Tinyqualityhomes.org
· VA offers treatment options that are proven to be very effective for most people, and many types of professionals at VA can help treat schizophrenia. Evidence-based therapies are among the most effective treatments for schizophrenia. They can include the following — which are in many cases available at a local VA medical center.
Curejoy.com
· Some organizations offer advice on how to get support in accessing treatments for schizophrenia. The NAMI offers advice on how to get help paying for medications. The Anxiety and Depression...
What is the best treatment center for schizophrenia?
· Schizophrenia Medication. A combination of psychotherapy and psychotropic medication is one of the most recommended treatment approaches for schizophrenia. Antipsychotic medications are often used ...
Where can I make friends with schizophrenics?
Acute Inpatient Treatment at Johns Hopkins Hospital Adult Outpatient Schizophrenia Clinic Outpatient care at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center EPIC (Outpatient Care) Early Psychosis Intervention Clinic (EPIC) at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center Clozapine Clinic Outpatient care at Johns Hopkins Hospital Contact Us 410-955-5 212
What is the best therapy for schizophrenia?
The Texas Medication Algorithm Project (TMAP) has provided a six-stage pharmacotherapeutic algorithm for the treatment of schizophrenia. Stage 1 is first-line monotherapy with an SGA. If the patient shows little or no response, he or she should proceed to stage 2, which consists of monotherapy with either another SGA or an FGA.
What is the best way to treat schizophrenia?
Your health care provider can refer you to a qualified mental health professional, such as a psychiatrist or psychologist who has experience treating schizophrenia. You can learn more about getting help on NIMH's Help for Mental Illness webpage.

Which doctor is best for schizophrenia?
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who are experts in mental health. They are specialists in diagnosing and treating people with schizophrenia. Psychiatrists have a medical degree plus extra mental health training.
What type of therapy is best for schizophrenia?
The most common types of therapy for schizophrenia include: Cognitive behavior therapy (CBT). This treatment helps you change how you think and react to things. It also teaches you to deal with negative feelings by thinking about them in a different way so you feel good instead.
Do hospitals treat schizophrenia?
Hospitals can be the best place for people with schizophrenia to learn to live with their illness. A hospital can help you get the full picture of your symptoms and learn how to treat them. You may need to go to one if you have hallucinations or if you want to harm yourself.
What happens if schizophrenia is left untreated?
Left untreated, schizophrenia can result in severe problems that affect every area of life. Complications that schizophrenia may cause or be associated with include: Suicide, suicide attempts and thoughts of suicide. Anxiety disorders and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Can schizophrenia go away?
While no cure exists for schizophrenia, it is treatable and manageable with medication and behavioral therapy, especially if diagnosed early and treated continuously.
Where do you go to diagnose schizophrenia?
If a diagnosis of schizophrenia is suspected, the GP should refer you to your local community mental health team (CMHT). CMHTs are made up of different mental health professionals who support people with complex mental health conditions.
When does someone with schizophrenia need to be hospitalized?
Except for the most severe cases, inpatient hospitalization is generally only needed for short periods of time so that acute psychotic episodes and crises can be intensively managed.
Are there stages of schizophrenia?
Phase 1, when they start to show up, is called prodromal. In phase 2, the active stage, your symptoms are most noticeable. The last stage is the residual phase of schizophrenia. In this phase, you're starting to recover, but still have some symptoms.
What is the role of medication in schizophrenia?
Medication. Medications play a crucial role in the treatment of schizophrenia and related conditions. Response to medications vary. Some individuals experience total or near total resolution of symptoms, and some notice smaller effects. For most individuals, symptoms are improved but are still present to some extent.
What is behavioral family therapy?
Behavioral Family Therapy (BFT) helps Veterans diagnosed with schizophrenia and their families learn about new communication and problem-solving skills, and also focuses on family education.
Does the VA treat schizophrenia?
No matter what you are experiencing, treatments and resources are available. VA offers treatment options that are proven to be very effective for most people, and many types of professionals at VA can help treat schizophrenia.
What is the treatment for schizophrenia?
This is known as treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Currently, the only known effective treatment for this is clozapine, an atypical antipsychotic.
What to do if someone close to you has schizophrenia?
If someone close to you has a mental health condition such as schizophrenia, it can help to show them that you believe in their ability to get better, and to support them to apply and grow their strengths.
How do antipsychotics help with schizophrenia?
Antipsychotic drugs reduce immediate symptoms, such as delusions and hallucinations, and helps stop them from coming back. Psychological treatments. Many types of therapy will reduce symptoms, relieve stress, and teach self-care methods. Where needed, therapy can also improve social and work skills. Experts are learning more about schizophrenia all ...
