sequence of interrelated steps is inherent to effective periodontaltreatment: early and accurate diagnosis, comprehensive treatment, andcontinued periodontal maintenance and monitoring. A primary goal ofperiodontal therapy is to reduce the burden of pathogenic bacteria andthereby reduce the potential for progressive inflammation and recur-rence of disease. Emerging evidence of possible perio-systemic linksfurther reinforces the need for good periodontal health. In the privatepractice setting, the treatment of patients with periodontal disease is bestaccomplished within the structure of a uniform and consistent Peri-odontal Treatment Protocol (PTP). Such a protocol would reinforceaccurate and timely diagnosis, treatment needs based on a specificdiagnosis, and continual assessment and monitoring of outcomes. Thisis best achieved if everyone in the practice setting has a general under-standing of the etiology of periodontal diseases, the benefits of treat-ment, and potential consequences of nontreatment. Communicationskills and patient education are vital components of effective therapysince slight and even moderate stages of the disease often have fewnoticeable symptoms to the patient. Accurate documentation and report-ing of procedures for dental insurance reimbursement, coupled withscheduling considerations, assist general practice settings in effectivelymanaging the increasing volume of patients that can benefit from earlydiagnosis and treatment of periodontal diseases. This article presentsthe essential elements of a PTP including diagnosis, treatment planning,implementation of therapy, assessment and monitoring of therapy, insur-ance coding, introduction of the patient to periodontal therapy, andenhanced verbal skills. In addition, considerations for implementation ofadjunctive local delivery antimicrobials is presented.
Full Answer
What is periodontal disease treatment?
Though beneficial in the treatment of periodontal disease, citric acid removes the smear layer, an important pulp protector. Cotton and Siegel reported that citric acid, when applied to freshly cut dentine, has a toxic effect on the human dental pulp.[ 21 ]
What are the goals of nonsurgical periodontal therapy?
Periodontal health is the absence of clinically detectable inflammation (<10% of sites bleeding on probing), on an intact periodontium, or a reduced periodontium where attachment loss …
What is the prognosis of primary periodontal disease?
following completion of treatment and arrest of inflammation, supportive periodontal therapy (spt) is employed to reduce the probability of re-infection and progression of the disease; to maintain teeth without pain, excessive mobility or persistent infection in the long term, and to prevent related oral diseases.according to the american academy …
What is the relationship between periodontal and endodontic treatment?
A sequence of interrelated steps is inherent to effective periodontal treatment: early and accurate diagnosis, comprehensive treatment, and continued periodontal maintenance and monitoring. A primary goal of periodontal therapy is to reduce the burden of pathogenic bacteria and thereby reduce the potential for progressive inflammation and recur-

What treatment is used for periodontal disease?
Antibiotics. Topical or oral antibiotics can help control bacterial infection. Topical antibiotics can include antibiotic mouth rinses or insertion of gels containing antibiotics in the space between your teeth and gums or into pockets after deep cleaning.Feb 14, 2020
How successful is periodontal treatment?
Periodontal Treatment Success Rate The overall success rate of both surgical and nonsurgical options is at around 87%.Oct 1, 2020
Which of the following are appropriate to include as initial periodontal therapy?
The initial-first phase in the treatment of periodontal disease typically involves Sanative Therapy ; a meticulous below the gum line cleaning that may include scaling, root planning, soft tissue curettage and dental prophylaxis.
What is the primary goal of periodontal therapy?
The goals of periodontal therapy are to preserve the natural dentition, periodontium and peri-implant tissues; to maintain and improve periodontal and peri-implant health, comfort, esthetics, and function.
What is the success and failure rate of periodontal maintenance?
Results. Overall 39% of the patients reached the successful treatment objective and a mean bleeding on pocket probing tendency of 14%. Treatment success appeared to be dependent on tooth type where the results at single‐rooted front teeth (85%) and premolar teeth (78%) were more successful than at molar teeth (47%).May 16, 2019
What helps bone loss in teeth naturally?
How to stop bone loss in teeth naturallyIncreasing your Calcium intake.Increasing your Vitamin D intake.Avoid smoking.Control your sugar intake.Take good care of your dental health.Visit your dentist on a regular basis.
How do you treat a deep gum pocket?
What Treatments Are Available to Treat Periodontal Pockets?Scaling and Root Planing. Scaling and root planing helps to deep clean in and around the periodontal pockets. ... Gingival Flap Surgery. Gingival flap surgery is when the gum tissue is folded back and the diseased tissue is removed. ... Gingivectomy. ... Gingivoplasty.
What is advanced periodontitis?
In addition to bone loss, advanced periodontal disease causes red, swollen gums that ooze pus, cold sensitivity, further loosening of teeth, painful chewing, and severe halitosis. This stage requires periodontal surgery or periodontal laser therapy in order to clean the deep bacteria-filled pockets that have formed.
