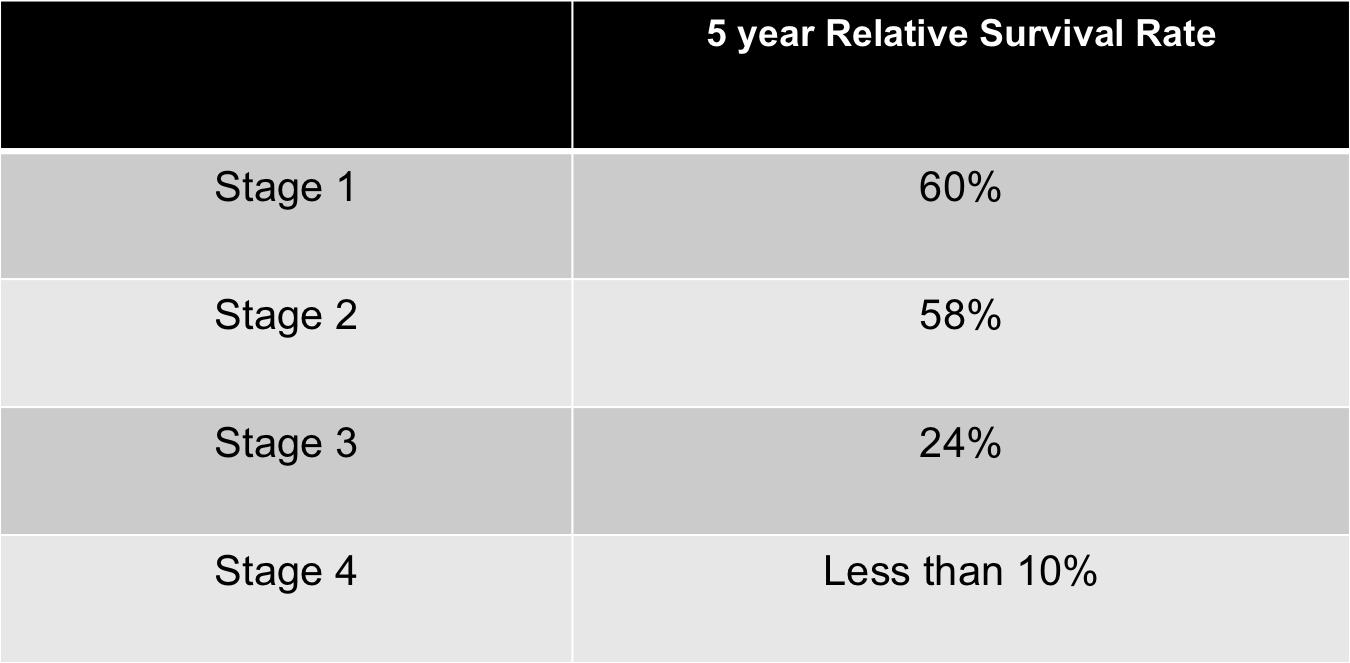
Can resolvins stop tumors from growing?
But researchers may now have found a way out of this conundrum. A new study has found that resolvins — compounds naturally secreted by our body in order to stop the inflammatory response — can stop tumors from growing when such growth is induced by cellular waste.
What increases the risk of developing a tumor?
Factors that increase the chances of developing a tumor include: Gene mutations (changes), such as mutated BRCA (breast cancer) genes. Inherited conditions, such as Lynch syndrome and neurofibromatosis (NFS). Family history of certain types of cancer like breast cancer or prostate cancer. Smoking, including exposure to secondhand smoke.
What is the tumor growth paradox and why does it matter?
In what has been referred to as the “ tumor growth paradox,” killing off cancer cells can sometimes cause more cancer cells to spread. This occurs because the cellular debris that is left behind triggers an inflammatory response from our immune system, which, in turn, can stimulate the production of more cancer cells.
What do solid tumors need to grow?
Solid tumors need oxygen and other nutrients to grow. Through a process called angiogenesis, tumors can prompt the formation of new blood vessels to ensure their survival. Cells can also enter the bloodstream and travel to distant sites.
Which of the following drug classes prevents formation of blood vessels that allow for tumor growth and invasion of surrounding tissues?
Angiogenesis inhibitors are unique cancer-fighting agents because they block the growth of blood vessels that support tumor growth rather than blocking the growth of tumor cells themselves. Angiogenesis inhibitors interfere in several ways with various steps in blood vessel growth.
What are two reasons why cells can form tumors?
When cells grow old or become damaged, they die, and new cells take their place. Sometimes this orderly process breaks down, and abnormal or damaged cells grow and multiply when they shouldn't. These cells may form tumors, which are lumps of tissue.
Which of the following is most likely to occur when a tumor suppressor gene is mutated?
