erythromycin for Chlamydia.
- Ceftriaxone, Cefixime, Ciprofloxacin, and Ofloxacin for Gonorrhea. ...
- Ceftriaxone with doxycycline or azithromycin for Gonorrhea and chlamydia.
- Penicillin G for Syphilis.
Which 4 STDs Cannot be cured with any medications?
- hepatitis B.
- herpes.
- HIV.
- HPV.
What are the 4 new STDs?
- Neisseria meningitidis. N. ...
- Mycoplasma genitalium. M. ...
- Shigella flexneri. Shigellosis (or Shigella dysentery) is passed on by direct or indirect contact with human faeces. ...
- Lymphogranuloma venereum (LGV)
Which STD is not curable?
Can amoxicillin treat STD in males?
Is amoxicillin good for STD?
What kind of STD does azithromycin treat?
What are 4/5 basic signs or symptoms of common STDs?
- Clear, white, greenish or yellowish vaginal discharge.
- Discharge from the penis.
- Strong vaginal odor.
- Vaginal itching or irritation.
- Itching or irritation inside the penis.
- Pain during sexual intercourse.
- Painful urination.
Can STD be cured permanently?
Can you live a normal life with STDs?
What is the treatment for STIs?
Effective treatment is currently available for several STIs. Three bacterial STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhoea and syphilis) and one parasitic STI (trichomoniasis) are generally curable with existing, effective single-dose regimens of antibiotics.
How many people have STIs in 2016?
In 2016, WHO estimated 376 million new infections with 1 of 4 STIs: chlamydia (127 million), gonorrhoea (87 million), syphilis (6.3 million) and trichomoniasis (156 million). More than 500 million people are living with genital HSV (herpes) infection and an estimated 300 million women have an HPV infection, the primary cause of cervical cancer.
How many different viruses are transmitted through sexual contact?
More than 30 different bacteria, viruses and parasites are known to be transmitted through sexual contact. Eight of these pathogens are linked to the greatest incidence of sexually transmitted disease. Of these 8 infections, 4 are currently curable: syphilis, gonorrhoea, chlamydia and trichomoniasis.
Can STIs be transmitted through blood?
Some STIs can also be spread through non-sexual means such as via blood or blood products. Many STIs—including syphilis, hepatitis B, HIV, chlamydia, gonorrhoea, herpes, and HPV—can also be transmitted from mother to child during pregnancy and childbirth.
How many STIs are there in the world?
Each year, there are an estimated 376 million new infections with 1 of 4 STIs: chlamydia, gonorrhoea, syphilis and trichomoniasis (1, 2). More than 500 million people are estimated to have genital infection with herpes simplex virus (HSV) ...
Is it safe to wear condoms for HIV?
When used correctly and consistently, condoms offer one of the most effective methods of protection against STIs, including HIV. Female condoms are effective and safe, but are not used as widely by national programmes as male condoms.
What is syndromic management?
Low- and middle-income countries rely on identifying consistent, easily recognizable signs and symptoms to guide treatment, without the use of laboratory tests. This is called syndromic management. This approach, which often relies on clinical algorithms, allows health workers to diagnose a specific infection on the basis of observed syndromes (e.g., vaginal discharge, urethral discharge, genital ulcers, abdominal pain).
2021 STI Treatment Guidelines
The guidelines provide CDC’s most current evidence-based recommendations for preventing, diagnosing and treating people who have, or are at risk for, STIs. Includes regimens, evidence tables, wall chart, and pocket guide.
Recommendations for Providing Quality STD Clinical Services (STD QCS)
Recommendations and tools intended to guide STD clinical practice standards in healthcare settings and optimize patient care. This is a companion piece to the 2021 STI Treatment Guidelines.
Expedited Partner Therapy
Providing prescriptions or medications to the patient to take to his/her partner without the health care provider first examining the partner.
Additional Resources
General STD treatment updates and resources, including Dear Colleague Letters, podcasts, and scientific articles.
Summary
These guidelines for the treatment of persons who have or are at risk for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) were updated by CDC after consultation with professionals knowledgeable in the field of STIs who met in Atlanta, Georgia, June 11–14, 2019. The information in this report updates the 2015 guidelines.
Introduction
The term “sexually transmitted infection” (STI) refers to a pathogen that causes infection through sexual contact, whereas the term “sexually transmitted disease” (STD) refers to a recognizable disease state that has developed from an infection. Physicians and other health care providers have a crucial role in preventing and treating STIs.
