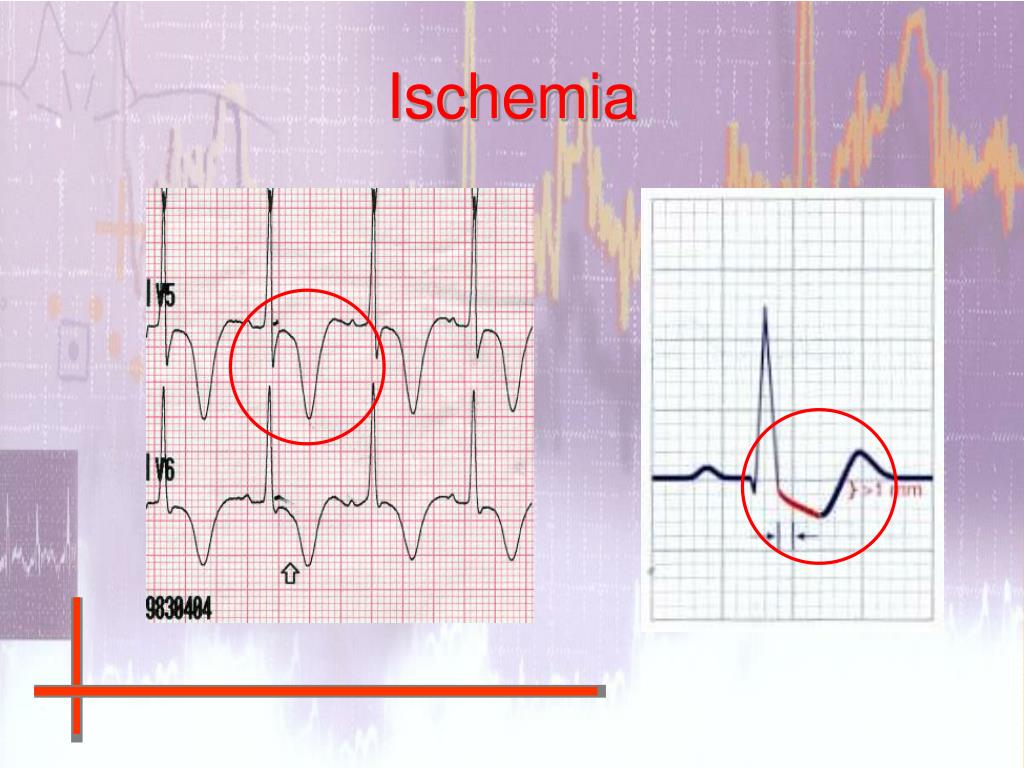
The ECG plays an important role in coronary reperfusion. ST segment elevation is one of the principal criteria for instituting thrombolytic therapy, and helps predict those who will most likely benefit from coronary reperfusion. The role of the ECG in evaluating the reperfusion status after coronary thrombolysis is not clear.
Full Answer
What are the indications for thrombolytic therapy?
During reperfusion of the infarct-related coronary artery, early signs of reperfusion were an increase of ST-segment deviation (30%), ST-segment normalization (70%), and terminal T-wave inversion (60%); only 11% of patients showed no ST-segment changes. Thrombolytic therapy was significantly more often accompanied by a transient increase in ST-segment deviation …
Can pulmonary embolism cause EKG changes?
Jun 17, 2021 · Pre-hospital thrombolytic therapy is a new treatment paradigm that can dramatically change patient outcomes. Several studies have shown that trained pre-hospital professionals may identify ST-segment elevation with 12 lead ECGs, thereby playing a role in pre-hospital administration of thrombolytic or advance notification to the coronary care facility.
Should we administer systemic thrombolytic therapy to patients with intermediate-risk peripheral tachycardia?
Of all patients 12% were excluded from thrombolytic therapy due to a negative initial ECG and yet developed a Q ware infarction. The one year mortality of patients not given thrombolysis and with a Q wave infarction was 24% (22/93, p = 0.02 as compared to patients with thrombolysis), in patients with non Q wave infarction it was 13% (11/82, p = 0.41) and in patients with …
When is catheter-directed thrombolytic intervention indicated in pulmonary embolism (PE)?
May 22, 2019 · Thrombolytic treatment accelerates the dissolution of thrombus in acute pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) and is potentially a lifesaving treatment. High-risk PTE is the clearest indication for this therapy, and its use in intermediate-risk cases is still controversial. A PTE response team may enable a rapid and effective determination of risk ...

What are the indications for thrombolytic therapy?
- Acute myocardial infarction (AMI)
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Pulmonary embolism (PE)
- Acute ischemic stroke (AIS)
- Acute peripheral arterial occlusion.
- Occlusion of indwelling catheters.
- Intracardiac thrombus formation.
What are the indications for thrombolytic therapy in a stroke?
What is a common adverse effect of thrombolytic therapy?
What is an indicator of myocardial reperfusion during thrombolytic therapy?
Which Laboratory test results must be reviewed before the initiation of thrombolytic therapy?
What test should be performed before administering tPA?
Which of the following is a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy?
When is fibrinolytic therapy indicated?
Which of the following is an absolute contraindication to the use of thrombolytic therapy?
How do you know if reperfusion is successful?
