
Drug-induced hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism
Over production of hormones by the thyroid gland located at the front of neck.
Hypothyroidism
A condition resulting from decreased production of thyroid hormones.
What foods are good and bad for hyperthyroidism?
Thyroid: Diet, foods to avoid and 7 best natural supplements for hypothyroidism
- Iodine. Found primarily in seafood, iodine is a mineral nutrient that our bodies need to produce thyroid hormones.
- Probiotics. Probiotics are “good” bacteria. ...
- Selenium. Selenium is an important nutrient found in muscle meats, fish, and eggs. ...
- Vitamin D. ...
- Chasteberry. ...
- Glutathione. ...
- Curcumin. ...
Can Synthroid be harmful to someone with hyperthyroidism?
This type of thyroiditis can recur, though. If it does, over time people with silent thyroiditis may develop long-term hypothyroidism. If you're already being treated for a thyroid problem, and your thyroid function begins to shift between underactive and overactive, thyroiditis probably isn't the source of the problem.
Is there a permanent cure for hyperthyroidism?
To cure hypothyroidism permanently, we start with diagnostic tests and assessments that point us to the root causes that apply to each individual patient. By addressing the underlying causes of Hashimoto’s disease (which accounts for 90% of hypothyroidism cases), we are almost always able to reverse these thyroid issues.
Can hyperthyroidism go away on its own?
Over time, you may notice that your heart is beating fast, that you feel anxious, or that you are having a lot of bowel movements. You may also feel like you just don't have as much energy as usual. Hyperthyroidism typically does not go away on its own. Most people need treatment to make hyperthyroidism go away.
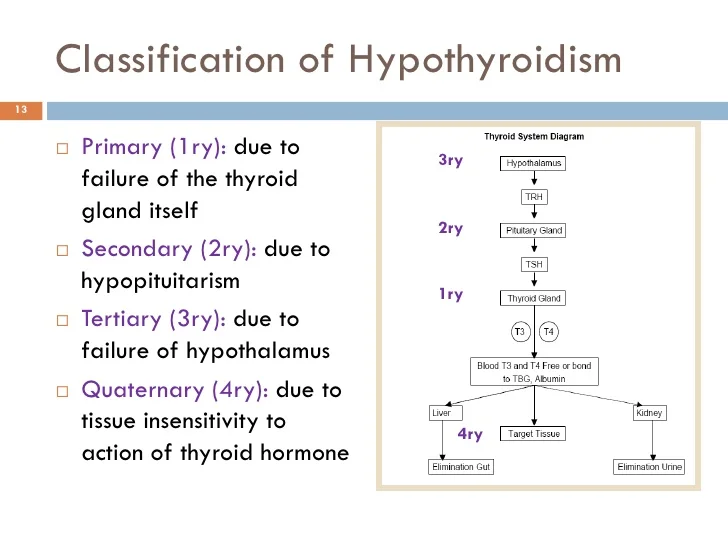
Can treatment of hyperthyroidism lead to hypothyroidism?
When people are treated for hyperthyroidism they sometimes develop hypothyroidism – an underactive thyroid. This is because the medication causes the thyroid to go from overactive to underactive if the correct dose is not taken.
Can hyperthyroidism cause hypothyroidism?
There have been cases of patients switching from hyperthyroidism to hypothyroidism, and even rarer patients flipping from hypothyroidism to hyperthyroidism. 1 However, a case of spontaneously alternating hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism in Graves' disease is comparably an even rarer phenomenon.
Which medications are most likely to cause hypothyroidism?
The group of drugs not used to treat thyroid dysfunction, which can result in drug-induced hypothyroidism includes amiodarone, nitroprusside, sulfonylureas, thalidomide, interleukin, lithium, perchlorate, and interferon-alpha therapy.
Can too much methimazole cause hypothyroidism?
Methimazole can cause hypothyroidism. [6] Therefore it is crucial to monitor T3 T4 levels in the serum, to adjust the dose to maintain a euthyroid state.
Can carbimazole cause hypothyroidism?
Placental transfer of the active metabolite of carbimazole can produce neonatal hypothyroidism, but propylthiouracil does not transfer in large enough quantities to cause problems.
What can cause hypothyroidism?
