17.2.2 Final outcomes for drug-susceptible TB and DR-TB
| Outcomes | TB | Definitions |
| Cured | DS TB | Patient initially bacteriologically conf ... |
| Cured | PDR-TB | Patient initially bacteriologically conf ... |
| Cured | MDR-TB | Patient initially bacteriologically conf ... |
| Completed | All | Patient who completed treatment AND has ... |
Full Answer
What does MDR TB stand for?
- Strengthening TB services for people living with HIV/AIDS;
- Guiding preparedness and outbreak investigation responses;
- Improving access to TB drugs;
- Conducting routine surveillance (including drug susceptibility) and periodic surveys;
- Implementing new, rapid diagnostic tests;
- Developing and promoting, national and international TB testing standards;
What drugs treat TB?
- Isoniazid 5 (mg/kg body weight) maximum (mg) 300
- Rifampicin 10 (mg/kg body weight) maximum (mg) 600
- Pyrazinamide 25 (mg/kg body weight)
- Ethambutol 15 (mg/kg body weight)
Who consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis?
The production of the WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis. Module 2: screeningwas coordinated and written by Cecily Miller, with support from Annabel Baddeley, Dennis Falzon and Matteo Zignol, under the overall direction of Tereza Kasaeva, Director of the World Health Organization (WHO) Global Tuberculosis Programme.
What is MDR and XDR TB?
in participants with XDR-TB, multidrug-resistant (MDR) TB treatment failure or intolerance. In this trial 9 out of 10 participants were cured. We describe a trial participant with XDR-TB who presented with new-onset seizures soon after BPaL treatment ...

WHO guidelines MDR-TB treatment?
Current policy recommendations on treatment and care for DR-TB. In patients with confirmed rifampicin-susceptible and isoniazid-resistant tuberculosis, treatment with rifampicin, ethambutol, pyrazinamide and levofloxacin is recommended for a duration of 6 months.
How often is treatment of MDR-TB successful?
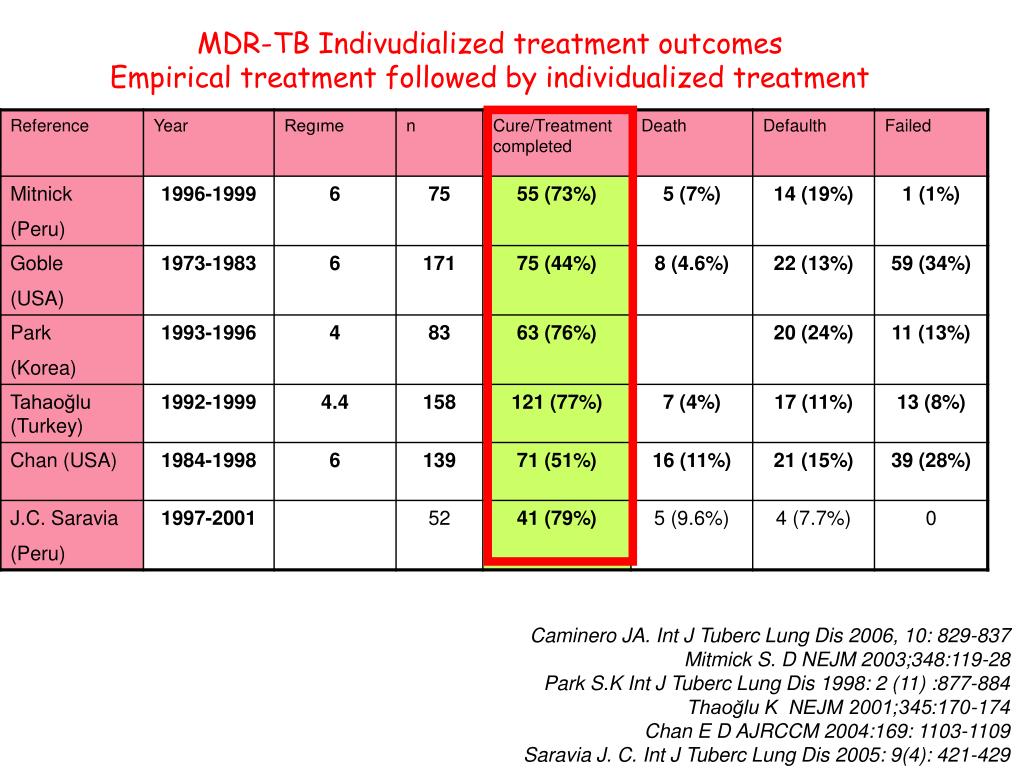
The overall treatment success rate for all patients was 57% (95% CI: 52%–61%), 58% for patients with MDR-TB (n = 272) and 30% for patients with XDR-TB (n = 3) (Table 1). Overall, 76 (21%) patients had poor treatment outcomes (13 patients died and 63 patients had treatment failure).
WHO tuberculosis treatment outcomes?
The treatment outcome of TB patients were 371 (10.8%) cured, 2234 (64.8) treatment completed, 119 (3.5%) died, 9 (0.3%) failed, 178 (5.1%) defaulted and 534 (15.5%) were transferred out. The overall treatment success rate was 89.5%.
