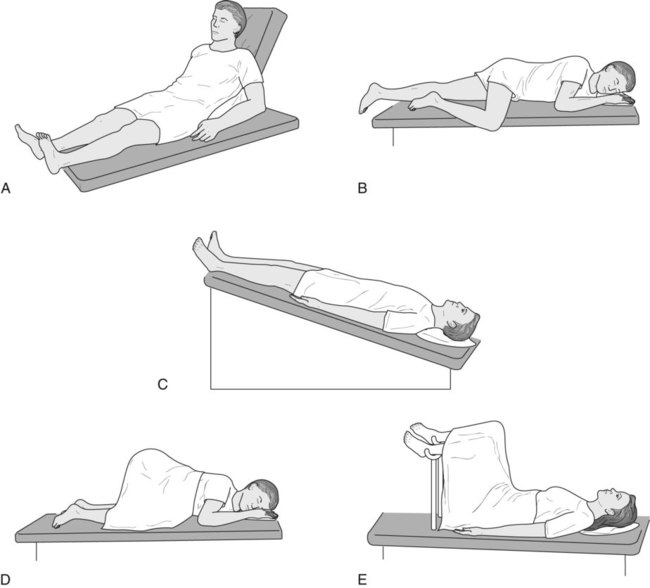
What is the correct position for a patient during a procedure?
The legs of the patient may be straight or bent. Supine position, also known as Dorsal Decubitus, is the most frequently used position for procedures. In this position, the patient is face-up. The patient's arms should be tucked at the patient's sides with a bedsheet, secured with arm guards to sleds.
What tests are done to diagnose shock?
People in shock have very low blood pressure. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick, noninvasive test records the electrical activity of your heart using electrodes attached to your skin. If you have damaged heart muscle or fluid buildup around your heart, the heart won't send electrical signals normally. Chest X-ray.
What is the true position for a chest xray?
True positioning is 90 degrees. Decubitus Lying down on dorsal (back), front (ventral) or side (lateral). Performed with central ray going horizontal. Essential for detecting air-fluid levels or free air in a body cavity such as the chest or abdomen, where the air rises to the uppermost part of the body cavity.
When managing a patient with shock what appropriate actions should the nurse take?
Septic shock Neurogenic shock Cardiogenic shock Anaphylactic shock Septic shock When managing a patient with shock, which appropriate actions should the nurse take as part of nutritional therapy? Select all that apply. Start enteral nutrition within the first 24 hours. Wait until the patient recovers to start with enteral nutrition.

What is the best position for a shock patient?
Lay the person down and elevate the legs and feet slightly, unless you think this may cause pain or further injury. Keep the person still and don't move him or her unless necessary. Begin CPR if the person shows no signs of life, such as not breathing, coughing or moving.
What are the treatment of shock?
Shock TreatmentCall 911.Lay the Person Down, if Possible.Begin CPR, if Necessary.Treat Obvious Injuries.Keep Person Warm and Comfortable.Follow Up.
How do you test for shock?
People in shock have very low blood pressure. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick, noninvasive test records the electrical activity of your heart using electrodes attached to your skin. If you have damaged heart muscle or fluid buildup around your heart, the heart won't send electrical signals normally.
What is the appropriate first line treatment for shock?
In general, fluid resuscitation (giving a large amount of fluid to raise blood pressure quickly) with an IV in the ambulance or emergency room is the first-line treatment for all types of shock.
Why do you elevate legs in shock?
Conclusion: Passive leg raising might be beneficial to be performed in patients with hypovolemic shock as it increases the venous blood return the heart.
What is the correct treatment for shock Hunter Ed?
To treat shock: Keep the victim lying on his or her back. In some cases, shock victims improve by raising their feet 8–10 inches. If the victim is having trouble breathing, raise the victim's head and shoulders about 10 inches rather than raising the feet.
What is shock investigation?
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS OF SHOCK In a patient with shock, a wide pulse pressure accompanied by warm extremities and brisk capillary refill is evidence of high cardiac output (CO; distributive shock). Alternatively, a narrow pulse pressure, cool extremities, and delayed capillary refill suggest low CO.
How is septic shock treated?
Treating septic shockoxygen therapy.fluids given directly through a vein (intravenously)medication to increase your blood flow.antibiotics.surgery (in some cases)
What is the recommended first line vasopressor for septic shock?
Objective. International guidelines recommend dopamine or norepinephrine as first-line vasopressor agents in septic shock. Phenylephrine, epinephrine, vasopressin and terlipressin are considered second-line agents.
What is the position of a patient in a sitting position?
Orthopneic or tripod position places the patient in a sitting position or on the side of the bed with an overbed table in front to lean on and several pillows on the table to rest on.
What is the importance of proper positioning in a patient?
Impaired venous return to the heart, and ventilation-to-perfusion mismatching are common complications. Proper positioning promotes comfort by preventing nerve damage and by preventing unnecessary extension or rotation of the body. Maintaining patient dignity and privacy.
What is a dorsal recumbent?
