
Key Points
- The treatment for HIV is called antiretroviral therapy (ART). ART involves taking a combination of HIV medicines (called an HIV treatment regimen) every day.
- ART is recommended for everyone who has HIV. ...
- A main goal of HIV treatment is to reduce a person’s viral load to an undetectable level. ...
What is art therapy&how does it work?
The treatment program incorporates memory visualization techniques that are enhanced by the use of horizontal eye movements, as well as memory reconsolidation, a way in which new information is incorporated into existing memories. Find a licensed & approved ART Therapist near you. Learn more about ART research & how it works.
How do you write a treatment plan for art?
Offer ART regimens that are highly effective; prescribe once daily or other simple regimens that reduce pill burden, dosing frequency, and dietary restrictions as much as possible. Explain that treatment is well tolerated. Prepare patients for the possibility of ART side effects and regularly evaluate and manage side effects should they arise.
What is art and who needs it?
ART is now available free to all those who need it. Public health facilities are mandated to ensure that ART is provided to people living with HIV/AIDS (PLHA). Special emphasis is given to the treatment of sero-positive women and infected children. When is ART Given? Start ATT first, initiate ART as early as possible between 2 weeks-2months.
What services do art centres provide?
A PLHA network person at each of the ART centre facilitates access to care and treatment services at these centres. ART centres also provide counselling and follow up on treatment adherence and support through community care centres.
How does art help with mental health?
How does art help us?
Why is art important for health?
How does art affect health?
See more
About this website
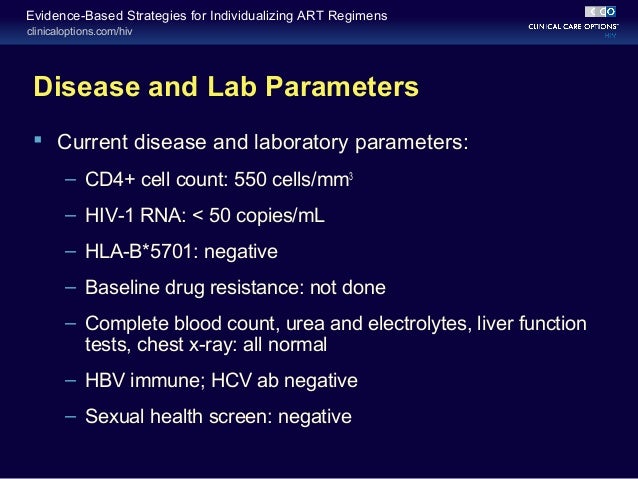
Who is eligible for ART treatment?
ART guidelines in use in industrialized countries recommend treatment for individuals with CD4 cell counts in the range of 200 – 350 cells/μL primarily for those with factors which may limit the effectiveness of ART if treatment is much delayed [17].
What is the difference between ARV and ART?
ART stands for ARV treatment. It is also called combination therapy or HIV treatment. ART usually includes two or three active HIV drugs, sometimes in a single pill. Sometimes ART includes a booster drug.
What is meant by ART treatment?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is treatment of people infected with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) using anti-HIV drugs. The standard treatment consists of a combination of drugs (often called "highly active antiretroviral therapy" or HAART) that suppress HIV replication.
What is the best ARV combination?
A triple-drug combination of zidovudine, didanosine and nevirapine has been found to outperform combination therapy with two nucleosides as demonstrated by changes in the viral load and the CD4+ count.
What is the name of the new ARV pill?
Early results from people taking a new antiretroviral medication called lenacapavir are promising. The long-acting drug is still at the research stage, but if the developers are able to pair it effectively with other drugs that also only needs to be taken twice a year, it could revolutionise HIV treatment.
How many types of Arvs are there?
Currently, there are eight FDA-approved NRTIs: abacavir (ABC, Ziagen), didanosine (ddI, Videx), emtricitabine (FTC, Emtriva), lamivudine (3TC, Epivir), stavudine (d4T, Zerit), zalcitabine (ddC, Hivid), zidovudine (AZT, Retrovir), and Tenofovir disoprovil fumarate (TDF, Viread), a nucleotide RT inhibitor (Fig. 3).
How long do Arvs take to work?
When a person living with HIV begins an antiretroviral treatment regimen, their viral load drops. For almost everyone who starts taking their HIV medication daily as prescribed, viral load will drop to an undetectable level in six months or less.
What is the long form of ARV?
Antiretroviral drug, any drug used to treat retroviral infections, primarily in the management of HIV/AIDS.
When should you start ART treatment?
Initiating Antiretroviral Therapy. ART is recommended for all individuals with HIV to reduce the morbidity and mortality associated with HIV infection (AI) and to prevent HIV transmission to sexual partners and infants (AI). ART should be initiated as soon as possible after HIV diagnosis (AII).
What are the 6 classes of antiretroviral drugs?
