
Explore
Box 3 4 provides a stepwise approach to stomatitis-associated symptoms. Commonly used mouthwashes used for prevention and treatment of stomatitis include club soda, alcohol-free mouthwashes, and benzydamine hydrochloride; hydrogen peroxide is not indicated. Many pharmacies have their own formulary mouthwashes for stomatitis—often referred to as “magic …
What is stomatitis and how is it treated?
Jun 09, 2017 · Types of topical treatment include: Topical corticosteroids: Often a rinse, these aim to eliminate symptoms to allow the person to eat, drink, and speak without pain or discomfort. Topical ...
Which medications are used in the treatment of recurrent aphthous stomatitis?
Your body has no way of expelling the virus that causes the sores. However, the outbreaks aren't severe, so this stomatitis treatment involves over-the-counter medications for pain relief and fever reduction. Children should also consume plenty of liquids during an outbreak.
Which mouthwash is best for stomatitis?
Anti-inflammatory drugs such as corticosteroids (including prednisone) are the most effective treatment for canker sores, as they will reduce swelling and pain.
What are the different types of stomatitis?
Sep 09, 2020 · Many treatment options are available for aphthous stomatitis, including topical agents such as local anesthetics (benzocaine), coating or occlusive agents (bismuth subsalicylate, sucralfate, 2-octyl cyanoacrylate, and various bioadherent emollient pastes), antiseptics (chlorhexidine gluconate and hydrogen peroxide), anti-inflammatory agents such …
Which medications are prescribed for severe inflammation that occurs in contact dermatitis?
Oral corticosteroids A doctor may prescribe an oral corticosteroid, such as prednisone, for severe allergy symptoms. Oral corticosteroids reduce inflammation and prevent severe allergic reactions. A doctor will monitor a person taking oral corticosteroids because the medication may cause severe side effects.
Which of the following is a skin inflammation that may be an allergic response to allergens such as chemical or foods?
Atopic dermatitis (eczema). Food allergy may cause a skin reaction, such as eczema.Dec 31, 2021
In which allergy test are extracts of suspected allergens applied to a patient's skin using a lancet?
A skin prick test, also called a puncture or scratch test, checks for immediate allergic reactions to as many as 50 different substances at once. This test is usually done to identify allergies to pollen, mold, pet dander, dust mites and foods. In adults, the test is usually done on the forearm.Jan 6, 2022
Which diagnostic test records the electrical activity of the heart?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) records the electrical signal from the heart to check for different heart conditions. Electrodes are placed on the chest to record the heart's electrical signals, which cause the heart to beat.Mar 19, 2022
How do you treat skin allergies?
Try these:Hydrocortisone cream.Ointments like calamine lotion.Antihistamines.Cold compresses.Oatmeal baths.Talk to your doctor about what's best for your specific rash. For example, corticosteroids are good for poison ivy, oak, and sumac. They can prescribe stronger medicines if needed, too.Jun 2, 2020
How do you treat an allergic reaction in your mouth?
For mild allergic reactions, symptoms generally go away on their own within a few minutes, either when you spit out the food that caused it, remove yourself from the allergen, or digest the problematic proteins. Sometimes, you may need to take an over-the-counter antihistamine to combat mild symptoms.
What do allergy tests detect?
Allergy testing identifies allergens, like mold, pet dander, bee stings and peanuts, that can cause allergies. During a skin prick test, a healthcare provider introduces allergens into your skin to check for a wheal (raised mark), rash or other reactions. Blood tests can check for IgE antibodies.Jul 2, 2021
What is patch testing for allergies?
Patch testing is a process to detect allergic contact dermatitis to something a person has contacted at home, leisure or at work. It involves applying patches with test substances in small chambers or discs to a person's back. The patches are secured with hypoallergenic tapes. No needle pricking is involved.Apr 20, 2017
What is allergy test procedure?
The test involves placing a small amount of the suspected allergy-causing substance (allergen) on the skin (usually the forearm, upper arm, or the back), and then scratching or pricking the skin so that the allergen is introduced under the skin surface.
Which of the following examination methods is used when the physician detects a fungal skin infection?