When a tumor suppressor gene mutates, cells grow uncontrollably. And they may eventually form a tumor.
What is gene therapy for cancer treatment?
Gene therapy, which involves replacement of a defective gene with a functional, healthy copy of that gene, is a potentially beneficial cancer treatment approach particularly over chemotherapy, which often lacks selectivity and can cause non-specific toxicity.
What is a tumor?
An abnormal mass of tissue that forms when cells grow and divide more than they should or do not die when they should. Tumors may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign tumors may grow large but do not spread into, or invade, nearby tissues or other parts of the body.
What mechanism is involved in the beginning of tumor growth?
The first step in the process, tumor initiation, is thought to be the result of a genetic alteration leading to abnormal proliferation of a single cell. Cell proliferation then leads to the outgrowth of a population of clonally derived tumor cells.
How does p53 work as a tumor suppressor?
If the DNA can be repaired, p53 activates other genes to fix the damage. If the DNA cannot be repaired, this protein prevents the cell from dividing and signals it to undergo apoptosis. By stopping cells with mutated or damaged DNA from dividing, p53 helps prevent the development of tumors.
Is p53 a tumor suppressor gene?
The p53 gene is a type of tumor suppressor gene. Also called TP53 gene and tumor protein p53 gene.
Why is p53 a tumor suppressor gene?
The tumor suppressor p53 is a phosphoprotein barely detectable in the nucleus of normal cells. Upon cellular stress, particularly that induced by DNA damage, p53 can arrest cell cycle progression, thus allowing the DNA to be repaired; or it can lead to apoptosis.
What are the types of gene therapy?
There are two different types of gene therapy depending on which types of cells are treated:Somatic gene therapy: transfer of a section of DNA to any cell of the body that doesn't produce sperm or eggs. ... Germline gene therapy: transfer of a section of DNA to cells that produce eggs or sperm.
Why is gene therapy better than chemotherapy?
Relatively gene therapy has better safety with tolerable adverse effects than chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer. In the future, tumor genomic analysis, assessment of host humoral and cellular immunity will facilitate a better selection of the most appropriate patient for gene therapy.
What is DNA treatment?
Gene therapy involves altering the genes inside your body's cells in an effort to treat or stop disease. Genes contain your DNA — the code that controls much of your body's form and function, from making you grow taller to regulating your body systems.
What is angiogenesis?
Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels. This process involves the migration, growth, and differentiation of endothelial cells , whic...
Why is angiogenesis important in cancer?
Angiogenesis plays a critical role in the growth of cancer because solid tumors need a blood supply if they are to grow beyond a few millimeters...
How do angiogenesis inhibitors work?
Angiogenesis inhibitors are unique cancer-fighting agents because they block the growth of blood vessels that support tumor growth rather than bl...
What angiogenesis inhibitors are being used to treat cancer in humans?
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a number of angiogenesis inhibitors to treat cancer. Most of these are targeted therapi...
Do angiogenesis inhibitors have side effects?
Side effects of treatment with VEGF-targeting angiogenesis inhibitors can include hemorrhage , clots in the arteries (with resultant stroke or hea...
Why do immunotherapy drugs cause cancer?
In a similar way, when an immunotherapy drug is used to treat cancer, it stimulates the production of immune cells to locate and destroy cancer cells, which may cause the tumor to temporarily grow.
What is immunotherapy used for?
September 5, 2018 | by CTCA. When an immunotherapy drug is used to treat cancer , it stimulates the production of immune cells to locate and destroy cancer cells, which may cause the tumor to temporarily grow.
Do you need multiple follow up tests for immunotherapy?
For that reason, multiple follow-up tests may be required for patients undergoing immunotherapy treatment . “Immunotherapy may take a longer time to determine results than other therapies,” Dr. Crilley says. That’s why it’s important to be patient when evaluating immunotherapy’s effect.
Overview
A tumor is a mass or group of abnormal cells that form in the body. If you have a tumor, it isn’t necessarily cancer. Many tumors are benign (not cancerous).
Symptoms and Causes
Your body is constantly making new cells to replace old or damaged ones that die off. Sometimes, the cells don’t die off as expected. Or, new cells grow and multiply faster than they should. The cells start to pile up, forming a tumor.
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider performs a biopsy to determine whether a tumor is cancer. A biopsy involves removing cell samples from a tumor. A pathologist (a medical doctor who studies diseases) examines the samples in a lab to make a diagnosis.
Management and Treatment
Treatments for a tumor depend on many factors, including the tumor type (malignant or benign) and location.
Prevention
Most tumors occur for no known reason. Still, these steps may lower your risk of developing a tumor:
Why are there drugs to stop tumors from growing?