Classes of antiretroviral agents include the following:Nucleoside or nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs)Protease inhibitors (PIs)Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs)Fusion inhibitors.CCR5 co-receptor antagonists (entry inhibitors)HIV integrase strand transfer inhibitors.
What is the evidence on the role of the arts in improving health and ...
Arts interventions, such as singing in a choir to improve chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are considered non-invasive, low-risk treatment options and
Society for the Arts in Healthcare - GuideStar Profile
EIN. 02-0479949. NTEE code info Professional Societies, Associations (A03) Professional Societies & Associations (E03) Alliance/Advocacy Organizations (A01)
How does art help with mental health?
They can also reduce stress, which help to prevent or slow the progression of a range of conditions including cardiovascular diseases and even some cancers. Creating and experiencing the arts can have profound effects for those affected by mental illness.
How does art help us?
The arts are uniquely suited to help us understand and communicate concepts and emotions by drawing on all our senses and capacity for empathy . In recent decades, we have come to understand the intrinsic health benefits to artistic and leisure activities. Art can help us to emotionally navigate the journey of battling an illness or injury, to process difficult emotions in times of emergency and trauma and even to physically recover more quickly from injury or disease. The creation and enjoyment of the arts helps promote holistic wellness and can be a motivating factor in recovery. Including the arts in health care delivery has been shown to increase positive clinical outcomes for patients while also supporting other stakeholders, including health care providers, the patient’s loved ones and the wider community. Benefits are seen across several markers, including health promotion, the management of health conditions and illness, and disease prevention.
Why is art important for health?
Art can help us to emotionally navigate the journey of battling an illness or injury, to process difficult emotions in times of emergency and trauma and even to physically recover more quickly from injury or disease.
How does art affect health?
The arts can affect the social determinants of health, support child development, encourage health-promoting behaviours, help to prevent health issues and support caregiving. They can also reduce stress, which help to prevent or slow the progression of a range of conditions including cardiovascular diseases and even some cancers. Creating and experiencing the arts can have profound effects for those affected by mental illness. Their ability to provoke cognitive stimulation is effective in the treatment of dementia and other conditions associated with ageing; the use of art to process emotion can be effective in treating depression and anxiety; and associated social interaction can be an effective way to prevent risk factors of mental illness including loneliness, discrimination and reduced social capital. The arts also play an integral role in health education campaigns. They can be used to communicate valuable messages across cultures and political divides, help affected communities understand the risks of certain diseases or behaviours and provide ways for affected populations to process and learn from traumatic events.
What is ART therapy?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) is recommended for all people living with HIV, regardless of CD4 cell count, to consistently suppress viral load, maintain high CD4 cell counts, prevent AIDS, prolong survival, and reduce risk of transmitting HIV to others. 1, 2, 3 Research demonstrates that the success of ART, however, depends on the extent to which a patient takes his or her treatment according to the prescribed doses, dosing intervals, and other medication instructions. 4, 5 Several studies have shown that health care providers can positively impact medication-taking behaviors among HIV-infected patients by engaging in regular, ongoing discussions at every office visit that describe the benefits of ART adherence; track clinical measures that are influenced by adherence, such as a viral load; identify barriers to adherence; offer adherence support services; and provide information on other interventions that can improve adherence and reduce the risk of HIV transmission to others. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
What Are Suggested Conversation Starters to Discuss Ongoing ART Adherence with Patients?
As recent research demonstrates, brief discussions about ART adherence at every follow-up visit can help improve patient success. 6 Following are a few questions probing ongoing adherence:
How Can HIV Care Providers Help Patients Address Barriers to ART Adherence?
Numerous studies show that through open discussion, HIV care providers and patients can uncover barriers, identify strategies, and set behavioral goals to improve adherence . 2, 3, 4, 5 Following are some suggestions for how HIV care providers may address barriers to ART adherence as they arise:
How Can Holding Brief Conversations with Patients at Every Visit Help Improve ART Adherence?
Establishing ongoing brief conversations with patients in a supportive and nonjudgmental way encourages trust and facilitates opportunities to identify teachable moments in which HIV care providers can better help patients achieve sustained viral suppression. For example, HIV care providers can communicate the benefits of adherence by explaining that with ART medications, patients can now expect to live longer lives if they adhere to their ART regimen exactly as prescribed. Patients entering care should also understand the potential negative consequences of nonadherence such as increased mortality and morbidity, drug resistance, and risk of transmitting HIV to others. 3, 6
What is the first step to successful ART adherence?
Recent findings show that assessing a patient’s ART readiness is the first step to successful ART adherence. 6 Patients starting ART should be willing and able to commit to treatment and understand the benefits and risks of therapy and the importance of adherence.
What are the barriers to adherence to ART?
Barriers to ART adherence may arise from a patient’s personal or cultural beliefs, cognitive abilities, or health status, including comorbidities. 3, 4, 5 A patient’s capacity for treatment competence or regimen-specific barriers also may impact adherence, as well as psychosocial or structural issues such as poor mental health, drug use, or even lack of housing or health insurance. 3, 4, 5
Helps People Rapidly Move Beyond Trauma
ART International Training and Research is committed to helping hundreds of thousands of people who suffer with post-traumatic stress (PTS) and other psychological traumas.
What is ART?
ART is an evidence–based novel psychotherapy that fosters rapid recovery by reprogramming how the brain stores traumatic memories and imagery. ART has roots in and includes elements of existing evidenced-based modalities.
Get An Autographed Book
Please make a minimum donation of $25.00 to receive a signed copy of Jessica’s best-selling book.
Understanding Symptoms
There are many symptoms of trauma including agitation, irritability, flashbacks, mistrust, anxiety, social isolation, loss of interest, insomnia and emotional detachment. A visit to a healthcare professional can help you understand the symptoms and identify therapies that can help you feel better.
A Symptom Not A Disorder
ART International considers post-traumatic stress a symptom and not a disorder. Post-traumatic stress and other traumas can be caused by exposure to war, natural disasters, sexual assault, physical and emotional abuse, accidents, death and other distressing situations that leave lasting memories which can interfere with life as usual.
What Is Antiretroviral Therapy?
Antiretroviral therapy (ART) involves using two or more antiretroviral drugs to suppress the virus to undetectable levels in the blood. This treatment can slow the progression of the disease to a point at which you can live a long, healthy life. 4
How It Works
Antiretroviral drugs do not kill HIV. Rather, they prevent the virus from making copies of itself by blocking stages in the virus's life cycle (also known as the replication cycle ). Antiretrovirals are so named because HIV is a type of virus known as a retrovirus. 4
Side Effects
While all drugs can cause side effects, current antiretrovirals tend to cause far fewer side effects than drugs of the past. Even so, side effects can occur and, in rare cases, be severe.
Tests
Once you have been diagnosed with HIV, your doctor will advise to you start treatment immediately to bring the virus under control. You will not only be counseled on how to take your drugs correctly (including dietary restrictions) but also advised on ways to maintain optimal adherence .
Other Treatments
There are no other medications other than antiretrovirals that can control HIV.
Talk to Your Doctor
The choice of ART relies heavily on the results of a genetic resistance test that helps determine which antiretrovirals work best based on your virus's genetic profile. But it is not the sole factor involved in the selection of ART. 17
Summary
Antiretroviral therapy is used to control HIV. It relies on drugs that inhibit points of the viral replication cycle so the virus cannot make copies of itself and infect immune system cells. Antiretroviral drugs are usually given daily in the form of a pill, which may contain a combination of drugs. These medications may have side effects.
What is the WHO guideline?
A WHO guideline is defined broadly as any information product developed by WHO that contains recommendations for clinical practice or public health policy. Recommendations are statements designed to help end-users make informed ...
What is the WHO guidelines review committee?
The Guidelines Review Committee ensure that WHO guidelines are of a high methodological quality and are developed through a transparent, evidence-based decision-making process.
How does art help with mental health?
They can also reduce stress, which help to prevent or slow the progression of a range of conditions including cardiovascular diseases and even some cancers. Creating and experiencing the arts can have profound effects for those affected by mental illness.
How does art help us?
The arts are uniquely suited to help us understand and communicate concepts and emotions by drawing on all our senses and capacity for empathy . In recent decades, we have come to understand the intrinsic health benefits to artistic and leisure activities. Art can help us to emotionally navigate the journey of battling an illness or injury, to process difficult emotions in times of emergency and trauma and even to physically recover more quickly from injury or disease. The creation and enjoyment of the arts helps promote holistic wellness and can be a motivating factor in recovery. Including the arts in health care delivery has been shown to increase positive clinical outcomes for patients while also supporting other stakeholders, including health care providers, the patient’s loved ones and the wider community. Benefits are seen across several markers, including health promotion, the management of health conditions and illness, and disease prevention.
Why is art important for health?
Art can help us to emotionally navigate the journey of battling an illness or injury, to process difficult emotions in times of emergency and trauma and even to physically recover more quickly from injury or disease.
How does art affect health?
The arts can affect the social determinants of health, support child development, encourage health-promoting behaviours, help to prevent health issues and support caregiving. They can also reduce stress, which help to prevent or slow the progression of a range of conditions including cardiovascular diseases and even some cancers. Creating and experiencing the arts can have profound effects for those affected by mental illness. Their ability to provoke cognitive stimulation is effective in the treatment of dementia and other conditions associated with ageing; the use of art to process emotion can be effective in treating depression and anxiety; and associated social interaction can be an effective way to prevent risk factors of mental illness including loneliness, discrimination and reduced social capital. The arts also play an integral role in health education campaigns. They can be used to communicate valuable messages across cultures and political divides, help affected communities understand the risks of certain diseases or behaviours and provide ways for affected populations to process and learn from traumatic events.
