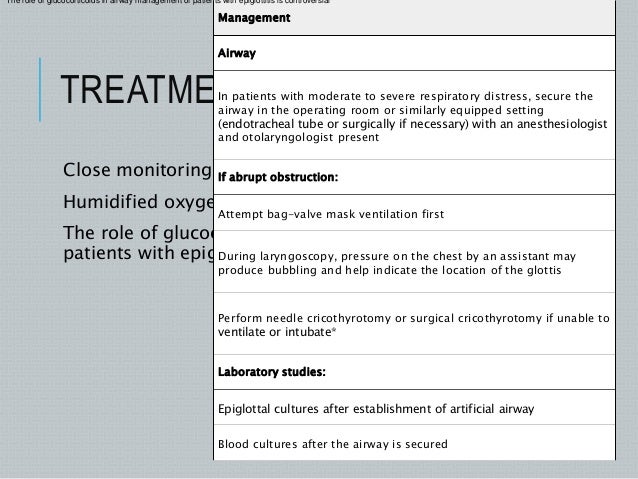
Treating Children in Respiratory Distress. The airway of the child with epiglottitis is best managed in the ED or operating room. If respiratory failure presents in the field, the airway can be managed with a BVM, maintaining proper head position and a tight seal. Extreme cases may require a surgical airway.
What are the nursing goals for a child with epiglottitis?
Treatments with epinephrine and steroids have been used but are not generally effective. As with the child with croup, interventions that could upset the child, such as IV therapy, should be...
What is epiglottitis in children?
Treatment involves emergency care and the opening the child’s airway with a breathing tube. Your child may also get antibiotics or other medicines. The Hib vaccine can prevent most cases of epiglottitis. Next steps Tips to help you get the most from a …
When should I Have my Child evaluated for epiglottitis?
Which treatment is appropriate for the child with epiglottitis and severe respiratory distress? 1 Antibiotics 2 Corticosteroids 3 Humidified oxygen via mask 4 …
What is the respiratory rate of a 4 year old with epiglottitis?
A 5 year old with acute epiglottitis is intubated for airway management. As the nurse you know that all of the following can be prescribed as treatment for this condition EXCEPT? * A. Intravenous fluids B. Antipyretics C. Corticosteroids D. Cough suppressants (NOTE: When you hit submit, it will refresh this same page.

When it is generally recommended that a child being treated for acute streptococcal pharyngitis may return to school?
Which medical device is appropriate for a 4 year old boy who Cannot coordinate his breathing?
Which clinical manifestations are appropriate for acute epiglottitis?
- Severe sore throat.
- Difficulty and pain when swallowing (a main symptom in older children and adults)
- Difficulty breathing (a main symptom in children), which may be helped by sitting up and leaning forward, or breathing with an open mouth and protruding tongue.
Which clinical manifestations are appropriate to identify in a child that indicates the need for an adenoidectomy?
Which purpose is appropriate for palivizumab medication?
Which intervention is appropriate for the infant hospitalized with bronchiolitis?
How do you treat a child with epiglottitis?
- IV (intravenous) therapy with antibiotics if the cause is a bacterial infection.
- Steroid medicine to ease airway swelling.
- IV fluids until the child can swallow again.
How is epiglottis treated?
- intravenous fluids for nutrition and hydration until you're able to swallow again.
- antibiotics to treat a known or suspected bacterial infection.
- anti-inflammatory medication, such as corticosteroids, to reduce the swelling in your throat.
Does amoxicillin treat epiglottitis?
How are adenoids treated?
If your child has minimal symptoms, no treatment is typically needed. Your doctor may recommend a nasal spray to help reduce swelling and potentially an antibiotic if the infection is bacterial. Another treatment for more severe cases is an adenoidectomy.
What is the treatment for adenoid hypertrophy?
What antibiotics treat adenoiditis?
What Is Epiglottitis?
Pathophysiology
Statistics and Incidences
Causes
Clinical Manifestations
Assessment and Diagnostic Findings
Medical Management
- Treatment in patients with epiglottitis is directed toward relieving the airway obstruction and eradicating the infectious agent. 1. Manage respiratory arrest. When a child has respiratory arrest, the first step is to administer bag-valve-mask ventilation with 100% oxygen; once the child is oxygenated and ventilated, the airway can be secured with ...
Practice Quiz: Epiglottitis