Because tumors cannot grow beyond a certain size or spread without a blood supply, scientists have developed drugs called angiogenesis inhibitors, which block tumor angiogenesis. The goal of these drugs, also called antiangiogenic agents, is to prevent or slow the growth of cancer by starving it of its needed blood supply.
How do tumors affect normal cells?
Tumors can also stimulate nearby normal cells to produce angiogenesis signaling molecules. The resulting new blood vessels “feed” growing tumors with oxygen and nutrients, allowing the tumor to enlarge and the cancer cells to invade nearby tissue, to move throughout the body, and to form new colonies of cancer cells, called metastases.
How effective are angiogenesis inhibitors?
Because angiogenesis inhibitors work by slowing or stopping tumor growth without killing cancer cells, they are given over a long period.
What happens when VEGF binds to endothelial cells?
When VEGF and other endothelial growth factors bind to their receptors on endothelial cells, signals within these cells are initiated that promote the growth and survival of new blood vessels. Other chemical signals, called angiogenesis inhibitors, interfere with blood vessel formation.
How is angiogenesis controlled?
The process of angiogenesis is controlled by chemical signals in the body. Some of these signals, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), bind to receptors on the surface of normal endothelial cells. When VEGF and other endothelial growth factors bind to their receptors on endothelial cells, signals within these cells are initiated ...
Why are angiogenesis inhibitors used in cancer treatment?
Angiogenesis inhibitors are unique cancer-fighting agents because they block the growth of blood vessels that support tumor growth rather than blocking the growth of tumor cells themselves. Angiogenesis inhibitors interfere in several ways with various steps in blood vessel growth.
Why is angiogenesis important for cancer?
Angiogenesis plays a critical role in the growth of cancer because solid tumors need a blood supply if they are to grow beyond a few millimeters in size. Tumors can actually cause this blood supply to form by giving off chemical signals that stimulate angiogenesis.
Is a benign tumor a malignant tumor?
A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells that serves no purpose. A benign tumor is not a malignant tumor, which is cancer. It does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body the way cancer can. In most cases, the outlook with benign tumors is very good. But benign tumors can be serious if they press on vital structures such as blood vessels or nerves. Therefore, sometimes they require treatment and other times they do not.
Can you treat a benign tumor?
In many cases, benign tumors need no treatment. Doctors may simply use "watchful waiting" to make sure they cause no problems. But treatment may be needed if symptoms are a problem. Surgery is a common type of treatment for benign tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor without damaging surrounding tissues. Other types of treatment may include medication or radiation.
Is apoptosis a cancer inhibitor?
Furthermore, it is considered to be a cancer inhibitor which has the ability to cause apoptosis. A type of cell death in which a series of molecular steps in a cell lead to its death. This is one method the body uses to get rid of unneeded or abnormal cells. The process of apoptosis may be blocked in cancer cells.
Does ellagic acid kill cancer cells?
The process of apoptosis may be blocked in cancer cells. Also called programmed cell death. or normal cell death in cancer cells. Working theories regarding the anti-cancer action of Ellagic Acid. First, ellagic acid kills cancer cells by promoting cell death (apoptosis). Second, ellagic acid stops the growth of tumors.
Why do tumors grow?
These cells grow into a benign tumor. The Cancer Center ’s theory is more specific: “Tumors grow because of a malfunction in cells’ DNA, mainly in genes that regulate cells’ ability ...
What is the best way to treat a benign tumor?
Benign Tumor Treatment. You may be asked to have a CT (computerized tomography) scan or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) to determine whether a tumor is or isn’t cancerous. In the case of an intestinal polyp, the recommendation may be a colonoscopy, where the tumor can be snipped off immediately.
What is malignant tumor?
Malignant means cancer. A malignant tumor’s cancerous cells divide and spread and can be difficult or impossible to stop. Benign tumor cells don’t spread, but they can grow. A benign tumor becomes dangerous if it begins to impinge on vital organs, like the brain, or body structures, like a blood vessel.
What happens if you have surgery for a benign tumor?
If you have surgery for a malignant tumor, the concern becomes whether the cells have already spread or were missed when the tumor was removed.
What is a biopsy of a tumor?
In a biopsy, the entire tumor or a sample of the tumor is removed surgically and sent to pathology for evaluation. There are three types of biopsies: Excisional biopsy: The entire suspicious area is removed. Fine-needle aspiration biopsy: Fluid or tissue is removed from the tumor using a needle.
What are benign tumors?
The term “benign tumor” includes a host of other terms you may be familiar with, including: Adenoma. Desmoid tumor. Fibroid. Fibroma. Growth. Hemangioma. Leiomyoma. Lipoma.
Can a benign tumor cause dizziness?