WHAT CAUSES HYPOTHYROIDISM?Autoimmune disease. ... Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland. ... Radiation treatment. ... Congenital hypothyroidism (hypothyroidism that a baby is born with). ... Thyroiditis. ... Medicines. ... Too much or too little iodine. ... Damage to the pituitary gland.More items...
Can antithyroid drugs cause hypothyroidism?
The drugs which may cause thyrotoxicosis include interferon, molecular-targeted agents, amiodarone, thyroid hormone itself and so on. Those which cause hypothyroidism include anti-thyroid drugs, lithium and iodine etc.
What medications cause low TSH?
Drugs that suppress serum TSH levelsGlucocorticoids. Glucocorticoids have long been known to affect serum TSH levels in humans (3;4). ... Dopamine/bromocryptine. ... Somatostatin analogs. ... Rexinoids. ... Other medications that may affect TSH levels.
How is methimazole induced hypothyroidism treated?
Hyperthyroidism may be treated with antithyroid meds (Methimazole, Propylthiouracil), radioactive iodine or surgery. Hypothyroidism: a condition where the thyroid gland is underactive and doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone. Treatment requires taking thyroid hormone pills.
Can methimazole make you hypo?
People diagnosed with hyperthyroidism usually take the medication methimazole to prevent the thyroid from producing excess hormones. This medication sometimes can initially decrease hormone production too much, and hypothyroidism results.
Which is better PTU or methimazole?
Methimazole — Methimazole is usually preferred over propylthiouracil because it reverses hyperthyroidism more quickly and has fewer side effects. Methimazole requires an average of six weeks to lower T4 levels to normal and is often given before radioactive iodine treatment.
Does methimazole cause low TSH?
After 18 months, methimazole was stopped in all patients, and T4 was continued in groups 2 and 3. In the absence of methimazole, serum TSH was suppressed into the low-normal range or below normal in all patients in groups 2 and 3.
What to do if you have hyperthyroidism?
If you've been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, the most important thing is to receive the necessary medical care. After you and your doctor have decided on a course of action, there are some things you can do that will help you cope with the condition and support your body during its healing process.
How to diagnose hyperthyroidism?
Diagnosis. Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed using: Medical history and physical exam. During the exam your doctor may try to detect a slight tremor in your fingers when they're extended, overactive reflexes, eye changes and warm, moist skin. Your doctor will also examine your thyroid gland as you swallow to see if it's enlarged, ...
Why is my thyroid leaking?
The most likely cause is either Graves' disease or hyperfunctioning thyroid nodules. If you have hyperthyroidism and your radioiodine uptake is low, this indicates that the thyroxine stored in the gland is leaking into the bloodstream, which may mean you have thyroiditis. Thyroid scan.
Why is TSH important?
The amount of TSH is important because it's the hormone that signals your thyroid gland to produce more thyroxine. These tests are particularly necessary for older adults, who may not have classic symptoms of hyperthyroidism.
What test can you take to check if you have hyperthyroidism?
If blood tests indicate hyperthyroidism, your doctor may recommend one of the following tests to help determine why your thyroid is overactive: Radioiodine uptake test. For this test, you take a small, oral dose of radioactive iodine (radioiodine) to see how much will collect in your thyroid gland.
How long does it take for iodine to go away?
Symptoms usually subside within several months. Excess radioactive iodine disappears from the body in weeks to months . This treatment may cause thyroid activity to slow enough to be considered underactive (hypothyroidism), and you may eventually need to take medication every day to replace thyroxine.
What happens when you have a thyroidectomy?
In a thyroidectomy, your doctor removes most of your thyroid gland. Risks of this surgery include damage to your vocal cords and parathyroid glands — four tiny glands situated on the back of your thyroid gland that help control the level of calcium in your blood.
What is the least used treatment for hyperthyroidism?
The least-used treatment for hyperthyroidism is surgery to remove part or most of the thyroid gland. Sometimes doctors use surgery to treat people with large goiters or pregnant women who cannot take antithyroid medicines.
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism?
Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder. With this disease, your immune system attacks the thyroid and causes it to make too much thyroid hormone.
How long does thyroiditis last?
The hypothyroidism usually lasts 12 to 18 months, but sometimes is permanent.
Why is radioactive iodine used for hypothyroidism?