What type of therapy is used for schizophrenia?
Types of psychotherapy used for schizophrenia include the following: Cognitive behavioral therapy (C BT) helps you build coping methods for symptoms that medication doesn’t resolve. CBT can also help you identify and achieve goals, both in treatment and in daily life.
How often do you take schizophrenia medication?
Schizophrenia medication comes in the form of pills you take every day or as a long-acting injectable (LAI). LAI is used with atypical antipsychotics. You receive them every few weeks or months. People often prefer this option, as it makes taking medication easier.
What is the role of antipsychotics in schizophrenia?
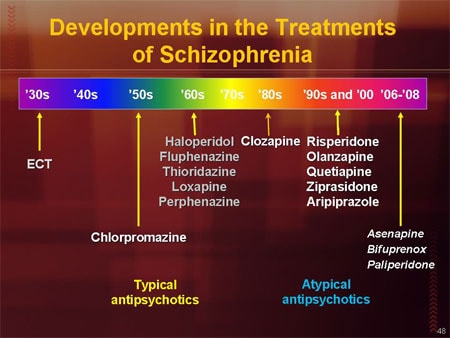
Available since the 1950s, traditional or typical antipsychotics primarily block dopamine receptors and effectively control the hallucinations, delusions , and confusion related to schizophrenia.
When were antipsychotics introduced?
Atypical antipsychotics were introduced in the 1990s. Some of these medications might work on both serotonin and dopamine receptors. Because of this, they might treat positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia.
What is the best treatment for schizophrenia?
A combination of psychotherapy and psychotropic medication is one of the most recommended treatment approaches for schizophrenia. Antipsychotic medications are often used to treat symptoms of schizophrenia. These medications affect neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin.
What do doctors do when you are hospitalized for schizophrenia?
If the person is visiting the hospital for schizophrenia for the first time, doctors may prescribe medication or other treatment to help manage the symptoms .
What is the purpose of antipsychotics for schizophrenia?
The aim of treating schizophrenia with antipsychotics is to control symptoms with the lowest possible dosage. Sometimes psychiatrists or physicians will try various medications, dosages, and combinations of drugs to achieve the best results for the person being treated.
How can family therapy help with schizophrenia?
As the family is, in some cases, the support network for someone with schizophrenia, family therapy can support people with schizophrenia by integrating their family or support network into therapeutic treatment . Psychoeducation may also be used to help inform people about their condition so they can better recognize their symptoms ...
How to help someone with schizophrenia?
When someone you care for has schizophrenia, it can be difficult to know what to say to support them or what to do if they are having trouble acknowledging or coming to terms with their condition. Some tips for helping a loved one with schizophrenia include: 1 Talk to someone with schizophrenia the same way you would talk to anyone else. In some cases, those with schizophrenia may appear disinterested, but this may not always indicate a wish to disengage. 2 Don’t tell a person with schizophrenia to “just stop listening” if they experience auditory hallucinations, as it is not an easy matter to “tune out” from them. 3 If your loved one is hospitalized, be there to support them during and after the visit. The first days or week after leaving the hospital may be difficult to cope with alone. 4 Don’t continually remind your loved one to take their medication. If forgetfulness is an issue, work with them to develop a plan for remembering to take it. 5 If someone with schizophrenia refuses to accept treatment, you cannot force them to do so. In most cases, treatment may only be mandated by law if the person is a danger to themselves or others.
What is the first generation of antipsychotics?
Typical (conventional) antipsychotics: These are also referred to as first-generation antipsychotics. They have a greater potential for causing side effects than newer atypical antipsychotics. This group contains drugs such as Thorazine (chlorpromazine), Prolixin (fluphenazine), Haldol (haloperidol), and Trilafon (perphenazine).
Can you tell someone with schizophrenia to stop listening?
Don’t tell a person with schizophrenia to “just stop listening” if they experience auditory hallucinations, as it is not an easy matter to “tune out” from them. If your loved one is hospitalized, be there to support them during and after the visit.
Lab Studies Dive Headfirst into Pathways Touched by Schizophrenia
Psychiatry researchers Akira Sawa (Director of The Johns Hopkins Schizophrenia Center)and Thomas Sedlak have found that glutamate in broccoli sprouts may improve chemical imbalances in people with schizophrenia.
Our Research
Our extensive research efforts are driven by that same passion to find the causes of schizophrenia and related disorders and to develop treatments to improve the lives of patients everywhere.
