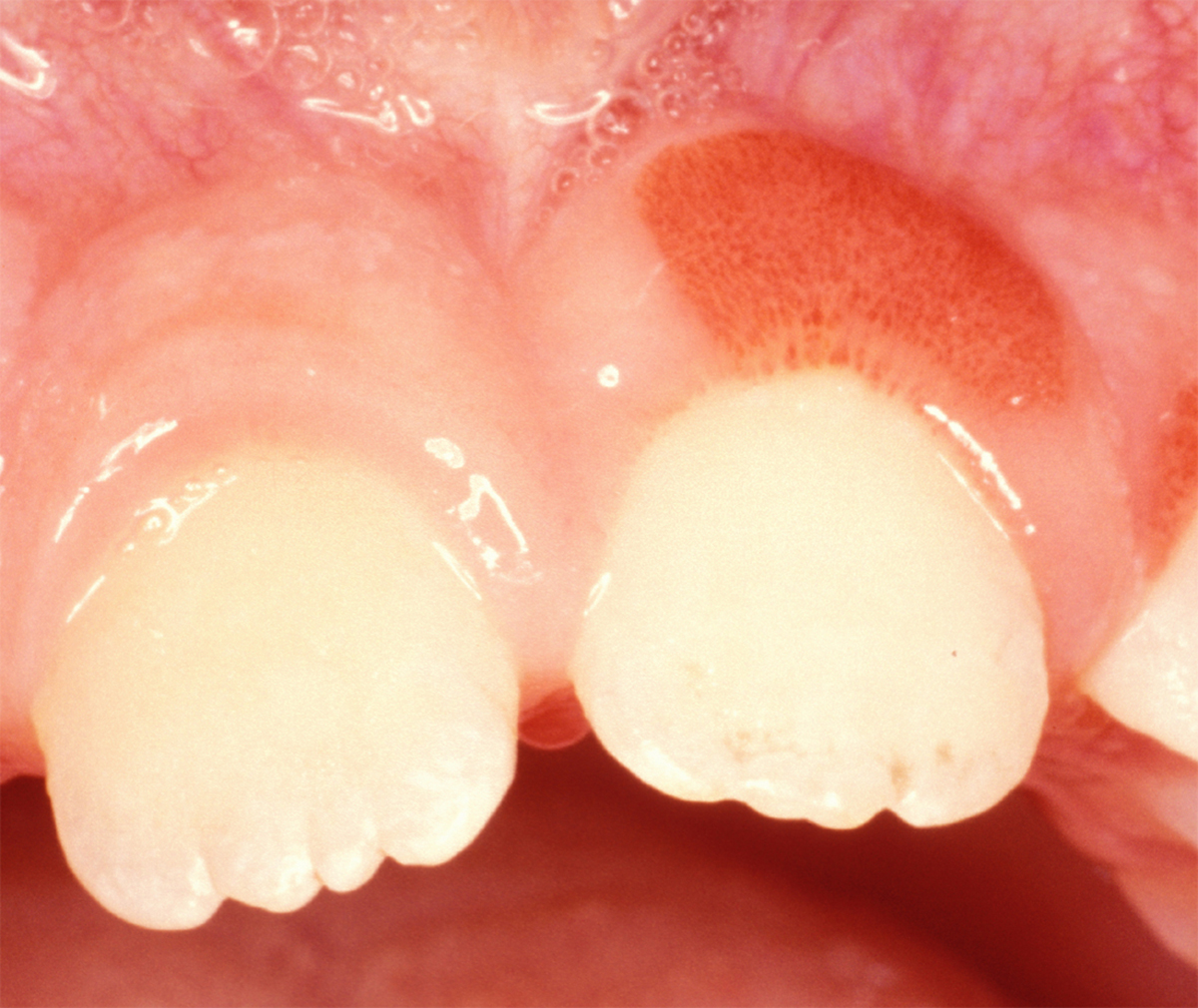
Symptoms
Reversing Gingivitis: 7 Tips to Make it Happen
- Get Regular Professional Cleanings. Seeing a hygienist or dentist for regular professional cleanings is one of the best ways to get rid of gingivitis for good.