Almost everyone who has radioactive iodine treatment later develops hypothyroidism because the thyroid hormone-producing cells have been destroyed. However, hypothyroidism is easier to treat and causes fewer long-term health problems than hyperthyroidism.
How much more likely is a woman to have hyperthyroidism than a man?
Women are 2 to 10 times more likely than men to develop hyperthyroidism. 2 You are more likely to have hyperthyroidism if you. have a family history of thyroid disease. have other health problems, including. pernicious anemia. NIH external link. , a condition caused by a vitamin B12 deficiency. type 1 diabetes.
What causes thyroid inflammation?
Rarely, hyperthyroidism is caused by a noncancerous tumor of the pituitary gland located at the base of the brain.
What is it called when your thyroid makes more hormones than your body needs?
Hyperthyroidism, also called overactive thyroid, is when the thyroid gland makes more thyroid hormones than your body needs. The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland in the front of your neck.
How do some medications cause hypothyroidism?
Your thyroid gland uses iodine to make two chemicals — thyroid hormones called T3 and T4 — that help your body control important processes like its heart rate, temperature, and metabolism. When the nearby pituitary gland releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), it tells your thyroid gland to send more T3 and T4 into the rest of your body.
How is drug-induced hypothyroidism treated?
If you notice, most of the medications covered in this article are pretty important. It’s not always feasible to stop the medication just because your thyroid levels are low. But since your thyroid health is important, too, you may have to replace those missing hormones.
What is the best treatment for hypothyroidism?
Standard treatment for hypothyroidism involves daily use of the synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine (Levo-T, Synthroid, others). This oral medication restores adequate hormone levels, reversing the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism. You'll likely start to feel better soon after you start treatment.
What are the side effects of a thyroid medication?
Excessive amounts of the hormone can cause side effects, such as: Increased appetite. Insomnia. Heart palpitations. Shakiness. If you have coronary artery disease or severe hypothyroidism, your doctor may start treatment with a smaller amount of medication and gradually increase the dosage.
What does a low TSH level mean?
A low level of thyroxine and high level of TSH indicate an underactive thyroid. That's because your pituitary produces more TSH in an effort to stimulate your thyroid gland ...
Why do you need a TSH test?
TSH tests also play an important role in managing hypothyroidism. They help your doctor determine the right dosage of medication, both initially and over time. In addition, TSH tests are used to help diagnose a condition called subclinical hypothyroidism, which usually causes no outward signs or symptoms.
Can TSH be elevated?
For a relatively mild increase in TSH, you probably won't benefit from thyroid hormone therapy , and treatment could even be harmful. On the other hand, for a higher TSH level, thyroid hormones may improve your cholesterol level, the pumping ability of your heart and your energy level.
Can a doctor check thyroid hormone?
Because the TSH test is the best screening test, your doctor will likely check TSH first and follow with a thyroid hormone test if needed. TSH tests also play an important role in managing hypothyroidism.
Does thyroid medication contain triiodothyronine?
These products contain both thyroxine and triiodothyronine. Synthetic thyroid medications contain thyr oxine only, and the triiodothyronine your body needs is derived from the thyroxine. Extracts are available by prescription only and shouldn't be confused with the glandular concentrates sold in natural foods stores.
What are the best treatments for hyperthyroidism?
There are 3 major options for treatment of hyperthyroidism: 1) antithyroid drugs, such as methimazole or PTU, that decrease the thyroid hormone production; 2) surgery to remove the overactive thyroid and 3) radioactive iodine that is taken up by the thyroid and destroys the gland.
Why do people get hospitalized for hyperthyroidism?
The most common reasons for hospitalization were high blood pressure and abnormal heart rhythms. The risk of hospitalization decreased after treatment of hyperthyroidism.
What is radioactive iodine?
Radioactive iodine (RAI): this plays a valuable role in diagnosing and treating thyroid problems since it is taken up only by the thyroid gland. I-131 is the destructive form used to destroy thyroid tissue in the treatment of thyroid cancer and with an overactive thyroid.
What is the difference between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism: a condition where the thyroid gland is overactive and produces too much thyroid hormone. Hyperthyroidism may be treated with antithyroid meds (Methimazole, Propylthiouracil), radioactive iodine or surgery. Hypothyroidism: a condition where the thyroid gland is underactive and doesn’t produce enough thyroid hormone. ...
