
What are the treatment options for diabetes?
Diabetes treatment: Lowering blood sugar. Improving the sensitivity of cells to insulin Inhibiting the reabsorption of glucose in the kidneys Slowing how quickly food moves through the stomach Each class of medicine has one or more drugs. Some of these drugs are taken orally, while others must be injected.
What are the medicines for type 2 diabetes?
You may need medicines along with healthy eating and physical activity habits to manage your type 2 diabetes. You can take many diabetes medicines by mouth. These medicines are called oral medicines. pills. Metformin also comes as a liquid.
What is the management of type 2 diabetes?
Management of type 2 diabetes includes: 1 Healthy eating 2 Regular exercise 3 Weight loss 4 Possibly, diabetes medication or insulin therapy 5 Blood sugar monitoring
What are the two types of diabetes?
The two types of diabetes are referred to as type 1 (insulin dependent) and type 2 (non-insulin dependent). Symptoms of diabetes include increased urine output, thirst, hunger, and fatigue. Treatment of diabetes depends on the type.

What is the treatment of diabetes?
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. Treatment of type 2 diabetes primarily involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with diabetes medications, insulin or both.
What are 5 treatments for diabetes?
TreatmentHealthy eating.Regular exercise.Weight loss.Possibly, diabetes medication or insulin therapy.Blood sugar monitoring.
What are the 4 essential components in treatment of diabetes?
ManagementMeals. Contrary to popular belief there is no specific diabetes diet. ... Movement. Movement or exercise helps the body utilize insulin more efficiently to keep blood sugar under control and it aids in weight management. ... Medication. ... Monitoring.
Which of the following is the treatment of choice for a Type I diabetic?
Insulin is the essential treatment to manage blood sugar in people with type 1 diabetes.
What is the most common treatment for diabetes?
Insulin is the most common type of medication used in type 1 diabetes treatment. If you have type 1 diabetes, your body can't make its own insulin. The goal of treatment is to replace the insulin that your body can't make. Insulin is also used in type 2 diabetes treatment.
What are the treatment options for type 2 diabetes?
Medications are often the first kind of medicine people with type 2 diabetes try when diet and exercise alone aren't enough to keep their blood sugar in a healthy range....You can take insulin in one of several ways:Injections with a needle and syringe. ... Insulin pump. ... Insulin pen. ... Inhaler. ... Injection port. ... Jet injector.
What is the goal of diabetes treatment?
The general goals of the treatment of diabetes are to avoid acute decompensation, prevent or delay the appearance of late disease complications, decrease mortality, and maintain a good quality of life.
How does insulin work for diabetics?
Insulin helps blood sugar enter the body's cells so it can be used for energy. Insulin also signals the liver to store blood sugar for later use. Blood sugar enters cells, and levels in the bloodstream decrease, signaling insulin to decrease too.
Is insulin the only treatment for type 1 diabetes?
Without insulin, blood glucose (sugar) levels become too high, and over time, this will harm the body. Diabetes mellitus is a lifelong condition that can be controlled with lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments. Insulin treatment is one component of a treatment plan for people with type 1 diabetes.
How was diabetes treated before insulin?
Before insulin was discovered in 1921, people with diabetes didn't live for long; there wasn't much doctors could do for them. The most effective treatment was to put patients with diabetes on very strict diets with minimal carbohydrate intake. This could buy patients a few extra years but couldn't save them.
What is insulin used for?
Human insulin is used to control blood sugar in people who have type 1 diabetes (condition in which the body does not make insulin and therefore cannot control the amount of sugar in the blood) or in people who have type 2 diabetes (condition in which the blood sugar is too high because the body does not produce or use ...
Diabetes Treatment: Lowering Blood Sugar
Several classes of type 2 diabetes medicines exist. Each class of medicine works in different ways to lower blood sugar. A drug may work by: 1. Sti...
Compare Diabetes Medications
Here's an at-a-glance comparison of common diabetes medications. More medications are available depending on your needs and situation. Ask your doc...
How to Choose Your Diabetes Medication
No single diabetes treatment is best for everyone, and what works for one person may not work for another. Your doctor can determine how a specific...
Diabetes type 1 and type 2 definition and facts
Controlling blood sugar (glucose) levels is the major goal of diabetes treatment, in order to prevent complications of the disease.
What is diabetes?
Insulin resistance means that although the body can produce insulin, the body's cells do not respond properly to the insulin that is made.
What is prediabetes? How is it treated?
Prediabetes is the term used to describe elevated blood sugar (glucose) that has not yet reached the level for a type 2 diabetes diagnosis. It can be treated by lifestyle changes such as consuming a healthy diet, weight loss, and regular exercise.
What is the treatment for diabetes?
The major goal in treating type 1 and type 2 diabetes is to control blood sugar (glucose) levels within the normal range, with minimal excursions to low or high levels.
Diabetes diet
Proper nutrition is essential for all people with diabetes. Control of blood glucose levels is only one goal of a healthy eating plan. A diabetic diet helps achieve and maintain a normal body weight, while preventing the common cardiac and vascular complications of diabetes.
