What are cervical cell changes?
Mar 22, 2022 · Treatment for high-grade cervical cell changes These treatments are used when a woman has high-grade cervical cell changes that have a high risk of developing into cancer. Treatments that remove abnormal cells are called excisional treatments: Cold knife conization: A scalpel is used to remove a cone-shaped section of abnormal tissue.
What are reactive cellular changes in cervical cancer?
An abnormal cervical screening test result does not mean that you have cervical cancer. It means that cervical cell changes were found or that cells are infected with HPV. Depending on the results, you may need follow-up testing or treatment. Treatment for cervical cell changes works well. HPV . cervical cancer . screening . HPV vaccination
What are the types of cervical cancer?
Feb 22, 2022 · Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women globally, with an estimated 604 000 new cases and 342 000 deaths in 2020. About 90% of the new cases and deaths worldwide in 2020 occurred in low- and middle-income countries (1). Two human papillomavirus (HPV) types (16 and 18) are responsible for nearly 50% of high grade cervical ...
What causes cervical cancer?
Jun 17, 2021 · Types of cervical cancer. The type of cervical cancer that you have helps determine your prognosis and treatment. The main types of cervical cancer are: Squamous cell carcinoma. This type of cervical cancer begins in the thin, flat cells (squamous cells) lining the outer part of the cervix, which projects into the vagina.

What cellular process is affected by cervical cancer?
Carcinogenesis is a process by which normal cells become abnormal and transform into cancer cells. Infection by high-risk HPVs leads to the development of precancerous lesions in the cervix.Jul 17, 2019
What causes cellular changes in the cervix?
Other things can cause cells to look abnormal, including irritation, some infections (such as a yeast infection), growths (such as polyps in the uterus), and changes in hormones that occur during pregnancy or menopause. Although these things may make cervical cells look abnormal, they are not related to cancer.
Which of the following is associated with cervical cancer?
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection Infection by the human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most important risk factor for cervical cancer. HPV is a group of more than 150 related viruses. Some of them cause a type of growth called papillomas, which are more commonly known as warts.
What is cellular changes in a Pap smear?
Minor cervical cell changes found during a Pap test may be caused by: Infection (including infection with the human papillomavirus, or HPV). Inflammation of cervical cells. Natural changes called atrophic vaginitis, caused by menopause.
What causes reactive cellular changes?
Specimens from some women may also show “reactive cellular changes”, which is the way cervical cells appear when infection or other inflammation is around.Jan 3, 2020
What's a colposcopy procedure?
Colposcopy (kol-POS-kuh-pee) is a procedure to closely examine your cervix, vagina and vulva for signs of disease. During colposcopy, your doctor uses a special instrument called a colposcope. Your doctor may recommend colposcopy if your Pap test result is abnormal.Apr 4, 2020
What increases cervical cancer?
Almost all cervical cancers are caused by HPV. Other things also can increase your risk of cervical cancer. Almost all cervical cancers are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), a common virus that can be passed from one person to another during sex. There are many types of HPV.
What causes cervical cancer in a woman?
Long-lasting infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV) is the main cause of cervical cancer. HPV is a common virus that is passed from one person to another during sex. At least half of sexually active people will have HPV at some point in their lives, but few women will get cervical cancer.
What are the preventive measures of cervical cancer?
To help prevent cervical cancer, ASCO recommends that girls receive HPV vaccination....PreventionDelaying first sexual intercourse until the late teens or older.Limiting the number of sex partners.Practicing safe sex by using condoms and dental dams.Avoiding sexual intercourse with people who have had many partners.More items...
What does cellular changes associated with inflammation are present mean on Pap smear?
Inflammation: Noncancerous changes are present. They may be due to normal cell repair. Or, they may be caused by an infection, such as HPV or yeast. Further testing may be needed. (Also called reactive cellular changes.)
What does reactive cellular changes and or repair are present?
“REACTIVE AND OR REPARATIVE CELLULAR CHANGES NOTED” Reactive changes that are benign in nature, associated with inflammation (includes typical repair), atrophy with inflammation (“atrophic vaginitis”), radiation, an IUD, and other nonspecific causes.
What is endocervical cells present in Pap smear?
Endocervical cells present. This phrase means that cells from the inside of your cervical canal were sampled at the time of the pap test, which is something your doctor tries to do.Jul 23, 2019
How to check for cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer screening tests are usually done during a pelvic exam. During this exam, you lie on your back . on an exam table, bend your knees, and put your feet into stirrups. The health care provider gently opens your vagina with a speculum to see the cervix.
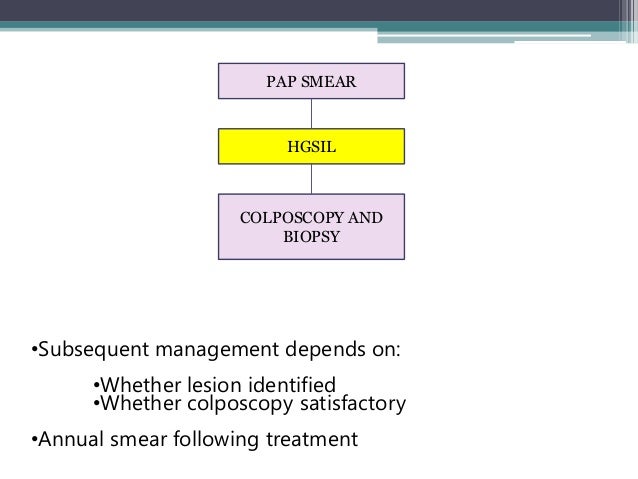
What is the first step in a cervical biopsy?