What is ST-segment resolution?
What is failed thrombolysis?
Can thrombolytics cause bleeding?
Thrombolytic therapy can moderately increase bleeding in menstruating women, but major hemorrhage is rare. Thus, menstruation is not a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy. Although the risk of maternal hemorrhage is high in pregnancy, a thrombolytic should be used in high-risk embolism patients. Table 2.
Is menstruation a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy?
Thus, menstruation is not a contraindication for thrombolytic therapy. Although the risk of maternal hemorrhage is high in pregnancy, a thrombolytic should be used in high-risk embolism patients. Table 2. Contraindications of thrombolytic treatment in acute pulmonary thromboembolism. Absolute contraindications.
What is the best thrombolytic agent for PTE?
Approved thrombolytic agents for the PTE treatment are streptokinase, urokinase, and alteplase. Currently, the most widely used agent is alteplase. It has a short infusion time (2 h) and a rapid effect. Newer, unapproved agents for the PTE treatment are tenecteplase and reteplase.
Does thrombolytic therapy help with pulmonary perfusion?
The active resolution of thrombus via thrombolytic agents improves rapidly pulmonary perfusion, hemodynamic defect, gas exchange, and right ventricular dysfunction. However, it is important to determine appropriate candidates carefully, to prevent hemorrhage, which is the most important side effect of these drugs.
What is the mortality rate of a PTE patient?
Pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE) is a common disease that may be life threatening. The mortality rate can reach up to 65% in high-risk patients [1]. Most deaths occur within the first hour of patients presenting with shock; therefore, the survival of these patients depends on rapid treatment [2–4].
Does COPD increase the risk of embolism?
The studies have shown that COPD both increases the risk of embolism and the risk of mortality in patients with embolism [8–10]. Risk assessment in patients diagnosed with PTE is important to initiate effective treatment as early as possible and prevent mortality.
Where is Tenecteplase used?
However, it is used in deep vein thrombosis and PTE worldwide, including in Turkey. Tenecteplase. Tenecteplase is produced in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line using the recombinant DNA technology. It is indicated in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction [35].
Is systemic thrombolysis recommended for right ventricular dysfunction?
Systemic thrombolysis is not recommended in this patients. In patients with hemodynamic stability but with right ventricular dysfunction (intermediate-high-risk group) systemic thrombolytic therapy is indicated to prevent potentially hemodynamic decompensation or collapse, if patients have low risk of bleeding.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
The main symptoms of pulmonary embolism are dyspnea, usually begin suddenly, and pleuritic chest pain. Pulmonary embolism may also present with pre-syncope or syncope, and in the most severe cases, with arterial hypotension and shock.
Is pulmonary embolism a DVT?
In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by a deep-vein thrombosis (DVT). The high effectiveness of the immediate treatment becomes vital early diagnosis, but sometimes it is difficult, because the clinical signs and symptoms are non-specific. Although the electrocardiogram in pulmonary embolism is not a test with high sensitivity ...
Can pulmonary embolism be suspected?
Pulmonary embolism should be suspected in patients with sudden dyspnea, chest pain or syncope, with predisposing factors. The electrocardiogram has an important role ruling out other diseases with similar symptoms ( acute myocardial infarction ). If the EKG changes previously described are present, suspicion of pulmonary embolism increases.
What is PE in electrocardiogram?
Electrocardiogram in Pulmonary Embolism. Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) is a relatively common medical emergency caused by occlusion of the pulmonary arteries. In most cases, pulmonary embolism is caused by a deep-vein thrombosis (DVT). The high effectiveness of the immediate treatment becomes vital early diagnosis, but sometimes it is difficult, ...
Is an electrocardiogram a sensitive test?
The electrocardiogram is not a sensitive test for the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism. In some cases appear certain changes that increase suspicion, helping in the diagnosis, but even in massive embolism, they are not always present 2.
What is the treatment for PE?
Systemic thrombolysis is the treatment of choice for patients with high-risk PE, and parenteral anticoagulation should be initiated with unfractionated heparin. In patients with contraindications to thrombolysis, or in whom thrombolysis has failed, surgical or percutaneous embolectomy is recommended.
Is potassium level correlated with ECG?
There is a rather strong correlation between plasma potassium level and ECG changes, as well as the risk of arrhythmia. Therefore the ECG may be used to estimate the severity of hyperkalemia.
Does potassium affect ECG?
Potassium. Potassium plays a key role in both depolarization and repolarization, which is why po tassium imbalance may cause dramatic ECG changes. These are of utmost clinical significance. There is a rather strong correlation between plasma potassium level and ECG changes, as well as the risk of arrhythmia.
Can electrolyte imbalance affect cardiac action potential?
The normal cardiac action potential may be altered by electrolyte imbalance, o wing to changes in intra- and extracellular electrolyte concentrations. Some electrolyte imbalances are clinically negligible (from an electrophysiological standpoint), whereas others may be life-threatening. The most common and clinically most relevant electrolyte ...
What is the earliest sign of hyperkalaemia?
The earliest sign of hyperkalaemia is the pointed T-waves. This is most pronounced in the precordial (chest) leads. Pointed T-waves are tall and narrow at the top. Refer to Figure 1.