Medications for type 2 diabetes
Note that these medications used to treat type 2 diabetes are typically not used in pregnant or breastfeeding women. At present the only recommended way of controlling diabetes in women who are pregnant or breastfeeding is by diet, exercise, and insulin therapy.
Metformin
Metformin is a biguanide drug that increases the sensitivity of the body’s cells to insulin. It also decreases the amount of glucose produced by the liver.. In 1994, the FDA approved the use of the biguanide called metformin ( Glucophage) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes.
What to do if you can't maintain your target blood sugar level?
If you can't maintain your target blood sugar level with diet and exercise, your doctor may prescribe diabetes medications that help lower insulin levels or insulin therapy. Drug treatments for type 2 diabetes include the following.
What is the normal blood sugar level for Type 2 diabetes?
This blood test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. Results are interpreted as follows: Below 5.7% is normal. 5.7% to 6.4% is diagnosed as prediabetes.
Why do we need wellness visits?
Keeping your annual wellness visits enables your health care provider to screen for diabetes and to monitor and treat conditions that increase your risk of diabetes — such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol or a high BMI.
What does 6.5% mean on A1C?
6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes. If the A1C test isn't available, or if you have certain conditions that interfere with an A1C test, your doctor may use the following tests to diagnose diabetes: Random blood sugar test. Blood sugar values are expressed in milligrams of sugar per deciliter ...
What does a blood sugar level of 200 mean?
Regardless of when you last ate, a level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests diabetes, especially if you also have signs and symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination and extreme thirst. Fasting blood sugar test.
Why is it important to monitor blood sugar levels?
Regularly monitoring your blood sugar levels is important to avoid severe complications. Also, be aware of signs and symptoms that may suggest irregular blood sugar levels and the need for immediate care:
Do people with type 2 diabetes need insulin?
Some people who have type 2 diabetes need insulin therapy . In the past, insulin therapy was used as a last resort, but today it may be prescribed sooner if blood sugar targets aren't met with lifestyle changes and other medications.
How does diabetes medicine work?
Each class of medicine works in different ways to lower blood sugar. A drug may work by: Stimulating the pancreas to produce and release more insulin. Inhibiting the production and release of glucose from the liver.
Can you take a single medication for type 2 diabetes?
However, you may need medications to achieve target blood sugar (glucose) levels. Sometimes a single medication is effective. In other cases, a combination of medications works better. The list of medications for type 2 diabetes is long and potentially confusing.
Is diabetes a single treatment?
No single diabetes treatment is best for everyone, and what works for one person may not work for another. Your doctor can determine how a specific medication or multiple medications may fit into your overall diabetes treatment plan and help you understand the advantages and disadvantages of specific diabetes drugs. Oct. 24, 2020.
How does Type 1 diabetes work?
Rationale: Type 1 DM is typically triggered by an autoimmune process in which the insulin-producing beta cells of the pancreas are destroyed, resulting in an absolute lack of insulin. This process is usually rapid, with a total insulin deficiency occurring within 1 year.
What are the complications of diabetes?
c. Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acute, or short-term, complications of diabetes result from extreme hyperglycemia or severe hypoglycemia. Let's start with hypoglycemia. Factors such as too much insulin, poor timing of insulin, too little food intake, and stressors can cause blood glucose levels to plummet.
What happens when you forget to take insulin?
When someone with type 1 diabetes forgets to take insulin or does not take enough insulin, blood glucose rises . The body cannot use the glucose and perceives starvation, and begins lipolysis. This fat breakdown leads to ketone formation.
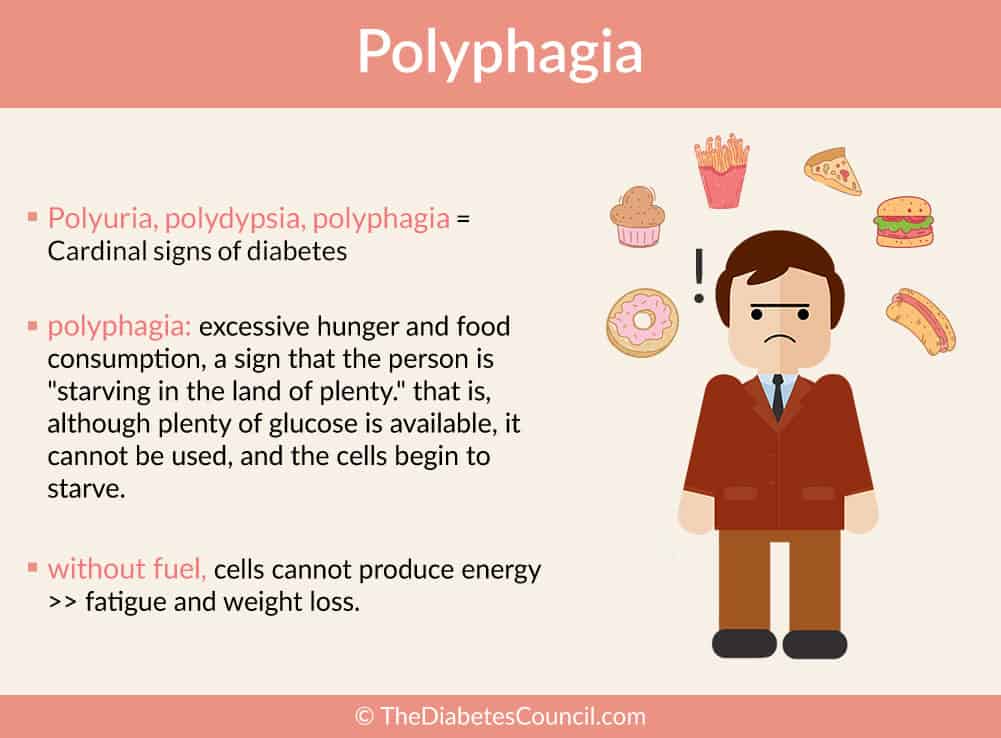
Why does the body not use glucose?