The first step is usually a colposcopy . A colposcopy is an exam that allows your . health care provider to take a closer look at your cervix and to remove a sample of cervical cells . for a pathologist to examine; this procedure is called a biopsy. The sample is then checked under a microscope for signs of disease.
What is the test called to see if you have abnormal cervix?
Your health care provider will probably recommend that you come in for a test called a colposcopy, which is used to take a closer look at your cervix and perform a biopsy. Based on the colposcopy findings, your health care provider will decide whether further testing or treatment is needed. Pap test result (. abnormal.
What does abnormal cervical screening mean?
It means that cervical cell changes were found or that cells are infected with HPV. Depending on the results, you may need follow-up testing or treatment.
What does a Pap test show?
Pap test results show if cervical cells are normal or abnormal. A Pap test may also come back as unsatisfactory. Next steps after a Pap test may include: Normal Pap test results: Your health care provider will usually recommend another screening exam in 3 to 5 years. A normal test result may also be called a .
What is the procedure to examine the cervix?
Colposcopy and biopsy: Your health care provider will examine your cervix using a colposcope and perform a biopsy. A colposcopy is a procedure to examine your cervix. During this procedure, your doctor inserts a speculum to gently open the vagina and see the cervix.
Do abnormal Pap results mean you have cervical cancer?
INTRODUCTION. You may be reading this guide because you had an abnormal Pap test or HPV test result. Although it’s common to feel uneasy, you should know that most women who have abnormal cervical screening test results do not have cervical cancer.
Key facts
Cervical cancer is the fourth most common cancer among women globally, with an estimated 604 000 new cases and 342 000 deaths in 2020. About 90% of the new cases and deaths worldwide in 2020 occurred in low- and middle-income countries (1).
Overview
Worldwide, cervical cancer is the fourth most frequent cancer in women with an estimated 604 000 new cases in 2020. Of the estimated 342,000 deaths from cervical cancer in 2020, about 90% of these occur in low- and middle-income countries.
HPV and cervical Cancer
A large majority of cervical cancer (more than 95%) is due to the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Cervical cancer control: A comprehensive approach
The Global strategy towards eliminating cervical cancer as a public health problem , adopted by the World Health Assembly in 2020, recommends a comprehensive approach to cervical cancer prevention and control. The recommended actions include interventions across the life course.
Treatment of cervical pre-cancer
If treatment of pre-cancer is needed and eligibility criteria are met, ablative treatment with cryotherapy or thermal ablation are recommended. Both treatments are equally effective and safe and can be performed in an outpatient clinic.
WHO response
The World Health Assembly adopted the global strategy to accelerate the elimination of cervical cancer as a public health problem. The definition of elimination of cervical cancer has been set up as a country reaching the threshold of less than 4 cases of cervical cancer per 100 000 women per year.
What is the test for cervical cancer?
A Pap test can detect abnormal cells in the cervix, including cancer cells and cells that show changes that increase the risk of cervical cancer. HPV DNA test.
What tests are done to determine if you have cervical cancer?
Your cancer's stage is a key factor in deciding on your treatment. Staging exams include: Imaging tests.
What is palliative care?
Palliative care is specialized medical care that focuses on providing relief from pain and other symptoms of a serious illness. Palliative care specialists work with you, your family and your other doctors to provide an extra layer of support that complements your ongoing care.
What is the instrument used to check for abnormal cells?
A special magnifying instrument (colposcope) is used to check for abnormal cells. During the colposcopic examination, your doctor is likely to take a sample of cervical cells (biopsy) for laboratory testing. To obtain tissue, your doctor may use:
What tests can be done to check if you have cancer?
Tests such as X-ray, CT, MRI and positron emission tomography (PET) help your doctor determine whether your cancer has spread beyond your cervix. Visual examination of your bladder and rectum. Your doctor may use special scopes to see inside your bladder and rectum.
Can you remove cancer from a small cervix?
Surgery to cut away the cancer only. For a very small cervical cancer, it might be possible to remove the cancer entirely with a cone biopsy. This procedure involves cutting away a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue, but leaving the rest of the cervix intact.
Can you use chemotherapy for cervical cancer?
Sometimes both methods are used. For locally advanced cervical cancer, low doses of chemotherapy are often combined with radiation therapy, since chemotherapy may enhance the effects of the radiation . Higher doses of chemotherapy might be recommended to help control symptoms of very advanced cancer.
How to reduce cervical cancer risk?
Reduce your risk of cervical cancer by taking measures to prevent sexually transmitted infections, such as using a condom every time you have sex and limiting the number of sexual partners you have. Don 't smoke. If you don't smoke, don't start. If you do smoke, talk to your doctor about strategies to help you quit.