Supine position, or dorsal recumbent, is wherein the patient lies flat on the back with head and shoulders slightly elevated using a pillow unless contraindicated (e.g., spinal anesthesia, spinal surgery). Variation in position. In supine position, legs may be extended or slightly bent with arms up or down.
What is a semiprone position?
Sims’ position or semiprone position is when the patient assumes a posture halfway between the lateral and the prone positions. The lower arm is positioned behind the client, and the upper arm is flexed at the shoulder and the elbow.
How to support prone patient?
To support a patient lying in prone, place a pillow under the head and a small pillow or a towel roll under the abdomen. In surgery. Prone position is often used for neurosurgery, in most neck and spine surgeries.
What is lithotomy position?
Lithotomy position is commonly used for vaginal examinations and childbirth. Modifications of the lithotomy position include low, standard, high, hemi, and exaggerated based on how high the lower body is raised or elevated for the procedure.
What is the position of the supine?
Supine position in surgery. Supine is frequently used on procedures involving the anterior surface of the body (e.g., abdominal area, cardiac, thoracic area). A small pillow or donut should be used to stabilize the head, as extreme rotation of the head during surgery can lead to occlusion of the vertebral artery.
What are the functions of a radiographic exam?
1. position body and align with the IR and CR. 2. Select radiation protection measures. 3. Select exposure factors (radiographic technique) on the control panel (generator) 4. Patient instructions related to respiration and initiation (making) of the exposure. 5.
Which part of the body is the most likely to detect air-fluid levels?
Essential for detecting air-fluid levels or free air in a body cavity such as the chest or abdomen, where the air rises to the uppermost part of the body cavity. left lateral decubitus. right lateral decubitus. dorsal decubitus.
What is the position of the lateral lithotomy?
Lateral position. Right lateral position is with right side of body closest to the IR in both erect and recumbent body positions. True positioning is 90 degrees.
What is a radiograph?
named positions, named for person who first described a specific position: Towne, Waters, Caldwell. Radiograph. An image produced by x-rays on an image receptor.
Which section runs lengthwise in the direction of the long axis of the body?
Can be sagittal, coronal and oblique - sections that run lengthwise in the direction of the long axis of the body or any of its parts, regardless of the position of the body, erect or recumbent. transverse or axial section. Sections at right angles along any point of the longitudinal axis of the body or its parts.
What is Trendelenburg position?
Trendelenburg - recumbent position with body tilted with head lower than feet. Fowler's position - recumbent position with body tilted with head higher than feet. Sims' position - when on left side, right knee and thigh are flexed and left arm behind back - used for rectal tube insertion for barium enema.
What is the most commonly used position for a patient?
Supine position, also known as Dorsal Decubitus, is the most frequently used position for procedures. In this position, the patient is face-up. The patient's arms should be tucked at the patient's sides with a bedsheet, secured with arm guards to sleds.
When positioning a patient in Fowler's position, should the surgical staff minimize the degree of the patient'
When positioning a patient in Fowler's position, the surgical staff should minimize the degree of the patient's head elevation as much as possible and always maintain the head in a neutral position. The patient's arms should be flexed and secured across the body, the buttocks should be padded, and the knees flexed 30 degrees.
What is a lithotomy position?
In Lithotomy position, the patient can be placed in either a boot-style leg holder or stirrup-style position. Modifications to this position include low, standard, high, exaggerated or hemi. This position is typically used for gynecology, colorectal, urology, perineal, or pelvis procedures. The risks posed to a patient in a Lithotomy position for a procedure include fractures, nerve injuries, hip dislocation, muscle injuries, pressure injuries, and diminished lung capacity. While positioning a patient in this position, surgical staff should avoid hyperabduction of the patient's hips and leaning against their inner thighs. Stirrups used on a patient in this position should disperse support and pressure over wide areas. 2,3
Why is patient positioning important?
THE IMPORTANCE OF PATIENT POSITIONING. Patient positioning is vital to a safe and effective surgical procedure. Proper patient positioning depends on the type and length of procedure, anesthesia access to the patient, devices required and other factors. Safely positioning the patient is a team effort. All members of the surgical team play ...
Why should a sufficient number of personnel be available during a patient procedure?
A sufficient number of personnel should always be available during a patient procedure to position the patient safely and effectively. General positioning practices include having an adequate number of personnel, devices, and equipment available during a procedure to ensure patient and staff safety.
What are the goals of proper patient positioning?
The goals of proper patient positioning include: Maintain the patient's airway and circulation throughout the procedure. Prevent nerve damage. Allow surgeon accessibility to the surgical site as well as for anesthetic administration. Provide comfort and safety to the patient. Prevent soft tissue or musculoskeletal and other patient injury.
What happens when you are in a supine position?
In Supine position, the patient may risk pressure ulcers and nerve damage. This position causes extra pressure on the skin and bony prominences over the occiput, scapulae, elbows, sacrum, coccyx and heels. 2,3.
Why is dextran used in shock therapy?
Check whether the patient is monitored for allergic reactions and acute renal failure. Use dextran, because it helps to control bleeding caused by thrombocytopenia. Use of dextran as a fluid therapy increases the risk of bleeding.
Why do you need dextran for shock?
