Medication
- Recognize signs of distention of the bladder. They must be able to recognize that the bladder is full and be able to communicate that to others.
- Awake and with a full bladder, children must learn to contract the pelvis muscles to retain urine until you reach the right place.
- Relax those muscles to start urination. Control the urine emptying. ...
Procedures
The sound waves or laser beam breaks the stones into tiny pieces. It is normal to have a small amount of blood in your urine for a few days to a few weeks after this procedure. You may have pain and nausea when the stone pieces pass. This can happen soon after treatment and may last for 4 to 8 weeks.
Nutrition
The prognosis is generally good as most cases of kidney stone spontaneously pass through the urine. Morbidity of kidney stones are those associated with urinary tract obstruction and upper urinary tract infection. The symptoms of Nephrolithiasis usually occur when the stones move within the kidney and passes through the ureter.
What are the causes and treatment of nephrolith?
Natural Remedies to Remove Kidney Stones. 1. Kidney Beans. Kidney beans that have a close resemblance to that of a kidney, is known to remove kidney stones effectively and cleanse the kidneys.
How long does it take to recover from laser lithotripsy?
What is the prognosis of nephrolithiasis?
How do you get rid of kidney stones naturally?
See more
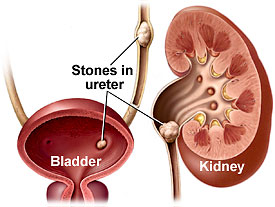
What is nephrolithiasis?
Nephrolithiasis, also known as kidney stones or renal calculi, refers to the presence of stones within the kidneys. It is one of the most common ki...
What does “nephrolithiasis” mean?
The word nephrolithiasis comes from “nephro,” which is the latin word for kidneys, and “lithiasis,” which is the medical term used to refer to stones.
Is nephrolithiasis the same as kidney stones?
Nephrolithiasis refers specifically to kidney stones, although it is broadly used to refer to stones in the urinary tract. Ureterolithiasis, on the...
What is hypocitraturic nephrolithiasis?
The vast majority of kidney stones are made out of calcium salts. Calcium oxalate stones are the most common type, followed by calcium phosphate st...
What are the other types of nephrolithiasis?
Other less frequent types of stones found in the urinary tract can be struvite stones, uric acid stones, cystine stones, or drug-induced stones.Str...
What are the signs and symptoms of nephrolithiasis?
The symptoms of nephrolithiasis depend on their size, shape, and location on the urinary tract. Initially, the stones are lodged in the renal pelvi...
How is nephrolithiasis diagnosed?
Asymptomatic nephrolithiasis may be detected as an incidental finding on imaging techniques or on urinalysis for hematuria.On the other hand, sympt...
How is nephrolithiasis treated?
To treat nephrolithiasis, the first step is pain control. This may include non steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce the inflammation...
What are the most important facts to know about nephrolithiasis?
Nephrolithiasis refers to the presence of stones within the kidneys. Calcium oxalate stones are the most common type, followed by calcium phosphate...
How do you know if you have nephrolithiasis?
Symptoms of Nephrolithiasis may include: Pain of sudden onset that radiates from the back, down the flank, and into the groin. Pain does not improve with body position. Pain is very severe and colicky but intermittent. Nausea and vomiting (reported by 50%) Blood in the urine (hematuria)
What to do if you suspect kidney stones?
If you suspect you may have a kidney stone, see your doctor . Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and may order a CT scan, ultrasonography, or other tests to aid the diagnosis.
How to prevent new stones from forming?
To prevent new stones from forming, adequate fluid intake should be maintained. Alkalinization of the urine may prevent recurrent uric acid and cystine stones.
What is the medical term for kidney stones?
The medical term for kidney stones is renal calculi.
What is the treatment for renal colic?
Acute medical treatment for suspected renal or ureteric colic includes conservative therapies such as hydration, analgesia (a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug [NSAID] such as diclofenac, indomethacin, or ketorolac, and/or an opioid such as morphine), and an anti-emetic (e.g., ondansetron). [55] .