- Brush and Floss Often. In addition to regular professional cleanings, simply brushing and flossing well at home is another way to reverse gingivitis.
- Use Antibacterial Mouthwash. ...
Causes
With severe gingivitis, gum recession can require surgical repair. It is important to understand that gingivitis is a product of a person's own local and systemic health and hygiene and is not a contagious condition. Therefore, controlling the risk factors individually will lead to a favorable prognosis in reversing and curing the disease.
Prevention
What is the best toothpaste for Gingivitis? parodontax Toothpastes for Gingivitis: parodontax Complete Protection in Pure Fresh Mint – a daily toothpaste with eight benefits for healthy gums and strong teeth. parodontax Extra Fresh – a daily toothpaste that works to remove the plaque bacteria that can cause bleeding gums – a sign of ...
Complications
What Can I Do At Home?
- Brush at least twice each day.
- Rinse after each meal.
- Floss daily.
- Make sure you are using a proper toothbrush with soft bristles.
- Use a natural mouthwash daily.
- Attend your regular exams and cleaning appointments at your dentist.
- Avoid foods and drinks high in sugar.
- Avoid using any tobacco products or smoking.
How to reverse gingivitis, and how to reverse it fast?
What is the prognosis of gingivitis?
What is the best toothpaste to fight gingivitis?
How to get rid of gum infection without antibiotics?
What is the fastest way to cure gingivitis?
How to Cure GingivitisBrush Your Teeth Twice a Day. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush to gently brush around each tooth. ... Floss Your Teeth Once a Day. Plaque loves to hide in between teeth where toothbrush bristles can't reach. ... Use a Fluoride Mouth Rinse. ... Don't Skip Dental Appointments. ... Avoid Sugary Foods and Beverages.
What is the best treatment for gingivitis?
Use a mouth rinse to help reduce plaque between your teeth. Supplement brushing and flossing with an interdental cleaner, such as a dental pick, interdental brush or dental stick specially designed to clean between your teeth. Get regular professional dental cleanings on a schedule recommended by your dentist.
Is gum gingivitis curable?
Because gingivitis is usually painless and has very mild symptoms, many people who have it are unaware of it. Is gingivitis curable and preventable? Absolutely! Gingivitis can be prevented, and existing gingivitis can be reversed, with good oral hygiene and a bit of help from your dentist and dental hygienist.
How do dentist treat gingivitis?
Your dentist or periodontist will thoroughly clean your teeth to remove harmful bacteria, plaque and tartar. Additional treatments include: Perform scaling and root planing: Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from teeth and from underneath your gums. Planing smooths the surfaces of the roots of the teeth.
How long does gingivitis take to heal?
In most cases, gingivitis usually clears up within 10 to 14 days. If your gingivitis is more serious, it could take longer to treat. Take charge of your dental health to prevent it from recurring.
Is gingivitis serious?
Untreated gingivitis can progress to gum disease that spreads to underlying tissue and bone (periodontitis), a much more serious condition that can lead to tooth loss.
What are the stages of gingivitis?
This article outlines the causes, symptoms, prevention and management methods and outlook for each one.Gingivitis. ... Periodontitis - Stage 1: Initial. ... Periodontitis - Stage 2: Moderate. ... Periodontitis - Stage 3: Severe (with potential for tooth loss) ... Periodontitis - Stage 4: Severe (with potential for the loss of all teeth)
What is a good toothpaste for gingivitis?
parodontax Toothpastes for Gingivitis: parodontax Extra Fresh – a daily toothpaste that works to remove the plaque bacteria that can cause bleeding gums – a sign of gingivitis. parodontax Clean Mint – a daily toothpaste for removing plaque bacteria that can cause bleeding gums, with a cool, refreshing mint flavor.