A Wood's lamp examination is a procedure that uses transillumination (light) to detect bacterial or fungal skin infections. It also can detect skin pigment disorders such as vitiligo and other skin irregularities.
What are the 3 types of ECG?
There are three main components to an ECG: the P wave, which represents depolarization of the atria; the QRS complex, which represents depolarization of the ventricles; and the T wave, which represents repolarization of the ventricles.
Why is ECG needed?
You may need an ECG test if you have risk factors for heart disease such as high blood pressure, or symptoms such as palpitations or chest pain. Or you may need it if you already have heart disease. But in other cases, you may think twice about having this test.
What diseases are associated with stomatitis?
certain diseases, including Behcet’s disease, Crohn’s disease, and lupus. medications, including sulfa drugs, anti-epileptics, and some antibiotics. nutritional deficiencies. allergic reactions. burns caused by hot food and drink. It is important to identify the cause of stomatitis in order to treat it properly.
What are the symptoms of stomatitis?
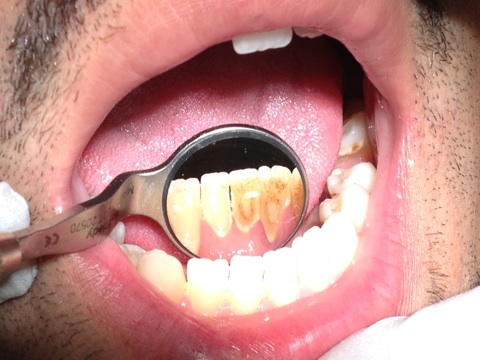
Symptoms. Stomatitis often results in pain, stinging, and soreness. Each person may experience different symptoms. These can include: mouth ulcers with a white or yellow layer and red base, usually inside the lips, cheek, or on the tongue. red patches .
What is a cold sore on the lips?
Cold sores are small, painful, fluid-filled sores that usually occur on or around the lips near the edge of the mouth. Caused by the herpes virus (HSV), the condition is also known as herpes stomatitis. A person may experience a tingling or burning sensation before the sore appears, as well as tenderness.
What is the disease of the mouth?
Diagnosis. Treatment. Prevention. Stomatitis is inflammation of the mouth. It affects the mucous membranes, which are the thin skin coverings on the inside surface of the mouth. The membranes produce the protective mucus, as well as lining the digestive system, from the mouth to the anus.
How long does a cold sore last?
Cold sores tend to last for around 5-7 days and can keep coming back. They are also very contagious. Stomatitis can be broken down into different categories, depending on which area of the mouth is affected: cheilitis – inflammation of the lips and around the mouth. glossitis – inflammation of the tongue.
What is the third stomatitis?
Denture Stomatitis and Treatment. This third stomatitis type, also known as thrush, can affect people who wear dentures, have diabetes, take oral steroids or have difficulties keeping their mouths clean, notes the Oral Health Foundation. Red areas under the dentures or red sores at the lip corners are signs to watch for.
What is the mouth used for?
Aphthous Stomatitis and Treatment. Denture Stomatitis and Treatment. The mouth helps in many important functions — communication, eating and breathing among them. But like other body parts and organs, things can go wrong inside the mouth.
What to do if you have a cold sore?
Home treatment options, such as fever reducers, pain relievers, and oral gels and rinses, may help bring you the relief you need.
How long does it take for a sore to form on the tongue?
Symptoms include a tingling or burning sensation on the tongue, inner lip or inner cheek. The sores take about two to three days to form, and they may be small or large. Smaller sores go away on their own in a couple of weeks without any scarring. Large sores tend to be painful and can leave scars.
Is stomatitis a common problem?
Stomatitis is a common problem many people deal with at some point, and there are different types. Here's what you need to know about stomatitis, treatment and finding relief from the pain.
Can you treat canker sores?
You can't prevent canker sores, and you can't treat them. However, you can treat the symptoms, such as the stinging pain. Eating bland foods, rinsing with warm water, and applying pain-relieving gels may ease symptoms. Larger sores might require steroid medications.
How to treat mouth sores?
