Which STDs do not have a cure?
The various antibiotics prescribed for different bacterial STDs are: Azithromycin, Doxycycline, and Erythromycin for Chlamydia. Ceftriaxone, Cefixime, Ciprofloxacin, and Ofloxacin for Gonorrhea. (In the event of ceftriaxone allergy, Gemifloxacin and …
What are 4 STDs that have no cure?
Mar 22, 2021 · The STDs chlamydia, gonorrhea, and trichomonas, which are caused by contracting common bacteria, can be cleared with a simple course of antibiotics. There are a number of common antibiotics used as STD treatments, each one targeting a different bacterium and different disease, so it’s important to consult a physician prior to beginning treatment.
What type of STD cannot be cured with antibiotics?
Sep 03, 2020 · Usage of Azithromycin for STDs In most cases, a single dose of this antibiotic is sufficient to cure syphilis, chlamydia and gonorrhea. Ofloxacin Ofloxacin belongs to a class of drugs referred to as quinolone antibiotics, and the mode of work is generally by stopping the growth of the bacteria, just like several other antibiotics.
Which STDs can be treated with over-the-counter medications?
Dec 24, 2015 · STDs/STIs caused by bacteria or parasites can be treated with antibiotics. These antibiotics are most often given by mouth (orally). However, sometimes they are injected or applied directly to the affected area. The treatments, complications, and outcomes for viral STIs depend on the particular virus (HIV, genital herpes, human papillomavirus, hepatitis, or …

What is the best antibiotic for STDs?
Doxycycline. This is an antibiotic for STDs which is used to treat a wide range of infections caused by bacteria. Doxycycline, which is also known as tetracycline, may also be used to prevent malaria.
What is the best antibiotic for gonococcal infections?
Azithromycin. Azithromycin inhibits the growth of bacteria by blocking the dissociation of peptidyl transfer ribonucleic acid from the ribosomes thereby allowing RNA-dependent protein in the body to synthesis arrest. This drug is very effective for gonococcal infections.
What are the side effects of antibiotics?
Side effects of antibiotics when administered to treat STDs 1 Diarrhea 2 Nausea and vomiting 3 Vaginal itching 4 Stomach pain 5 Vaginal discharge.
How often do you use antibiotics?
Almost every person will use antibiotics at least once in their life. Antibiotics are prescription drugs and are used for bacterial infections. Various kinds of antibiotics can be used for the treatment of STDs. In this article we list the most commonly used and effective antibiotics. 03 September 2020.
Is amoxicillin a penicillin?
This STD antibiotic is regarded as a penicillin-type of antibiotic whose mode of operation is to stop the growth of bacteria. Amoxicillin is very effective for treating STDs like chlamydia, but its effectiveness can, however, be reduced when it is misused or not administered in the correct dosage.
What is the mode of work of ofloxacin?
Ofloxacin belongs to a class of drugs referred to as quinolone antibiotics, and the mode of work is generally by stopping the growth of the bacteria, just like several other antibiotics.
Can you take erythromycin on an empty stomach?
Doctors mostly prescribe that it should be taken before a meal by mouth. Erythromycin is best absorbed when it is taken on an empty stomach. As a result of its bitter taste, patients are advised to swallow it without crushing or chewing.
Why is it important to get tested for STIs?
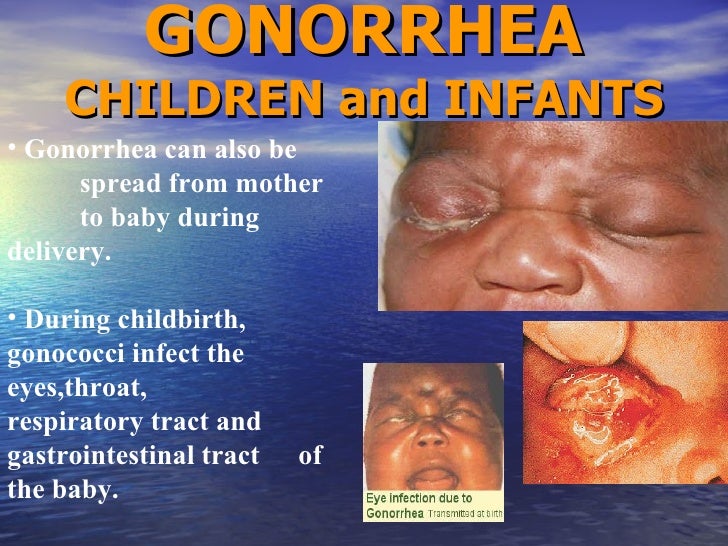
Getting tested and treated for STIs is especially important for pregnant women because some STIs may be passed on during pregnancy or delivery. Testing women for these STIs early in their pregnancy is important so that steps can be taken to help ensure delivery of a healthy infant.
Can you give antibiotics to STIs?
STDs/STIs caused by bacteria or parasites can be treated with antibiotics. These antibiotics are most often given by mouth (orally). However, sometimes they are injected or applied directly to the affected area.