Professional Education
We take our mission to educate the next generation very seriously by providing a range of professional learning environments from the bedside to the lab. Our varied programs train undergraduates, graduate students, residents, and postdoctoral fellows.
Message from the Director
We have assembled here in the Schizophrenia Center a broad and deep pool of expertise in the Hopkins tradition that integrates patient care, research, and public health. Thank you for your interest in our work.
Featured Article Schizophrenia
Learn important facts about Schizophrenia and what you need to know such as: causes, symptoms and treatments for it.
Outreach
We collaborate across divisions, departments, institutions and patients and families who participate in our research studies to expand our knowledge of schizophrenia and related conditions. We do this through:
How to diagnose schizophrenia?
A diagnosis of schizophrenia is reached through an assessment of patient-specific signs and symptoms, as described in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders,Fifth Edition (DSM-5).12The DSM-5states that “the diagnostic criteria [for schizophrenia] include the persistence of two or more of the following active-phase symptoms, each lasting for a significant portion of at least a one-month period: delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech, grossly disorganized or catatonic behavior, and negative symptoms.”12At least one of the qualifying symptoms must be delusions, hallucinations, or disorganized speech.12
What is schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a complex, chronic mental health disorder characterized by an array of symptoms, including delusions, hallucinations, disorganized speech or behavior, and impaired cognitive ability. The early onset of the disease, along with its chronic course, make it a disabling disorder for many patients ...
What are the side effects of schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia medications can cause a variety of other adverse effects, including the following: 1 Antipsychotic medications with anticholinergic effects have been shown to worsen narrow-angle glaucoma, and patients should be appropriately monitored.49Chlorpromazine is most commonly associated with opaque deposits in the cornea and lens.2Because of the risk of cataracts, eye examinations are recommended for patients treated with quetiapine.50Those using thioridazine at doses exceeding 800 mg daily are at risk of developing retinitis pigmentosa.2 2 Low-potency FGAs and clozapine have been associated with urinary hesitancy and retention.2The incidence of urinary incontinence among patients taking clozapine can be as high as 44% and can be persistent in 25% of patients.2,51 3 FGAs and risperidone have a greater tendency to cause sexual dysfunction compared with SGAs.2,52 4 Treatment with antipsychotics can cause transient leukopenia.2,53 5 The three antipsychotics with the greatest risk for hematological complications are clozapine, chlorpromazine, and olanzapine.54Clozapine is associated with an especially high risk for the development of neutropenia or agranulocytosis.54 6 On rare occasions, dermatological allergic reactions have occurred at approximately eight weeks after the initiation of antipsychotic therapy.2 7 Both FGAs and SGAS can cause photosensitivity, leading to severe sunburn.2 8 Clozapine has been reported to cause sialorrhea in approximately 54% of patients with schizophrenia.2The mechanism of this effect is unknown.2
How many nonadherence rates are there in schizophrenia?
Not only do nonpharmacological therapies fill in gaps in pharmacological treatments; they can help to ensure that patients remain adherent to their medications.18Nonadherence rates in schizophrenia range from 37% to 74%, depending on the report.19Individuals with mental disorders tend to be less adherent for several reasons. They may deny their illness; they may experience adverse effects that dissuade them from taking more medication; they may not perceive their need for medication; or they may have grandiose symptoms or paranoia.2
What are the factors that contribute to schizophrenia?
Environmental and social factors may also play a role in the development of schizophrenia, especially in individuals who are vulnerable to the disorder.1Environmental stressors linked to schizophrenia include childhood trauma, minority ethnicity, residence in an urban area, and social isolation.1In addition, social stressors, such as discrimination or economic adversity, may predispose individuals toward delusional or paranoid thinking.1
What neurotransmitter is involved in schizophrenia?
Another theory for the symptoms of schizophrenia involves the activity of glutamate, the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. This theory arose in response to the finding that phenylciclidine and ketamine, two noncompetitive NMDA/glutamate antagonists, induce schizophrenia-like symptoms.6This, in turn, suggested that NMDA receptors are inactive in the normal regulation of mesocortical dopamine neurons, and pointed to a possible explanation for why patients with schizophrenia exhibit negative, affective, and cognitive symptoms.7
How many patients report favorable treatment outcomes for schizophrenia?
The prognosis for patients with schizophrenia is generally unpredictable.2Only 20% of patients report favorable treatment outcomes.12The remaining patients experience numerous psychotic episodes, chronic symptoms, and a poor response to antipsychotics.2
How to help people with schizophrenia?