The following strategies might help to ease the pain and inflammation of mouth sores: Avoid hot beverages and foods as well as salty, spicy, and citrus-based foods. Use pain relievers like Tylenol or ibuprofen. Gargle with cool water or suck on ice pops if you have a mouth burn.
What is the term for a sore mouth?
Stomatitis. Stomatitis, a general term for an inflamed and sore mouth, can disrupt a person's ability to eat, talk, and sleep. Stomatitis can occur anywhere in the mouth, including the inside of the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and palate.
How to treat canker sores in children?
Try the following: Drink more water. Rinse with salt water. Practice proper dental care. Apply a topical anesthetic such as lidocaine or xylocaine to the ulcer ( not recommended for children under 6) .
How long does a mouth sore last?
Mouth sores generally don't last longer than two weeks, even without treatment. If a cause can be identified, your doctor may be able to treat it. If a cause cannot be identified, the focus of treatment shifts to symptom relief. Avoid hot beverages and foods as well as salty, spicy, and citrus-based foods.
What diseases affect the mucosal lining of the mouth?
Having certain autoimmune diseases affecting the mucosal lining of the mouth, such as lupus, Crohn's disease, or Behcet's disease. Taking certain drugs such as chemotherapy, antibiotics, medications used for rheumatoid arthritis, or epilepsy medications. Receiving radiation as part of cancer treatment.
Can cold sores be on the roof of your mouth?
They rarely form on the gums or the roof of the mouth. Cold sores later crust over with a scab and are usually associated with tingling, tenderness, or burning before the actual sores appear. Mouth irritation. The irritation can be caused by: Biting your cheek, tongue, or lip.
Can cold sores be treated?
There is no cure for cold sores. Treatment includes: Taking a dose of valacyclovir (Valtrex) at the first sign of an attack. Coating the lesions with a protective ointment such as an antiviral agent (for example, 5% acyclovir ointment) Applying ice to the lesion.
Types of Stomatitis
Depending on the cause that caused the development of the pathology, medical practice distinguishes between two types of stomatitis – infectious and non-infectious.
Diagnosis
A visual examination of the patient is usually sufficient to make a diagnosis. If stomatitis is suspected to be the result of internal diseases, consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed.
Methods of Treatment
If the pathology is of non-infectious origin, symptomatic treatment is carried out at home. For this purpose, decoctions and tinctures of medicinal herbs are often prescribed. With infectious stomatitis used medications aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, and the removal of painful symptoms.
Treatment in Adults
Therapy is carried out on the same principle as in children. If the causative agent of stomatitis is diseases of the internal organs, the patient is referred for consultation to the appropriate specialist, who will prescribe diagnosis and treatment.
What is the best treatment for aphthous stomatitis?
First-line treatment of major or minor aphthous stomatitis with significant symptoms is typical with topical steroids in gel or emollient paste (e.g., Orabase) to shorten the duration. Another option would be a one-time local steroid injection, such as triamcinolone.
What is aphthous stomatitis?
Aphthous stomatitis is a common ailment, idiopathic in nature, with recurrent painful aphthous ulcers ( commonly termed “ canker sores”) on the non-keratinized oral mucous membranes. [1][2][3] Etiology.
How long does it take for aphthous stomatitis to heal?
Minor aphthous ulcerations, the most common form of aphthous stomatitis, are less than 1 cm in diameter, round or oval in shape, with yellow or gray pseudomembrane surrounded by an inflammatory red halo, and heal typically within 7-14 days.
What is the pathophysiology of aphthous ulcers?
Aphthous ulcerations are initially and primarily the result of T cell-mediated immune dysfunction but also may involve neutrophil and mast cell-mediated destruction of the mucosal epithelium.
How to prevent aphthous ulcers?
Practice good oral hygiene and avoidance of local trauma or oral hygiene products of known sensitivity. Consider taking dietary supplements with iron, zinc, or vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, or C if a vitamin or mineral deficiency is identified.
How common is aphathous stomatitis?
Aphthous stomatitis affects approximately 20% of the general population. It is slightly more common in girls and women as well as among affluent socioeconomic classes and countries. Race does not appear to be a factor in the disease.
Where do aphathous ulcers occur?