What is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States?
Treatment requires taking thyroid hormone pills. Graves’ disease : the most common cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States. It is caused by antibodies that attack the thyroid and turn it on.
What is the cause of hyperthyroidism?
The main cause of hyperthyroidism in the United States is Graves’ disease. This is an autoimmune disease where the body makes an antibody that attacks and turns on the thyroid.
Can antithyroidism cause heart problems?
Hyperthyroidism can cause major problems and symptoms such as irregular heart rhythms and palpitations. Rarely, these problems can lead to death.
What is the best treatment for hyperthyroidism?
In the United States, iodine-131 is the most common treatment for hyperthyroidism. Radioiodine is often recommended as the treatment of choice for Graves disease and toxic nodular goiter in all patients, including children. Dosage of iodine-131 is difficult to adjust because the response of the gland cannot be predicted; some physicians give a standard dose of 8 to 15 millicurie. Others adjust the dose based on estimated thyroid size and the 24-hour uptake to provide a dose of 80 to 120 microcurie/g thyroid tissue.
What are the symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
Symptoms are many and include tachycardia, fatigue, weight loss, nervousness, and tremor. Diagnosis is clinical and with thyroid function tests. Treatment depends on cause.
How much iodine is needed for thyroid?
Others adjust the dose based on estimated thyroid size and the 24-hour uptake to provide a dose of 80 to 120 microcurie/g thyroid tissue.
What is a thyroid storm?
Thyroid storm is an acute form of hyperthyroidism that results from untreated or inadequately treated severe hyperthyroidism. It is rare, occurring in patients with Graves disease or toxic multinodular goiter (a solitary toxic nodule is a less common cause and generally causes less severe manifestations). It may be precipitated by infection, trauma, surgery, embolism, diabetic ketoacidosis, or preeclampsia.
What hormones are produced by thyroid stimulators?
Hyperthyroidism may result from increased synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones (thyroxine [T4] and triiodothyronine [T3]) from the thyroid, caused by thyroid stimulators in the blood or by autonomous thyroid hyperfunction.
Why does T3 increase?
Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism. In hyperthyroidism, serum T3 usually increases more than does T4, probably because of increased secretion of T3 as well as conversion of T4 to T 3 in peripheral tissues. In some patients, only T3 is elevated (T3 toxicosis).
Can thyroid hormones cause radioactive iodine uptake?
When hyperthyroidism is due to hormone overproduction, radioactive iodine uptake by the thyroid is usually elevated. When hyperthyroidism is due to thyroiditis, iodine ingestion, or overtreatment with thyroid hormones, radioactive iodine uptake is low. TSH receptor antibodies can be measured to detect Graves disease.

Diagnosis
Treatment
- Several treatments for hyperthyroidism exist. The best approach for you depends on your age, physical condition, the underlying cause of the hyperthyroidism, personal preference and the severity of your disorder. Possible treatments include: 1. Radioactive iodine. Taken by mouth, radioactive iodine is absorbed by your thyroid gland, where it causes...
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Once you begin treatment, symptoms of hyperthyroidism should subside and you should start feeling much better. However, your doctor may recommend that you watch out for iodine in your diet because it can cause hyperthyroidism or make it worse. Kelp, dulse and others types of seaweed contain a lot of iodine. Cough syrup and multivitamins also may contain iodine.
Coping and Support
- If you've been diagnosed with hyperthyroidism, the most important thing is to receive the necessary medical care. After you and your doctor have decided on a course of action, there are some things you can do that will help you cope with the condition and support your body during its healing process. 1. Get regular exercise.Exercise in general will help you feel better and improv…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You'll likely start by seeing your primary care doctor. However, in some cases, you may be referred immediately to a doctor who specializes in the body's hormone-secreting glands (endocrinologist). If you have eye involvement, you may also be referred to an eye doctor (ophthalmologist). It's good to prepare for your appointment. Here's some information to help yo…
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Standard treatment for hypothyroidism involves daily use of the synthetic thyroid hormone levothyroxine (Levo-T, Synthroid, others). This oral medication restores adequate hormone levels, reversing the signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism. You'll likely start to feel better soon after you start treatment. The medication gradually lowers cholesterol...
Alternative Medicine
Preparing For Your Appointment