Cognitive behavioral therapy, behavioral skills training, supported employment, and cognitive remediation interventions may help address the negative and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. A combination of these therapies and antipsychotic medication is common. Psychosocial treatments can be helpful for teaching and improving coping skills to address the everyday challenges of schizophrenia. They can help people pursue their life goals, such as attending school, working, or forming relationships. Individuals who participate in regular psychosocial treatment are less likely to relapse or be hospitalized. For more information on psychosocial treatments, see the Psychotherapies webpage on the NIMH website.
When does schizophrenia start?
Onset and Symptoms. Schizophrenia is typically diagnosed in the late teen years to the early thirties and tends to emerge earlier in males (late adolescence – early twenties) than females (early twenties – early thirties).
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
The symptoms of schizophrenia generally fall into the following three categories: Psychotic symptoms include altered perceptions (e.g., changes in vision, hearing, smell, touch, and taste), abnormal thinking, and odd behaviors.
How does psychosocial therapy help?
They can help people pursue their life goals, such as attending school, working, or forming relationships. Individuals who participate in regular psychosocial treatment are less likely to relapse or be hospitalized. For more information on psychosocial treatments, see the Psychotherapies webpage on the NIMH website.
How does schizophrenia affect the brain?
Brain structure and function: Scientists think that differences in brain structure, function, and interactions among chemical messengers (called neurotransmitters) may contribute to the development of schizophrenia. For example, differences in the volumes of specific components of the brain, in the way regions of the brain are connected and work together, and in neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, are found in people with schizophrenia. Differences in brain connections and brain circuits seen in people with schizophrenia may begin developing before birth. Changes to the brain that occur during puberty may trigger psychotic episodes in people who are vulnerable due to genetics, environmental exposures, or the types of brain differences mentioned above.
What is schizophrenia mental illness?
Overview. Schizophrenia is a serious mental illness that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may seem like they have lost touch with reality, which causes significant distress for the individual, their family members, and friends. If left untreated, the symptoms of schizophrenia can be persistent and disabling.
What does it mean when you are psychotic?
People with psychotic symptoms may lose a shared sense of reality and experience themselves and the world in a distorted way. Specifically, individuals typically experience: Hallucinations, such as hearing voices or seeing things that aren’t there.
What do specialists do for people with schizophrenia?
Here, specialists may help you manage living skills, daily tasks, medications, and meals. You might share bathrooms and common areas with other people with schizophrenia or similar conditions. Sometimes, blocks of apartments are turned into group homes for people with mental illnesses. They may be for only men or women.
What is live in treatment?
With this type of live-in treatment, you get care for any medical issues you may have, as well as mental health treatment. Specialists assist with tasks like bathing and dressing, if needed. You’ll also get help with meals and managing your medications and behavior. This is usually a permanent option. Pagination.
What is residential treatment?
A residential treatment program gives you the skills you need to live on your own. Most follow a structured schedule, with each day broken into hourlong blocks. Your daily activities are based on your personal needs. You can learn to manage everyday tasks and adopt healthy routines.
How long do you stay in a hospital after a syphilis?
This type is best after you finish treatment for an acute episode at a hospital or other facility. You’ll stay an average of 8 to 12 weeks. This may be when you get your symptoms under control. You’ll take a break from work or school. You may take classes to prepare you to get a job or go back to school.
Do live in treatment facilities accept people with schizophrenia?
Many live-in treatment facilities accept people with different mental health conditions. Ask about the number of people with schizophrenia who get care. Also find out about staff qualifications and the ratio of staff members to residents.
Does health insurance cover live in treatment?
The cost for live-in treatment facilities varies, based on the type of care and how long you’re there. Health insurance may cover some of it. But at most facilities, you’ll have to pay out-of-pocket.
Can a doctor help you decide on a facility?
Your doctor can help you decide on a facility. Each one is different, with its own feel and set of programs.
Listen and Empathize
In terms of getting someone to engage in treatment, we advise family members to listen. Don’t just hear, but listen to what their experience is. Their reality is different than most people’s reality. I wouldn’t say you should agree with what they say if it’s delusional. But you can empathize.
At First, Treatment Is Trial and Error
A lot of people stop treatment because honestly, the medication available for schizophrenia isn’t always effective. It can have horrible side effects and people lose hope, so they stop.
Explain What The Medications Do
People with schizophrenia should be fully aware and informed about anything they put in their bodies. Part of them being a participant in their treatment is understanding the pros and cons of any type of medication and how you hope it will affect them.
Positive Reinforcement
Once the medication has become effective and the symptoms have receded, you can have a conversation about it. “Remember last month when you were hearing voices and couldn’t sleep? Remember how scary and awful that was? Now that the medications are working, it’s a good thing. A really important step.”