Aphthous ulcers occur on non-keratinized oral mucosae such as along the labial or buccal surfaces, soft palate, the floor of the mouth, the ventral or lateral surface of the tongue, tonsillar fauces, free (marginal or unattached) gingiva adjacent to teeth, and alveolar gingiva in the maxillary and mandibular sulci.
How to prevent aphthae infection?
If food exposure is thought to be the culprit, a food diary can be helpful. [ 121, 122, 123] Advise avoidance of salt and hot spices to prevent pain from unnecessary aphthae irritation.
Can probiotics help with aphthous stomatitis?
Probiotic lozenges: Studies have suggested that probiotic lozenges, specifically one containing Lactobacillus reuteri, may be helpful for pain relief and ulcer healing in recurrent aphthous stomatitis, with further research warranted. [ 115, 116]
Does nicotine help with aphthous ulcers?
Other, less harmful treatments are available. Nicotine replacement therapy may help ameliorate lesions that have resulted from cessation of a tobacco habit. [ 128] It has been suggested that various foods and environmental triggers have a role in causing or exacerbating recurrent aphthous ulcers.
What is the best medicine for stomatitis?
Licorice root is a great natural remedy for stomatitis of any kind. It contains glycyrhizic acid thought to help prevent the virus responsible for cold sores from spreading further. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that can help soothe the symptoms of both types of stomatitis.
What are the two types of stomatitis?
Types of Stomatitis. There are two main types of stomatitis and treatment or home remedies will depend on which type you have. Herpes stomatitis more commonly called a cold sore and canker sores known medically as aphthous stomatitis. Canker Sores.
How to use chamomile for sores?
The easiest way to use chamomile for your sores is to use a ready made chamomile teabag.
How to treat stomatitis with licorice root?
Simply drinking up a few cups of licorice root tea each day will help deal with the symptoms of stomatitis. Alternatively you can apply licorice root topically to your sores. Get a tablespoon of powdered licorice root and mix it with a little water to form a nice thick paste.
What causes a blister on the back of the stoma?
Causes of Stomatitis. In the case of herpes stomatitis, the blister is caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). This type of stomatitis can occur any time but young children are more at risk especially those under the age of 5.
How to treat herpes stomatitis?
Vanilla Extract. Organic extract of vanilla is another very good remedy for herpes stomatitis. Being alcohol based, it may work to heal the sores more quickly and reduce the severity of your sores. Soak up your vanilla extract with a cotton ball or a s wab.
What is the term for soreness in the mouth?
Stomatitis is actually the general term used to refer to an inflammation and soreness in the mouth. It can occur pretty much anywhere in your mouth including the gums, cheeks, palate, tongue and lips. It can be very painful and irritating and makes everyday functions like eating and speaking very difficult.

Types of Stomatitis
Causes
Diagnosis
- A visual examination of the patient is usually sufficient to make a diagnosis. If stomatitis is suspected to be the result of internal diseases, consultations with narrow specialists are prescribed. If the disease is of infectious origin, the patient is referred for laboratory tests: 1. oral smear to determine the type of pathogenic microorganisms; 2. Blood tests to detect antibodies t…
Methods of Treatment
- If the pathology is of non-infectious origin, symptomatic treatment is carried out at home. For this purpose, decoctions and tinctures of medicinal herbs are often prescribed. With infectious stomatitis used medications aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease, and the removal of painful symptoms.
Treatment of Stomatitis in Children
- Therapeutic measures vary depending on the type of pathology: 1. Fungal stomatitis is treated with antiseptics and antifungal drugs. Rinsing of the mouth cavity is carried out at least five times a day. 2. With herpetic stomatitis, irritating foods – spicy, sour, salty, fried, sweets, spices – are excluded from the diet. Of the medications used are...
Treatment in Adults
- Therapy is carried out on the same principle as in children. If the causative agent of stomatitis is diseases of the internal organs, the patient is referred for consultation to the appropriate specialist, who will prescribe diagnosis and treatment. Depending on the type of stomatitis, the following groups of drugs are used: 1. antibiotics; 2. antifungal; 3. antiviral; 4. anti-inflammatory; …