What is the best treatment for STIs?
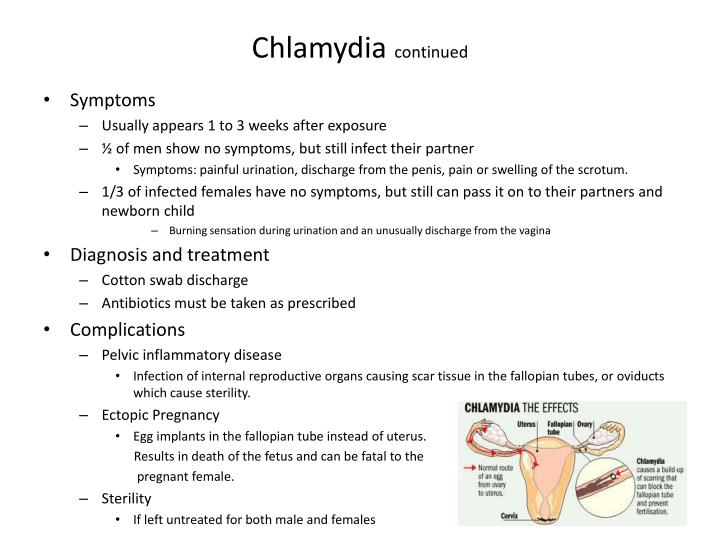
Treatment for STIs usually consists of one of the following, depending on the infection: Antibiotics. Antibiotics, often in a single dose, can cure many sexually transmitted bacterial and parasitic infections, including gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia and trichomoniasis. Typically, you'll be treated for gonorrhea and chlamydia at ...
What to do if you think you have an STI?
What you can do in the meantime. If you think you might have an STI, it's best to not to be sexually active until you've talked with your doctor. If you do engage in sexual activity before seeing your doctor, be sure to follow safe sex practices, such as using a condom. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
What is it called when you don't have symptoms?
Testing for a disease in someone who doesn't have symptoms is called screening . Most of the time, STI screening is not a routine part of health care, but there are exceptions:
Can STIs be cured?
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) or sexually transmitted infections (STIs) caused by bacteria are generally easier to treat. Viral infections can be managed but not always cured. If you are pregnant and have an STI, getting treatment right away can prevent or reduce the risk of your baby becoming infected.
Do men have STIs?
Compared with other groups, men who have sex with men run a higher risk of acquiring STIs. Many public health groups recommend annual or more-frequent STI screening for these men. Regular tests for HIV, syphilis, chlamydia and gonorrhea are particularly important. Evaluation for hepatitis B also may be recommended.
Can you get tested for hepatitis B?
Evaluation for hepatitis B also may be recommended. People with HIV. If you have HIV, it dramatically raises your risk of catching other STIs. Experts recommend immediate testing for syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia and herpes after being diagnosed with HIV.
Can you get gonorrhea and chlamydia at the same time?
Once you start antibiotic treatment, it's necessary to follow through. If you don't think you'll be able to take medication as prescribed, tell your doctor.
Answer
The only disease you can treat with antibiotics is the one caused by bacteria.
New questions in Biology
All of the following are ways to distinguish types of conifers EXCEPT the type of cone. the height of the tree. the shape of the needles. how the need …#N#les are attached to the stalk.
2021 STI Treatment Guidelines
The guidelines provide CDC’s most current evidence-based recommendations for preventing, diagnosing and treating people who have, or are at risk for, STIs. Includes regimens, evidence tables, wall chart, and pocket guide.
Recommendations for Providing Quality STD Clinical Services (STD QCS)
Recommendations and tools intended to guide STD clinical practice standards in healthcare settings and optimize patient care. This is a companion piece to the 2021 STI Treatment Guidelines.
Expedited Partner Therapy
Providing prescriptions or medications to the patient to take to his/her partner without the health care provider first examining the partner.
Additional Resources
General STD treatment updates and resources, including Dear Colleague Letters, podcasts, and scientific articles.
Diagnosis
- If your sexual history and current signs and symptoms suggest that you have a sexually transmitted disease (STD) or a sexually transmitted infection (STI), your doctor will do a physical or pelvic exam to look for signs of infection, such as a rash, warts or discharge.
Treatment
- STDs or STIscaused by bacteria are generally easier to treat. Viral infections can be managed but not always cured. If you are pregnant and have an STI, getting treatment right away can prevent or reduce the risk of your baby becoming infected. Treatment for STIsusually consists of one of the following, depending on the infection: 1. Antibiotics. Antibiotics, often in a single dose, can cure …
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- It can be traumatic to find out you have an STD or STI. You might be angry if you feel you've been betrayed or ashamed if you might have infected others. At worst, an STIcan cause chronic illness and death, even with the best care that's available. These suggestions may help you cope: 1. Hold off placing blame.Don't assume that your partner has been unfaithful to you. One (or both) of yo…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Most people don't feel comfortable sharing the details of their sexual experiences, but the doctor's office is one place where you have to provide this information so that you can get the right care.