Because the body cannot use the glucose, it responds as if it were in starvation, increasing hunger and elevating blood glucose further. Now, let's look at specific acute complications for each form of diabetes, beginning with type 1 and diabetic ketoacidosis, or DKA.
What are the symptoms of hypoglycemia?
This response causes the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia, such as sweating, dizziness, confusion, hunger and heart palpitations.
Is Prediabetes a type 2 diabetes?
This results in insulin resistance that requires an increased level of insulin to drive glucose into the cells. Prediabetes is a warning sign of Type 2 DM. Prescribed oral hypoglycemic agents are included in the treatment plan for a client who is diagnosed with type 2 DM. A known complication for type 2 DM is HHS.
Does DKA cause electrolytes imbalance?
In addition, fluid and electrolytes imbalance may occur. Treatment of DKA includes insulin to enable the body to use glucose, fluid replacement, and giving potassium. People with type 2 diabetes are at a greater risk for developing hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome, or HHS. Let's consider the name.
What are the best ways to treat diabetes?
Treatment. Depending on what type of diabetes you have, blood sugar monitoring, insulin and oral medications may play a role in your treatment. Eating a healthy diet, maintaining a healthy weight and participating in regular activity also are important factors in managing diabetes.
How to treat type 1 diabetes?
Treatment for type 1 diabetes involves insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump, frequent blood sugar checks, and carbohydrate counting. Treatment of type 2 diabetes primarily involves lifestyle changes, monitoring of your blood sugar, along with diabetes medications, insulin or both.
What does A1C mean?
It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells. The higher your blood sugar levels, the more hemoglobin you'll have with sugar attached. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates that you have diabetes.
How to prevent prediabetes?
Make physical activity part of your daily routine. Regular exercise can help prevent prediabetes and type 2 diabetes, and it can help those who already have diabetes to maintain better blood sugar control. A minimum of 30 minutes of moderate exercise — such as brisk walking — most days of the week is recommended.
What is the best diet for diabetics?
Contrary to popular perception, there's no specific diabetes diet. You'll need to center your diet on more fruits, vegetables, lean proteins and whole grains — foods that are high in nutrition and fiber and low in fat and calories — and cut down on saturated fats, refined carbohydrates and sweets.
What blood test is used to determine blood sugar levels?
Tests for type 1 and type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test. This blood test, which doesn't require fasting, indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. It measures the percentage of blood sugar attached to hemoglobin, the oxygen-carrying protein in red blood cells.
What is the blood sugar level of a diabetic?
Regardless of when you last ate, a blood sugar level of 200 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) — 11.1 millimoles per liter (mmol/L) — or higher suggests diabetes. Fasting blood sugar test. A blood sample will be taken after an overnight fast.
Diagnosis
Treatment
- Management of type 2 diabetes includes: 1. Healthy eating 2. Regular exercise 3. Weight loss 4. Possibly, diabetes medication or insulin therapy 5. Blood sugar monitoring These steps will help keep your blood sugar level closer to normal, which can delay or prevent complications.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
- Careful management of type 2 diabetes can reduce your risk of serious — even life-threatening — complications. Consider these tips: 1. Commit to managing your diabetes.Learn all you can about type 2 diabetes. Make healthy eating and physical activity part of your daily routine. 2. Work with your team.Establish a relationship with a diabetes educator, and ask your diabetes treatment tea…
Alternative Medicine
- Many alternative medicine treatments claim to help people living with diabetes. According to the National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, studies haven't provided enough evidence to recommend any alternative therapies for blood sugar management. Research has shown the following results about popular supplements for type 2 diabetes: 1. Chromiumsupple…
Coping and Support
- Type 2 diabetes is a serious disease, and following your diabetes treatment plan takes round-the-clock commitment. To meet the demands of diabetes management, you may need a good support network. Anxiety and depression are common in people living with diabetes. Talking to a counselor or therapist may help you cope with the lifestyle changes or stressors that come with …
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Keeping your annual wellness visits enables your health care provider to screen for diabetes and to monitor and treat conditions that increase your risk of diabetes — such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol or a high BMI. If you are seeing your health care provider because of symptoms that may be related to diabetes, you can prepare for your appointment by being ready to answer …