What is the main cause of periodontal disease?
Overview. Periodontal (gum) disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. It's typically caused by poor brushing and flossing habits that allow plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—to build up on the teeth and harden.
Introduction
Whilst several conditions may affect the tooth-supporting tissues referred to as the periodontium or gums, the following sections focus on the most...
Definitions
The 2017 World Workshop classification of periodontal and peri-implant conditions (3, 4), can be summarised as follows.Periodontal healthPeriodonta...
Epidemiology
Some level of irreversible periodontitis affects almost half of UK adults (5), although this might underestimate true disease levels.Similar levels...
Risk or susceptibility and protective factors
In addition to plaque build-up, tobacco (smoking or chewing) and alcohol use, several general health conditions are risk factors for periodontal di...
Primary prevention of periodontitis
Risk factor controlThe primary prevention of periodontitis and gingivitis involves control of any risk factors. An overview of risk factors and the...
Secondary prevention of periodontitis
Early detection and management pathways: basic periodontal examinationEarly detection and treatment of periodontitis increases the likelihood of to...
Tertiary prevention of periodontitis
Supportive periodontal care (SPC) after treatment for periodontitisPeriodontitis is a chronic disease that will recur and worsen without good plaqu...
Mouthrinses, mouthwashes and sprays
There is a range of mouthrinses, mouthwashes and sprays available to the public, in addition to mechanical plaque control with dentifrices, for lon...
Peri-implant health
Dental implants may be used to replace missing teeth. However, the soft tissues and bone around dental implants (75), are at the same risk of infla...
Prevention of peri-implantitis
The principles of prevention around implants are the same as for teeth and focus on effective control of plaque and management of other risk factor...
What is the goal of periodontitis treatment?
The goal of periodontitis treatment is to thoroughly clean the pockets around teeth and prevent damage to surrounding bone. You have the best chance for successful treatment when you also adopt a daily routine of good oral care, manage health conditions that may impact dental health and stop tobacco use.
Why do periodontists make incisions in gums?
Your periodontist makes tiny incisions in your gum so that a section of gum tissue can be lifted back, exposing the roots for more effective scaling and root planing. Because periodontitis often causes bone loss, the underlying bone may be recontoured before the gum tissue is sutured back in place.
How to tell if you have periodontitis?
To determine whether you have periodontitis and how severe it is, your dentist may: Review your medical history to identify any factors that could be contributing to your symptoms, such as smoking or taking certain medications that cause dry mouth. Examine your mouth to look for plaque and tartar buildup and check for easy bleeding.
What happens when you lose gum tissue?
When you lose gum tissue, your gumline recedes. You may need to have some of the damaged soft tissue reinforced. This is usually done by removing a small amount of tissue from the roof of your mouth (palate) or using tissue from another donor source and attaching it to the affected site.
What is the procedure to cover exposed roots?
This can help reduce further gum recession, cover exposed roots and give your teeth a more pleasing appearance. Bone grafting. This procedure is performed when periodontitis has destroyed the bone surrounding your tooth root.
What is the best treatment for bacterial infection?
Antibiotics. Topical or oral antibiotics can help control bacterial infection.
How to get ready for an appointment?
To get ready for your appointment, make a list of: Any symptoms you're experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for your appointment. Key personal information, such as any medical conditions you may have.
Introduction
Whilst several conditions may affect the tooth-supporting tissues referred to as the periodontium or gums, the following sections focus on the most common forms of periodontal diseases, called ‘gingivitis’ (inflammation of the gums that can be reversed) and ‘periodontitis’ (inflammation that results in loss of periodontal attachment) (1).
Definitions
The 2017 World Workshop classification of periodontal and peri-implant conditions (3, 4), can be summarised as follows.
Epidemiology
Some level of irreversible periodontitis affects almost half of UK adults (5), although this might underestimate true disease levels.
Risk or susceptibility and protective factors
In addition to plaque build-up, tobacco (smoking or chewing) and alcohol use, several general health conditions are risk factors for periodontal diseases. Conversely, there are risks to general health resulting from having active periodontal diseases.
Primary prevention of periodontitis
The primary prevention of periodontitis and gingivitis involves control of any risk factors. An overview of risk factors and their management is presented in Chapter 2: Table 2. As gingivitis is a predictor of developing periodontitis (33), and thereafter tooth loss (34), its prevention also helps in the primary prevention of periodontitis.
Secondary prevention of periodontitis
Early detection and treatment of periodontitis increases the likelihood of tooth retention (49). One screening tool that is well known and quick to use is the Basic Periodontal Examination ( BPE) (50). The BPE uses the WHO BPE probe and is suitable for routine assessment of all dentate adults (Table 5.1).