Don’t ignore these symptoms. Symptoms of a benign tumor depend largely upon where the tumor is. For instance, vaginal bleeding might indicate a uterine tumor. Dizziness could be a sign of a brain benign tumor. Symptoms of a tumor can include: Abnormal bleeding.
What is the grade of a tumor?
Based on how abnormal they appear under a microscope, tumors are graded as follows: GX: undetermined. G1: well-differentiated or low-grade.
Why is chemotherapy used for cancer?
Chemotherapy is used to kill cancer, slow its growth, and reduce the chance that new tumors will form. It’s useful when cancer has spread beyond the primary tumor or if you have a type of cancer for which there are no targeted therapies.
How does cancer spread?
Cancer can spread through: Tissue. A growing tumor can push through surrounding tissues or into organs. Cancer cells from the primary tumor can break away and form new tumors nearby. The lymph system. Cancer cells from the tumor can enter nearby lymph nodes.
How does surgery help with cancer?
When surgery is used to remove a tumor, the surgeon also removes a small margin of tissue around the tumor to lower the chances of leaving cancer cells behind. Surgery can also help stage the cancer. For example, checking the lymph nodes near the primary tumor can determine if cancer has spread locally.
What is it called when cancer cells break out of the tissue?
And they’re very good at hiding from the immune system. When cancer cells are still contained in the tissue where they developed, it’s called carcinoma in situ (CIS). Once those cells break outside the tissue’s membrane, it’s called invasive cancer.
Why does cancer happen?
Cancer occurs when there are more abnormal cells than the immune system can handle. Instead of dying, abnormal cells continue to grow and divide, piling up in the form of tumors.
What is the term for cancer of the blood?
For example, leukemias are cancers of the blood that doctors refer to as “liquid tumors.”. Exactly where cancer cells will spread next is dependent on their location in the body, but it’s likely to spread nearby first. Cancer can spread through: Tissue.
Abstract
In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions.
1. Introduction
Archaeobotanical evidence and written records found in ancient texts of Ayurvedic medicine and the first known Pharmacopoeia “Shen Nung Pen Ts’ao Ching” describe medical use of cannabis for several thousand years.
2. Cannabinoids
More than 100 cannabinoids have been isolated from the plant Cannabis sativa [ 28 ]. Cannabinoids derive from cannabigerolic acid and differ mainly in the way this precursor is cyclized ( Figure 1 ). Phytocannabinoids can be found in other plant species besides cannabis.
3. Terpenes
More than 20,000 terpenes appear in nature, from every plant, flower, and even some insects. Relatively few of these compounds–about 200–are found in cannabis. According to recent publications [ 142, 143 ], 50 cannabis terpenes can be found in North American chemovars, but some are more commonly found ( Figure 2 ).
4. Flavonoids
Flavonoids are by far the largest class of polyphenols and have been estimated to contain over 8000 metabolites with vast structural and functional diversity. Flavonoids have been subdivided into six major subclasses: flavones, flavonols, flavanones, flavanols, isoflavones and anthocyanidins [ 325 ].
5. Entourage Effect
It was first suggested by Drs. Mechoulam and Ben-Shabat that the endocannabinoid system demonstrated an effect known as the entourage effect, where a multitude of metabolites and related molecules modified the activity of the endogenous cannabinoids anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol [ 442 ].
6. Conclusions
Studies of individual pure compounds found in cannabis have demonstrated, as highlighted in this review article, that many of the compounds present in cannabis could be part of a therapeutic solution for specific problems found during cancer treatment.

Overview
- A tumor is an abnormal growth of cells that serves no purpose. A benign tumor is not a malignant tumor, which is cancer. It does not invade nearby tissue or spread to other parts of the body the way cancer can. In most cases, the outlook with benign tumors is very good. But benign tumors can be serious if they press on vital structures such as blood vessels or nerves. Therefore, some…
Causes
- What causes a benign tumor to form? Often the cause is unknown. But the growth of a benign tumor might be linked to:
Treatment
- In many cases, benign tumors need no treatment. Doctors may simply use \"watchful waiting\" to make sure they cause no problems. But treatment may be needed if symptoms are a problem. Surgery is a common type of treatment for benign tumors. The goal is to remove the tumor without damaging surrounding tissues. Other types of treatment may include me...
Types
- There are many different types of benign tumors arising from different structures in the body. These are some of the most common types of benign tumors:
Pathophysiology
- Adenomas are benign tumors starting in the epithelial tissue of a gland or gland-like structure. The epithelial tissue is the thin layer of tissue covering organs, glands, and other structures. A common type of adenoma is a polyp in the colon. Adenomas might also grow in the liver or the adrenal, pituitary, or thyroid gland.
Prognosis
- If needed, adenomas can often be removed with surgery. Although not common, this type of tumor can become malignant. In the colon, less than 1 out of every 10 adenomas become cancerous.