Can gingivitis be permanent?
While tooth problems may be frustrating and overwhelming, gingivitis doesn't have to be. However, it is an early stage of gum disease, a destructive periodontal disease that can lead to bigger problems. Thankfully, gingivitis isn't permanent, but ignoring it could be a problem.
Is salt good for gingivitis?
Salt water can help to remove the plaque and bacteria from your teeth and gums. Salt has healing properties that can treat and heal inflamed or swollen gums caused by gum disease. Even though salt water is extremely effective in helping to treat gum disease, salt water cannot cure gum disease.
How do I brush my gums with gingivitis?
Your healing gums might require a gentler touch first, so make sure you are using a soft-bristled brush and applying the right amount of pressure. Use a water flosser or interdental brush to get between your teeth and under your gumline to remove irritants like bacteria and food debris and help reduce inflammation.
How long before gingivitis turns into periodontitis?
Slight Periodontal Disease During the early gingivitis stages, gum inflammation can occur in as little as five days. Within two to three weeks, the signs of generalized gingivitis become more noticeable. If you still leave this untreated, it would progress to slight periodontal disease.
What causes gingivitis in the mouth?
Causes. The most common cause of gingivitis is the accumulation of bacterial plaque between and around the teeth. The plaque triggers an immune response, which, in turn, can eventually lead to the destruction of gingival, or gum, tissue. It may also, eventually, lead to further complications, including the loss of teeth.
How can gingivitis be reversed?
Treatment. If diagnosis happens early, and if treatment is prompt and proper, gingivitis can be successfully reversed. Treatment involves care by a dental professional, and follow-up procedures carried out by the patient at home.
What is the best way to check for periodontitis?
Checking for signs of periodontitis may also be recommended. This may be done by X-ray or periodontal probing, using an instrument that measures pocket depths around a tooth.
What are the two types of gingival diseases?
Types. There are two main categories of gingival diseases: Dental plaque-induced gingival disease: This can be caused by plaque, systemic factors, medications, or malnutrition. Non-plaque induced gingival lesions: This can be caused by a specific bacterium, virus, or fungus.
What is the term for the inflammation of the gums?
Gingivitis means inflammation of the gums, or gingiva. It commonly occurs because a film of plaque, or bacteria, accumulates on the teeth. Gingivitis is a non-destructive type of periodontal disease, but untreated gingivitis can progress to periodontitis. This is more serious and can eventually lead to loss of teeth.
How do you know if you have gingivitis?
In mild cases of gingivitis, there may be no discomfort or noticeable symptoms. Signs and symptoms of gingivitis might include: bright red or purple gums. tender gums that may be painful to the touch. bleeding from the gums when brushing or flossing. halitosis, or bad breath.
Why is gingivitis so sensitive?
The gingiva might become more sensitive, raising the risk of inflammation. Some diseases: Cancer, diabetes, and HIV are linked to a higher risk of gingivitis.
How does gingivitis clear up?
Gingivitis usually clears up after a thorough professional cleaning — as long as you continue good oral hygiene at home. Your dentist will help you plan an effective at-home program and a schedule of regular professional checkups and cleaning.
How to diagnose gingivitis?
Dentists usually diagnose gingivitis based on: Review of your dental and medical history and conditions that may contribute to your symptoms. Examination of your teeth, gums, mouth and tongue for signs of plaque and inflammation. Measuring the pocket depth of the groove between your gums and your teeth by inserting a dental probe beside your tooth ...
How to get rid of plaque between teeth?
Consider using an electric toothbrush, which may be more effective at removing plaque and tartar. Floss daily. Use a mouth rinse to help reduce plaque between your teeth.
What does it mean when your gums are deeper than 4mm?
Pockets deeper than 4 mm may indicate gum disease . Dental X-rays to check for bone loss in areas where your dentist sees deeper pockets. Other tests as needed. If it's not clear what has caused your gingivitis, your dentist may recommend that you get a medical evaluation to check for underlying health conditions.