Use dextran in limited quantities for shock therapy because it has side effects. Check whether the patient is monitored for allergic reactions and acute renal failure. The nurse is taking care of a patient with cardiogenic shock due to a myocardial infarction.
What tests are done to check for shock?
Doctors will check for signs and symptoms of shock, and will then perform tests to find the cause. Tests might include: Blood pressure measurement. People in shock have very low blood pressure. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick, noninvasive test records the electrical activity of your heart using electrodes attached to your skin.
How to treat cardiogenic shock?
Medical procedures to treat cardiogenic shock usually focus on restoring blood flow through your heart. They include: 1 Angioplasty and stenting. If a blockage is found during a cardiac catheterization, your doctor can insert a long, thin tube (catheter) equipped with a special balloon through an artery, usually in your leg, to a blocked artery in your heart. Once in position, the balloon is briefly inflated to open the blockage.#N#A metal mesh stent might be inserted into the artery to keep it open over time. In most cases, you doctor will place a stent coated with a slow-releasing medication to help keep your artery open. 2 Balloon pump. Your doctor inserts a balloon pump in the main artery off of your heart (aorta). The pump inflates and deflates within the aorta, helping blood flow and taking some of the workload off your heart. 3 Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). ECMO helps improve blood flow and supplies oxygen to the body. Blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body.
How does ECMO work?
ECMO helps improve blood flow and supplies oxygen to the body. Blood is pumped outside of your body to a heart-lung machine that removes carbon dioxide and sends oxygen-filled blood back to tissues in the body. If medications and other procedures don't work to treat cardiogenic shock, your doctor might recommend surgery.
What is the procedure to bypass a blocked artery?
Coronary artery bypass surgery. This surgery uses a healthy blood vessel in your leg, arm or chest to create a new pathway for blood so it can flow around a blocked or narrowed artery. Your doctor might suggest this surgery after your heart has had time to recover from your heart attack.
What blood test is done to check for organ damage?
You'll have blood drawn to check for organ damage, infection and heart attack. An arterial blood gas test might be done to measure oxygen in your blood. Echocardiogram. Sound waves produce an image of your heart. This test can help identify damage from a heart attack.
Can a mechanical device be implanted into the abdomen and attached to the heart to help it pump?
A mechanical device can be implanted into the abdomen and attached to the heart to help it pump. A VAD might extend and improve the lives of some people with end-stage heart failure who are waiting for new hearts or aren't able to have a heart transplant. Heart transplant.
Do you need oxygen for cardiogenic shock?
Most people who have cardiogenic shock need extra oxygen. If necessary, you'll be connected to a breathing machine (ventilator). You'll receive medications and fluid through an IV line in your arm.
What is positioning in nursing?
As a nurse, you know that positioning can be about so much more than just patient comfort. The right position can have a huge impact on patient health and recovery, and knowing the correct position for each patient care situation is crucial.
What is the position of the head after neck surgery?
A position where the patient lies on his stomach with his back up. The head is typically turned to one side. This position allows for drainage of the mouth after oral or neck surgery. It also allows for full flexion of knee and hip joints.
What is a prone lateral position?
A prone/lateral position in which the patient lies on his side with his upper leg flexed and drawn in towards the chest, and the upper arm flexed at the elbow. Sim’s position is useful for administering enemas, perineal examinations, and for comfort in pregnancy.
What is the upside down position?
This position involves a supine patient and sharply lowering the head of the bed and raising the foot , creating an “upside down” effect. In the past, this position was frequently used to treat hypotension, although this has fallen out of favor in recent years due to studies showing it to be ineffective and potentially dangerous. It is helpful during gynecological and abdominal hernia surgeries, and in the placement of central lines.
What is the most natural position for a patient to be at rest?
A position where the patient is flat on his back. Supine is considered the most natural “at rest” position, and is often used in surgery for abdominal, facial, and extremity procedures.
What is a Fowler's position?
Fowler’s. A bed position where the head and trunk are raised, typically between 40-90°. This position is often used for patients who have cardiac issues, trouble breathing, or a nasogastric tube in place.

The Importance of Patient Positioning
Patient Positioning Guidelines
- Following standard patient positioning guidelines and practices helps to ensure patient safety and physical well-being before, during and after a procedure. A sufficient number of personnel should always be available during a patient procedure to position the patient safely and effectively. General positioning practices include having an adequate number of personnel, devices, and equ…
Patient Positioning Risk Factors
- Various factors play a role in risk during a patient procedure as a result of positioning. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors can interact to contribute to the risk of developing pressure sores. Extrinsic factors may include pressure intensity and duration and overall effects of anesthesia. Intrinsic factors can include the overall health of the patient, and preexisting conditions such as respirato…
Common Patient Positions
- Of the common patient positions, there are variations of different patient positions which play a key role in minimizing the risk of positioning related issues, such as: respiratory problems, circulatory problems, nerve or muscle injuries, and soft tissue injuries.
Patient Positioning by Surgical Procedure
- The different positioning of patients to be used also depends on the type of procedure, with the purpose to both provide optimal exposure and access to the surgical site and maintain patient comfort, among several other reasons.