Methods
These guidelines were developed by CDC staff who worked with subject matter experts with expertise in STI clinical management from other federal agencies, nongovernmental academic and research institutions, and professional medical organizations.
Clinical Prevention Guidance
Prevention and control of STIs are based on the following five major strategies ( 3 ):
STI Detection Among Special Populations
Intrauterine or perinatally transmitted STIs can have debilitating effects on pregnant women, their fetuses, and their partners. All pregnant women and their sex partners should be asked about STIs, counseled about the possibility of perinatal infections, and provided access to recommended screening and treatment, if needed.
HIV Infection
Infection with HIV causes an acute but brief and nonspecific influenza-like retroviral syndrome that can include fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy, pharyngitis, arthritis, or skin rash. Most persons experience at least one symptom; however, some might be asymptomatic or have no recognition of illness ( 406 – 409 ).
Diseases Characterized by Genital, Anal, or Perianal Ulcers
In the United States, the majority of young, sexually active patients who have genital, anal, or perianal ulcers have either genital herpes or syphilis. The frequency of each condition differs by geographic area and population; however, genital herpes is the most prevalent of these diseases.
Is ivermectin FDA approved?
Both topical and oral ivermectin have been used successfully to treat lice; however, only topical ivermectin lotion currently is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for treatment of lice. Oral iver mectin is not FDA-approved for treatment of lice. Gonorrhea Treatment.
What is scabicide used for?
Products used to treat scabies are called scabicides because they kill scabies mites; some also kill mite eggs. Scabicides used to treat human scabies are available only with a doctor’s prescription. No “over-the-counter” (non-prescription) products have been tested and approved to treat scabies. Syphilis Treatment.
How long does erythromycin last?
Erythromycin base 500 mg orally four times a day for 7 days. Erythromycin ethylsuccinate 800 mg orally four times a day for 7 days. A lice-killing lotion containing 1% permethrin or a mousse containing pyrethrins and piperonyl butoxide can be used to treat pubic (“crab”) lice.
Can you use lindane on a baby?
Lindane should not be used to treat premature infants, persons with a seizure disorder, women who are pregnant or breast-feeding, persons who have very irritated skin or sores where the lindane will be applied, infants, children, the elderly, and persons who weigh less than 110 pounds.
What is the WHO guideline?
A WHO guideline is defined broadly as any information product developed by WHO that contains recommendations for clinical practice or public health policy. Recommendations are statements designed to help end-users make informed ...
What is the WHO guidelines review committee?
The Guidelines Review Committee ensure that WHO guidelines are of a high methodological quality and are developed through a transparent, evidence-based decision-making process.
What is a recommendation?
Recommendations are statements designed to help end-users make informed decisions on whether, when and how to undertake specific actions such as clinical interventions, diagnostic tests or public health measures, with the aim of achieving the best possible individual or collective health outcomes .
Prepared by
Kimberly A. Workowski, MD 1, 2#N#Laura H. Bachmann, MD 1#N#Philip A. Chan, MD 1, 3#N#Christine M. Johnston, MD 1, 4#N#Christina A. Muzny, MD 1, 5#N#Ina Park, MD 1, 6#N#Hilary Reno, MD 1, 7#N#Jonathan M. Zenilman, MD 1, 8#N#Gail A. Bolan, MD 1
Summary
These guidelines for the treatment of persons who have or are at risk for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) were updated by CDC after consultation with professionals knowledgeable in the field of STIs who met in Atlanta, Georgia, June 11–14, 2019. The information in this report updates the 2015 guidelines.
Introduction
The term “sexually transmitted infection” (STI) refers to a pathogen that causes infection through sexual contact, whereas the term “sexually transmitted disease” (STD) refers to a recognizable disease state that has developed from an infection. Physicians and other health care providers have a crucial role in preventing and treating STIs.
Public Domain and Reprinting
General text information, publications available for download, and graphs developed by CDC and presented on CDC’s website are works of the United States Government and are in the public domain. This means that they are meant for public use and are not subject to copyright law protections. Permission is not required for use of public domain items.

Scope of The Problem
Prevention of STIs
Diagnosis of STIs
Treatment of STIs
STI Case Management
Controlling The Spread
Who Response
- Our work is currently guided by the Global health sector strategy on sexually transmitted infections, 2016–2021.Within this framework, WHO: 1. develops global norms and standards for STI treatment and prevention 2. support the estimation the disease and economic burden of STIs 3. globally monitors antimicrobial resistance to gonorrhoea 4. leads the...