Tertiary prevention of periodontitis
Periodontitis is a chronic disease that will recur and worsen without good plaque control (8, 56). This is the basis for providing SPC, which involves a long-term commitment from the patient and an intensive level of support, monitoring and care from the dental team.
What is the primary goal of nonsurgical periodontal therapy?
The primary goal of nonsurgical periodontal therapy is to control microbial periodontal infection by removing bacterial biofilm, calculus, and toxins from periodontally involved root surfaces. A review of the scientific literature indicates that mechanical nonsurgical periodontal treatment predictab ….
What is supracrestal periodontal therapy?
The supracrestal therapy includes the treatment of gingivitis, nonsurgical coverage of recession-type defects, treatment of suprabony defects and papilla reconstruction techniques. Within subcrestal periodontal therapy, it is of paramount importance to preserve both marginal tissues and connective fibers inserted in the root cementum at ...
Can plaque induced periodontitis be treated?
The successful treatment of plaque-induced periodontitis will restore periodontal health, but with reduced periodontium. In such cases, anatomical damage from previous periodontal disease will persist and inverse architecture of soft tissue may impair home plaque removal.
Does mechanical periodontal treatment reduce inflammation?
A review of the scientific literature indicates that mechanical nonsurgical periodontal treatment predictably reduces the levels of inflammation and probing pocket depths, increases the clinical attachment level and results in an apical shift of the gingival margin.
What happens when you don't treat gingivitis?
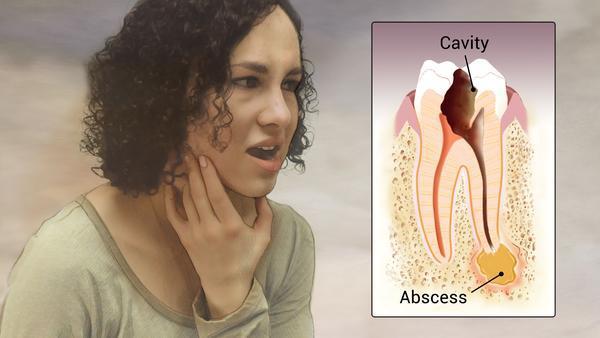
When gingivitis is not treated, it can advance to “periodontitis” (which means “inflammation around the tooth”). In periodontitis, gums pull away from the teeth and form spaces (called “pockets”) that become infected. The body’s immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line. Bacterial toxins and the body’s natural response to infection start to break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. If not treated, the bones, gums, and tissue that support the teeth are destroyed. The teeth may eventually become loose and have to be removed.
How to remove plaque from gums?
The dentist, periodontist, or dental hygienist removes the plaque through a deep-cleaning method called scaling and root planing. Scaling means scraping off the tartar from above and below the gum line. Root planing gets rid of rough spots on the tooth root where the germs gather, and helps remove bacteria that contribute to the disease. In some cases a laser may be used to remove plaque and tartar. This procedure can result in less bleeding, swelling, and discomfort compared to traditional deep cleaning methods.
What causes red gums and bleed?
The longer plaque and tartar are on teeth, the more harmful they become. The bacteria cause inflammation of the gums that is called “gingivitis.” In gingivitis, the gums become red, swollen and can bleed easily. Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that can usually be reversed with daily brushing and flossing, and regular cleaning by a dentist or dental hygienist. This form of gum disease does not include any loss of bone and tissue that hold teeth in place.
Can periodontal disease cause teeth to be lost?
If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you’re not alone. Many adults in the U.S. currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases range from simple gum inflammation to serious disease that results in major damage to the soft tissue and bone that support the teeth. In the worst cases, teeth are lost.

Diagnosis
- To determine whether you have periodontitis and how severe it is, your dentist may: 1. Review your medical historyto identify any factors that could be contributing to your symptoms, such as smoking or taking certain medications that cause dry mouth. 2. Examine your mouthto look for plaque and tartar buildup and check for easy bleeding. 3. Measure the pocket depthof the groov…
Treatment
- Treatment may be performed by a periodontist, a dentist or a dental hygienist. The goal of periodontitis treatment is to thoroughly clean the pockets around teeth and prevent damage to surrounding bone. You have the best chance for successful treatment when you also adopt a daily routine of good oral care, manage health conditions that may impact dental health and stop tob…
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Try these measures to reduce or prevent periodontitis: 1. Brush your teeth twice a day or, better yet, after every meal or snack. 2. Use a soft toothbrush and replace it at least every three months. 3. Consider using an electric toothbrush, which may be more effective at removing plaque and tartar. 4. Floss daily. 5. Use a mouth rinse to help reduc...
Preparing For Your Appointment
- You may start by seeing your dentist. Depending on the extent of your periodontitis, your dentist may refer you to a specialist in the treatment of periodontal disease (periodontist). Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and what you can do to prepare.