What is cervical cancer?
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix — the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Various strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection, play a role in causing most cervical cancer. When exposed to HPV, the body's immune system typically prevents ...
What type of cancer is squamous cell carcinoma?
Types of cervical cancer. The type of cervical cancer that you have helps determine your prognosis and treatment. The main types of cervical cancer are: Squamous cell carcinoma. This type of cervical cancer begins in the thin, flat cells (squamous cells) lining the outer part of the cervix, which projects into the vagina.
What type of cancer is found in the cervix?
Most cervical cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. Adenocarcinoma. This type of cervical cancer begins in the column-shaped glandular cells that line the cervical canal. Sometimes, both types of cells are involved in cervical cancer. Very rarely, cancer occurs in other cells in the cervix.
What are the risk factors for cervical cancer?
Risk factors for cervical cancer include: Many sexual partners. The greater your number of sexual partners — and the greater your partner's number of sexual partners — the greater your chance of acquiring HPV. Early sexual activity. Having sex at an early age increases your risk of HPV.
What are the two types of cells that line the surface of the cervix?
Two types of cells line the surface of the cervix, and both can become cancerous. One type (glandular cells) has a column-shaped appearance. The other type (squamous cells) is thin and flat. The boundary between the two types of cells is where cervical cancer most commonly occurs.
What happens when a mutation is found in a cell?
The mutations tell the cells to grow and multiply out of control, and they don't die. The accumulating abnormal cells form a mass (tumor). Cancer cells invade nearby tissues and can break off from a tumor to spread (metastasize) elsewhere in the body.
What is the procedure to take a sample from the endocervix?
A small brush or a cotton-tipped swab is then inserted into the opening of the cervix to take a sample from the endocervix . If your cervix has been removed (because you had a trachelectomy or hysterectomy) as a part of the treatment for a cervical cancer or pre-cancer, the cells from the upper part of the vagina (known as the vaginal cuff) ...
What are the three main categories of Pap results?
There are 3 main categories, some of which have sub-categories: Negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy. Epithelial cell abnormalities.
What are atypical squamous cells?
Atypical squamous cells (ASCs) This category includes two types of abnormalities: 1 Atypical squamous cells of uncertain significance (ASC-US) is used to describe when there are cells that look abnormal, but it is not possible to tell if this is caused by infection, irritation, or a pre-cancer. Most of the time, cells labeled ASC-US are not pre-cancer, but more testing, like an HPV test, is needed to be sure. 2 Atypical squamous cells where high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) can’t be excluded (ASC-H) is used to describe when the cells look abnormal but are more concerning for a possible pre-cancer that needs more testing and may need treatment.
How long before a Pap test can you use a tampon?
Don't use tampons, birth-control foams or jellies, other vaginal creams, moisturizers, or lubricants, or vaginal medicines for 2 to 3 days before the Pap test. Don't douche for 2 to 3 days before the Pap test. Don’t have vaginal sex for 2 days before the Pap test.
What is glandular cell abnormality?
Glandular cell abnormalities. Atypical glandular cells: When the glandular cells do not look normal, but they have concerning features that could be cancerous, the term used is atypical glandular cells (AGC). In this case, the patient should have more testing done.
Can squamous cell carcinoma cure SIL?
If treatment is needed, it can cure most SILs and prevent invasive cancer from forming. Squamous cell carcinoma: This result means that the woman is likely to have an invasive cancer. Further testing will be done to be sure of the diagnosis before treatment can be planned.
Is a Pap test good for cancer?
Although the Pap test has been more successful than any other screening test in preventing a cancer, it’s not perfect. One of the limitations of the Pap test is that the results need to be examined by the human eye, so an accurate analysis of the hundreds of thousands of cells in each sample is not always possible.

Diagnosis
- Screening
Screening tests can help detect cervical cancer and precancerous cells that may one day develop into cervical cancer. Most guidelines suggest beginning screening for cervical cancer and precancerous changes at age 21. Screening tests include: 1. Pap test. During a Pap test, your do… - Diagnosis
If cervical cancer is suspected, your doctor is likely to start with a thorough examination of your cervix. A special magnifying instrument (colposcope) is used to check for abnormal cells. During the colposcopic examination, your doctor is likely to take a sample of cervical cells (biopsy) for l…
Treatment
- Treatment for cervical cancer depends on several factors, such as the stage of the cancer, other health problems you may have and your preferences. Surgery, radiation, chemotherapy or a combination of the three may be used.
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- No one can be prepared for a cancer diagnosis. You can, however, try to manage the shock and fear you're feeling by taking steps to control what you can about your situation. Everyone deals with a cervical cancer diagnosis in his or her own way. With time, you'll discover what helps you cope. Until then, you can start to take control by attempting to: 1. Learn enough about cervical c…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms that worry you. If you're thought to have cervical cancer, you may be referred to a doctor who specializes in treating cancers that affect the female reproductive system (gynecologic oncologist). Here's some information to help you get ready for your appointment and what to expect from your doctor.