What is the best treatment for urinary calculi?
Patients with obstructed urinary calculi with infection require emergency urologic consultation and surgical drainage, with intravenous antibiotics and supportive measures (hydration, analgesia with a non steroidal anti-inflammatory drug such as diclofenac, indomethacin, or ketorolac, and/or an opioid such as morphine, and an anti-emetic such as ondansetron) as necessary.
What is the purpose of potassium citrate and thiazide diuretics?
Thiazide diuretics are generally combined with potassium citrate to prevent the development of hypokalemia and hypocitraturia associated with this therapy.
What is the best treatment for acute stone?
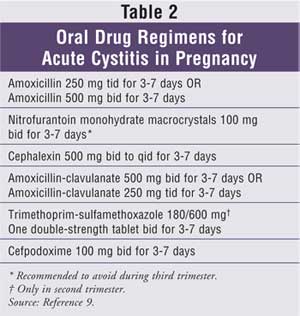
However, analgesics, antibiotics, anti-emetics, and intravenous fluids are given relative to their safety and risk for that particular trimester. For example, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided, particularly during the first and third trimesters. Alpha-blockers (e.g., tamsulosin) are are not recommended as there are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women.
Is PCNL invasive?
Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy (PCNL) is minimally invasive and usually reserved for renal and proximal ureteric stones (i.e., in the lower pole) and those that are large (>20 mm), have failed therapy with ESWL and ureteroscopy, or are associated with complex renal anatomy. [48] Assimos D, Krambeck A, Miller NL, et al. Surgical management of stones: American Urological Association/Endourological Society Guideline. 2016 [internet publication]. http://www.auanet.org/education/guidelines/surgical-management-of-stones.cfm
Can a urologist perform renal drainage?
Drainage can be accomplished in two ways. In the acute setting, a urologist can place a ureteric stent past the obstructing stone and achieve renal drainage . Alternatively, percutaneous nephrostomy by an interventional radiologist may be performed.
When should empiric antibiotics be started?
Empiric antibiotic therapy should be started pending sensitivity results based on urinalysis cultures. The empiric regimen depends on various factors, including the type of infection, patient factors, and local antibiotic resistance patterns; consult local guidelines for more information on choice of antibiotics.
What should be the focus of treatment for renal failure?
In emergency settings where concern exists about possible renal failure, the focus of treatment should be on correcting dehydration, treating urinary infections, preventing scarring, identifying patients with a solitary functional kidney, and reducing risks of acute kidney injury from contrast nephrotoxicity, particularly in patients with preexisting azotemia (creatinine > 2 mg/dL), diabetes, dehydration, or multiple myeloma.
What is the treatment for stone disease?
Medical therapy for stone disease takes both short- and long-term forms. The former includes measures to dissolve the stone (possible only with noncalcium stones) or to facilitate stone passage, and the latter includes treatment to prevent further stone formation.
What are the procedures for urology?
About 15-20% of patients require invasive intervention due to stone size, continued obstruction, infection, or intractable pain. Techniques available to the urologist when the stone fails to pass spontaneously include the following [ 49] : 1 Stent placement 2 Percutaneous nephrostomy 3 Extracorporeal shockwave lithotripsy (ESWL) 4 Ureteroscopy (URS) 5 Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy (PNCL) or mini PNCL 6 Open nephrostomy - largely supplanted by less-invasive techniques 7 Anatrophic nephrolithotomy - increasingly performed using a laparoscopic or robotic approach
How to tell if a kidney is pyonephrosis?
Renal ultrasonography or CT may distinguish pyonephrosis from simple hydronephrosis by demonstrating a fluid-fluid level in the renal pelvis (urine on top of purulent debris). In two small studies, ultrasonographic sensitivity for pyonephrosis was found to be 62-67%. CT sensitivity for pyonephrosis has not been reliably determined. [ 47, 48] The emergency physician must maintain a high index of suspicion. [ 49]
Is it a hospitalization for a renal colic attack?