How to prevent gingivitis?
Good oral hygiene is the key to preventing gingivitis: Brush teeth twice a day. Hit all the surfaces of each tooth, and don’t forget your gums, your tongue and the roof of your mouth. Don’t use tobacco products. Floss between the teeth once a day.
How to get rid of gum disease?
Floss every day to remove bacteria between the teeth. Limit food and drinks with lots of sugar, including alcohol. See a dentist at least once a year for checkups, and more often if you have any symptoms. If people in your family have gum disease, you may face a greater risk of developing it.
What causes red gums?
Gingivitis. Gingivitis is a mild, early form of gum disease that occurs when bacteria and plaque build up in the mouth and lead to infection. While gingivitis doesn’t always cause symptoms, it can make the gums red, swollen and tender. Regular checkups with a dentist and good oral hygiene at home can clear up gingivitis ...
What does it mean when your dentist says you have gum disease?
Signs of infection such as redness and swelling. Loose teeth. Gums that are pulling away from the teeth. If your dentist suspects gum disease, X-rays can show if it has affected the bones underneath. Your dentist may also refer you to a periodontist, a gum disease specialist.
What happens if you don't clean your teeth?
If you don’t clean your teeth regularly and thoroughly, the bacteria and plaque can cause an infection where your teeth meet your gums. That is gingivitis. Plaque eventually hardens and becomes tartar, which is harder to remove. Tartar can trap more bacteria, worsening gingivitis.
Can gingivitis cause redness?
Gingivitis happens when bacteria infect the gums, often making them swollen, red and quick to bleed. You can successfully manage gingivitis, especially with the help of a dentist. But left untreated, the condition can lead to periodontitis , a more severe type of gum disease.
Is gum disease more common in older adults?
Gingivitis is very common. Almost half of all adults older than 30 have some kind of gum disease. Gum disease is more likely to occur in: Men, though researchers aren’t sure why. It could have to do with hormones or that men are more likely to get related diseases. Men also tend not to go to the dentist as often.
Why do I have gingivitis?
Gingivitis forms due to the long-term buildup of plaque, which is a sticky film that coats teeth and contains decay-causing bacteria. When plaque is not completely removed, the gums become inflamed and irritated over time.
How to prevent gingivitis?
The best way to prevent gingivitis and more severe gum diseases is by brushing and flossing regularly, using mouthwash, and visiting the dentist for professional teeth cleanings. Since gingivitis is reversible, good oral hygiene is the best way to prevent the disease.
What is the earliest stage of periodontal disease?
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease (PD), which is a severe form of gum disease that develops from untreated gingivitis due to long-term plaque buildup. Periodontal disease permanently damages the gums and bones, and surgery is the only treatment option for this form of gum disease.
What is gingivitis reversible?
Gingivitis, also referred to as mild gum disease, is characterized by the inflammation of the gum tissue. In gingivitis, the damage is reversible and the supporting structures of the teeth, such as your bones, are not permanently lost. Gingivitis is the earliest stage of periodontal disease ...
How does gingivitis reversal work?
The reversal of early gingivitis is relatively simple and focuses on the removal of plaque during professional teeth cleanings. During treatment, a dentist or dental hygienist examines the patient’s teeth and cleans them with small instruments. These instruments remove plaque and tartar that a normal toothbrush cannot reach.
How many people in the US have gingivitis?
More than half of American adults are affected by gingivitis and the prevalence is even higher as people age. Children and teens are also at risk of developing gingivitis, especially during puberty. Many people do not find out they had gingivitis until periodontal disease forms.
Why do pregnant women have gum disease?
Hormonal Changes. Hormonal changes are linked to gum disease. Pregnant women are most at risk because extreme hormonal changes occur during pregnancy. Puberty, menopause, and menstruation also cause gum sensitivity and inflammation. Roughly 60 to 75 percent of pregnant women develop gingivitis.
Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Preparing For Your Appointment