What are the MDR-TB suspect criteria?
A confirmed MDR TB case is an MDR TB suspect who is sputum culture positive and whose TB is due to bacilli that are resistant in-vitro to at least isoniazid and rifampicin (the DST result being from an RNTCP accredited IRL).
What is the total duration of treatment of Multi Drug Resistant Tuberculosis?
Treatment of MDR-TB lasts for a long duration of approximately 2 years and consists of a combination of multiple second-line drugs, which are more expensive, less effective, and more toxic than the first-line drugs. Therefore, treatment outcomes for MDR-TB are poor, with a success rate of approximately 54% [2].
How long does it take to cure XDR TB?
MDR- and XDR-TB need prolonged treatment duration, from 18 to 24 months after sputum culture conversion, as recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) [2]. A prolonged duration of treatment may lead to poor adherence, higher cost and undue toxicity.
Which treatment outcomes are considered as treatment success for TB patient?
Of the total TB patients with known treatment outcome, the overall treatment success rate was 82.5%. Of these 65 (28%) were cured and 126 (54.3%) had completed their treatment. The treatment success rate of HIV-co-infected TB patients (n=40) included in TB treatment outcome analysis was 77.5%.
What is treatment outcome?
Treatment outcome research was defined by Mowrer (1953) as a situation whereby the “emphasis is upon measuring significant aspects of personality before and after treatment and noting the nature and extent of the resulting changes” (p. 4).
WHO latent TB Guidelines 2020?
Key RecommendationsThe first of three preferred regimens is once-weekly isoniazid plus rifapentine, for 3 months. ... The second preferred regimen, daily rifampin for 4 months, is also strongly recommended, especially for HIV-negative persons, and has perhaps the lowest toxicity.More items...•
How do you know if TB treatment is working?
After taking TB medicine for several weeks, a doctor will be able to tell TB patients when they are no longer able to spread TB germs to others. Most people with TB disease will need to take TB medicine for at least 6 months to be cured.
Can MDR-TB be cured completely?
The Grim Facts of Today's TB Therapy The pandemic can't be overcome without improved cures. Only about half the people with MDR-TB around the world are successfully cured. TB treatment is lengthy and burdensome to patients and treatment providers alike.
WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis Module 3 diagnosis?
WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis Module 3: Diagnosis - Rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detection. The political declaration of the first United Nations (UN) high-level meeting on tuberculosis (TB) calls countries to diagnose and treat 40 million people with TB globally between 2018 and 2022.
What is the WHO guideline?
In November 2015, the World Health Organization (WHO) convened a meeting of a Guideline Development Group (GDG) for the update of policy recommendations on the treatment of drug-resistant TB. The GDG was composed of a multidisciplinary group of tuberculosis (TB) and drug-resistant TB experts external to WHO. Before the meeting, the members of the GDG and the WHO Guideline Steering Committee had decided upon the priority questions in the treatment and care of patients with drug-resistant TB to be considered for the update of the guidelines. The scope of the 2016 update comprised the following: 1 The optimal combination of medicines and approach towards regimen design for TB patients (both adults and children) with isoniazid-resistant, rifampicin-resistant (RR-TB), multidrug-resistant (MDR-TB), and extensively drug-resistant (XDR-TB) forms of TB, as well as for patients with M. bovis disease. 2 The effectiveness and safety of standardized regimens lasting up to 12 months for the treatment of patients with MDR-TB (“shorter regimens”) when compared with longer treatment. 3 The effect of delay in starting treatment on treatment outcomes for patients with drugresistant TB. 4 The effect of surgical interventions on treatment outcomes for patients with drug-resistant TB.
How long does a standardized regimen last?
The effectiveness and safety of standardized regimens lasting up to 12 months for the treatment of patients with MDR-TB (“shorter regimens”) when compared with longer treatment.
Abstract
Antimicrobial resistance is a major public health problem globally. Likewise, forms of tuberculosis (TB) resistant to first- and second-line TB medicines present a major challenge for patients, healthcare workers and healthcare services.
Short abstract
New WHO guidelines on the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB) contain the latest recommendations on shorter or longer all oral treatment regimens for patients with drug-resistant TB, including the medicines to be used and other supportive measures https://bit.ly/2UJeib7
Introduction
Antimicrobial resistance is a major public health problem globally and has become a health security concern worldwide [ 1, 2 ]. Drug-resistant bacterial infections are on the rise globally, which has placed sharp focus on drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB), its diagnosis and treatment [ 3 ].
Process of guideline development
Overall, guideline development within the WHO is coordinated by technical programmes, ensuring that the process is evidence based and transparent, firmly relying on the highest ethical standards in science.
The scope of the updated guidelines
The scope of the 2020 guidelines update covered four areas, as follows.
Analysis and review of evidence
Detailed statistical analysis plans were prepared for the analytical approach to each PICO question. Descriptive analyses were performed to determine population characteristics and to provide information on the variables needed for matching and adjustment.
Summary of evidence and analyses
The evidence reviewed on the shorter all-oral bedaquiline-containing regimen was derived from programmatic data from South Africa's Electronic Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis Register ( www.edrweb.net ).