The decision to hospitalize a patient with a stone is usually made based on clinical grounds rather than on any specific finding on a radiograph. Generally, hospitalization for an acute renal colic attack is now officially termed an observation because most patients recover sufficiently to go home within 24 hours. The admission rate for patients with acute renal colic is approximately 20%.
Can a chemical composition analysis be done for long term nephrolithiasis?
A chemical composition analysis of the stone should be performed whenever possible, and information should be provided to motivated patients about possible 24-hour urine testing for long-term nephrolithiasis prophylaxis. This is particularly important in patients with only a single functioning kidney, those with medical risk factors, and children. However, any strongly motivated patients can benefit from a prevention analysis and prophylactic treatment if they are willing to pursue long-term therapy.
What is nephrolithiasis in the kidney?
What is Nephrolithiasis? Nephrolithiasis is characterized by the formation of crystalline material in the kidney and the urinary tract. Nephrolithiasis is also known as kidney stones and is formed as a result of a decrease in the volume of urine or an increase in the substances in urine that can form stones in the kidney or in the urinary tract.
What is the best test to confirm kidney stones?
Imaging tests are done to confirm the formation of kidney stones. A helical CT scan is the imaging test of choice that is usually done without contrast materials. This imaging test can identify stones and obstruction within the urinary tract.
How long does it take for a kidney stone to go away?
Most kidney stones usually resolve within 48 hours with sufficient amount of fluid intake to help wash away the stone through the urine. Small stones that have minimal symptoms can be treated with the following: Increase fluid intake. Pain relieving medications.
What is the procedure to remove large stones?
A large stone formation that leads to manifestation of symptoms can be treated with the following: Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is a procedure that utilizes sound waves to break the stones. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy is a surgical removal procedure recommended for large stone formation. Nephrolithiasis.
Can nephrolithiasis cause kidney stones?
Nephrolithiasis has no single cause and the stone formation results when the urine has more stone forming substances than fluid composition that the urine can dilute. Several risk factors on the other hand are considered to result in the formation of kidney stones.
Does diet affect nephrolithiasis?
Diet can also affect or influenced the incidence of Nephrolithiasis. Diet that includes high protein, sugar and sodium potentially increases the risk for kidney stone formation.
Is nephrolithiasis more common in Asians?
Nephrolithiasis on the other hand is far more common in Asians and to those living in hot and dry areas. The prognosis is generally good as most cases of kidney stone spontaneously pass through the urine. Morbidity of kidney stones are those associated with urinary tract obstruction and upper urinary tract infection.
How to remove kidney stones?
A procedure called percutaneous nephrolithotomy (nef-row-lih-THOT-uh-me) involves surgically removing a kidney stone using small telescopes and instruments inserted through a small incision in your back.
How to remove a small stone in the kidney?
To remove a smaller stone in your ureter or kidney, your doctor may pass a thin lighted tube (ureteroscope) equipped with a camera through your urethra and bladder to your ureter. Once the stone is located, special tools can snare the stone or break it into pieces that will pass in your urine.
What tests can you do if you have a kidney stone?
If your doctor suspects that you have a kidney stone, you may have diagnostic tests and procedures, such as: Blood testing . Blood tests may reveal too much calcium or uric acid in your blood. Blood test results help monitor the health of your kidneys and may lead your doctor to check for other medical conditions. Urine testing.
What is the procedure to break a kidney stone?
For certain kidney stones — depending on size and location — your doctor may recommend a procedure called extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL). ESWL uses sound waves to create strong vibrations (shock waves) that break the stones into tiny pieces that can be passed in your urine.
How to prepare for a kidney appointment?
To prepare for your appointment: Ask if there's anything you need to do before your appointment, such as limit your diet. Write down your symptoms, including any that seem unrelated to kidney stones. Keep track of how much you drink and urinate during a 24-hour period.
What is the best way to diagnose kidney stones?
Ultrasound, a noninvasive test that is quick and easy to perform, is another imaging option to diagnose kidney stones.
What to take for pain after passing a stone?
To relieve mild pain, your doctor may recommend pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve).